NIH research could lead to new treatment strategies for stomach cancer
Credit: Jonathan Busada, Ph.D./NIEHS
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health determined that stomach inflammation is regulated differently in male and female mice after finding that androgens, or male sex hormones, play a critical role in preventing inflammation in the stomach. The finding suggests that physicians could consider treating male patients with stomach inflammation differently than female patients with the same condition. The study was published in Gastroenterology.
Researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) made the discovery after removing adrenal glands from mice of both sexes. Adrenal glands produce glucocorticoids, hormones that have several functions, one of them being suppressing inflammation. With no glucocorticoids, the female mice soon developed stomach inflammation. The males did not. However, after removing androgens from the males, they exhibited the same stomach inflammation seen in the females.
“The fact that androgens are regulating inflammation is a novel idea,” said co-corresponding author John Cidlowski, Ph.D., deputy chief of the NIEHS Laboratory of Signal Transduction and head of the Molecular Endocrinology Group. “Along with glucocorticoids, androgens offer a new way to control immune function in humans.”
While this study provides insight into how inflammation is being regulated in males, Cidlowski said additional research is underway to understand the process in females. The scientist handling this phase of research is co-corresponding author Jonathan Busada, Ph.D., assistant professor at West Virginia University School of Medicine in Morgantown. When Busada started the project several years ago, he was a postdoctoral fellow working in Cidlowski’s group.
Whether inflammation is inside the stomach or elsewhere in the body, Busada said rates of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases vary depending on sex. He said eight out of 10 individuals with autoimmune disease are women, and his long-term goal is to figure out how glucocorticoids and androgens affect stomach cancer, which is induced by chronic inflammation.
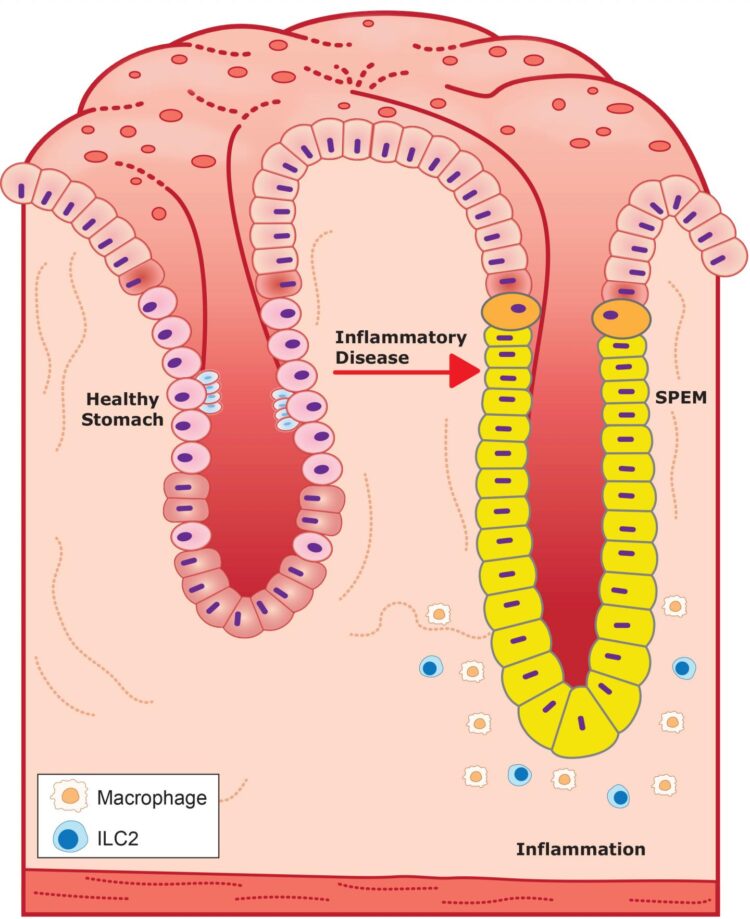
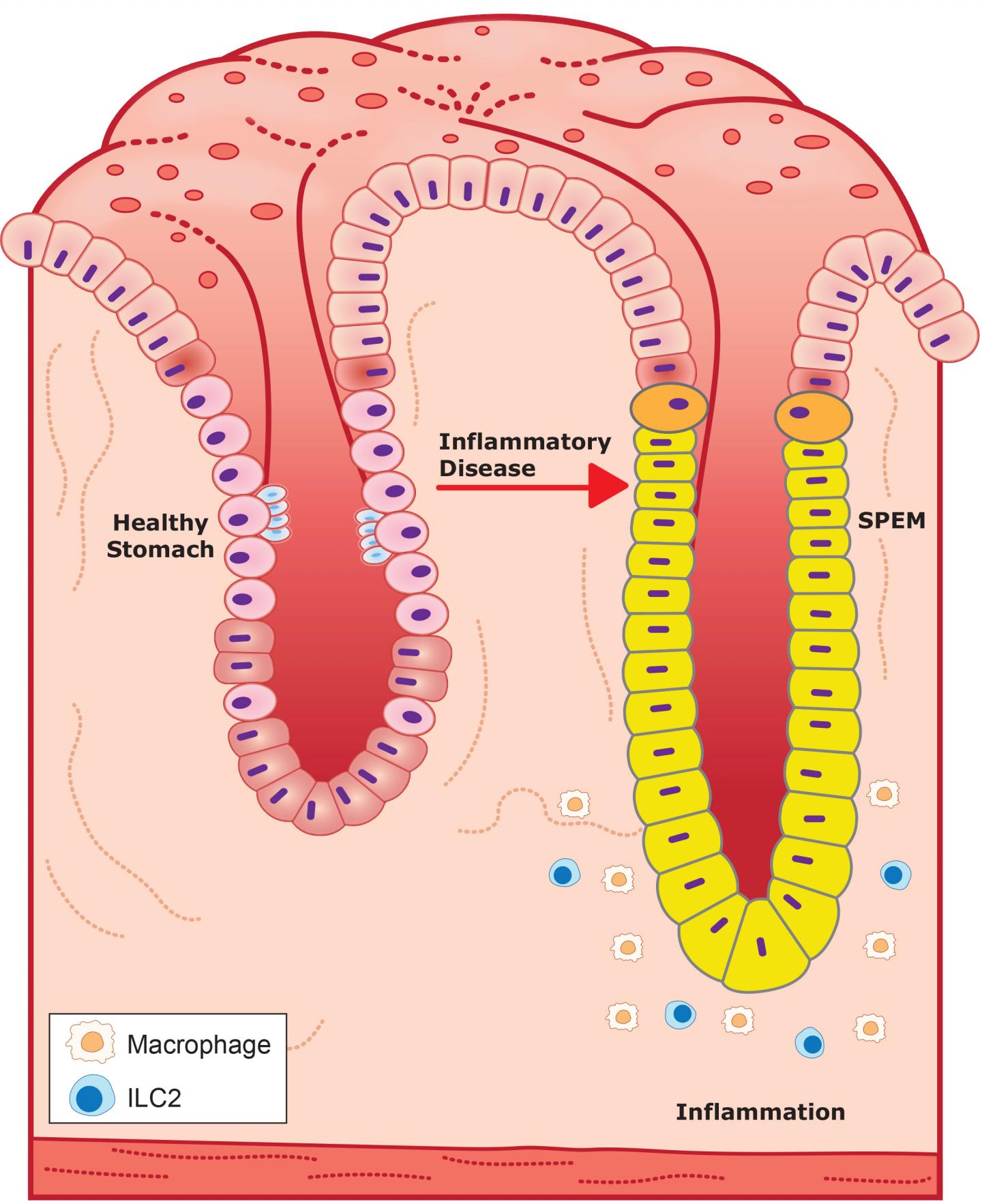
The current research focused on stomach glands called pits, which are embedded in the lining of the stomach.
Busada said the study showed that glucocorticoids and androgens act like brake pedals on the immune system and are essential for regulating stomach inflammation. In his analogy, glucocorticoids are the primary brakes and androgens are the emergency brakes.
“Females only have one layer of protection, so if you remove glucocorticoids, they develop stomach inflammation and a pre-cancerous condition in the stomach called spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia (SPEM),” Busada said. “Males have redundancy built in, so if something cuts the glucocorticoid brake line, it is okay, because the androgens can pick up the slack.”
The research also offered a possible mechanism — or biological process — behind this phenomenon. In healthy stomach glands, the presence of glucocorticoids and androgens inhibit special immune cells called type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). But in diseased stomach glands, the hormones are missing. As a result, ILC2s may act like a fire alarm, directing other immune cells called macrophages to promote inflammation and damage gastric glands leading to SPEM and ultimately cancer.
“ILC2s are the only immune cells that contain androgen receptors and could be a potential therapeutic target,” Cidlowski said.
###
About the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS): NIEHS supports research to understand the effects of the environment on human health and is part of the National Institutes of Health. For more information on NIEHS or environmental health topics, visit
http://www.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.
Grant Numbers:
ZIAES090057
Fi2GM123974
P20GM103434
P20GM121322
U54GM104942
P30GM103488
Reference: Busada JT, Peterson KN, Khadka S, Xu, X, Oakley RH, Cook DN, Cidlowski JA. 2021. Glucocorticoids and androgens protect from gastric metaplasia by suppressing group 2 innate lymphoid cell activation. Gastroenterology: doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.04.075 [Online 7 May 2021].
Media Contact
Robin Arnette
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.