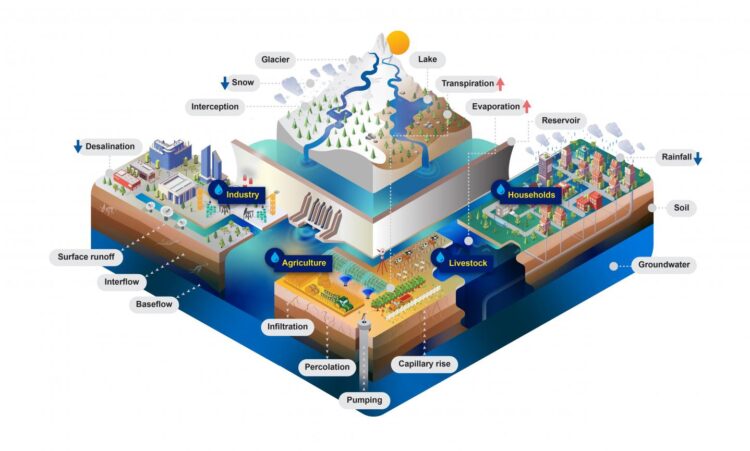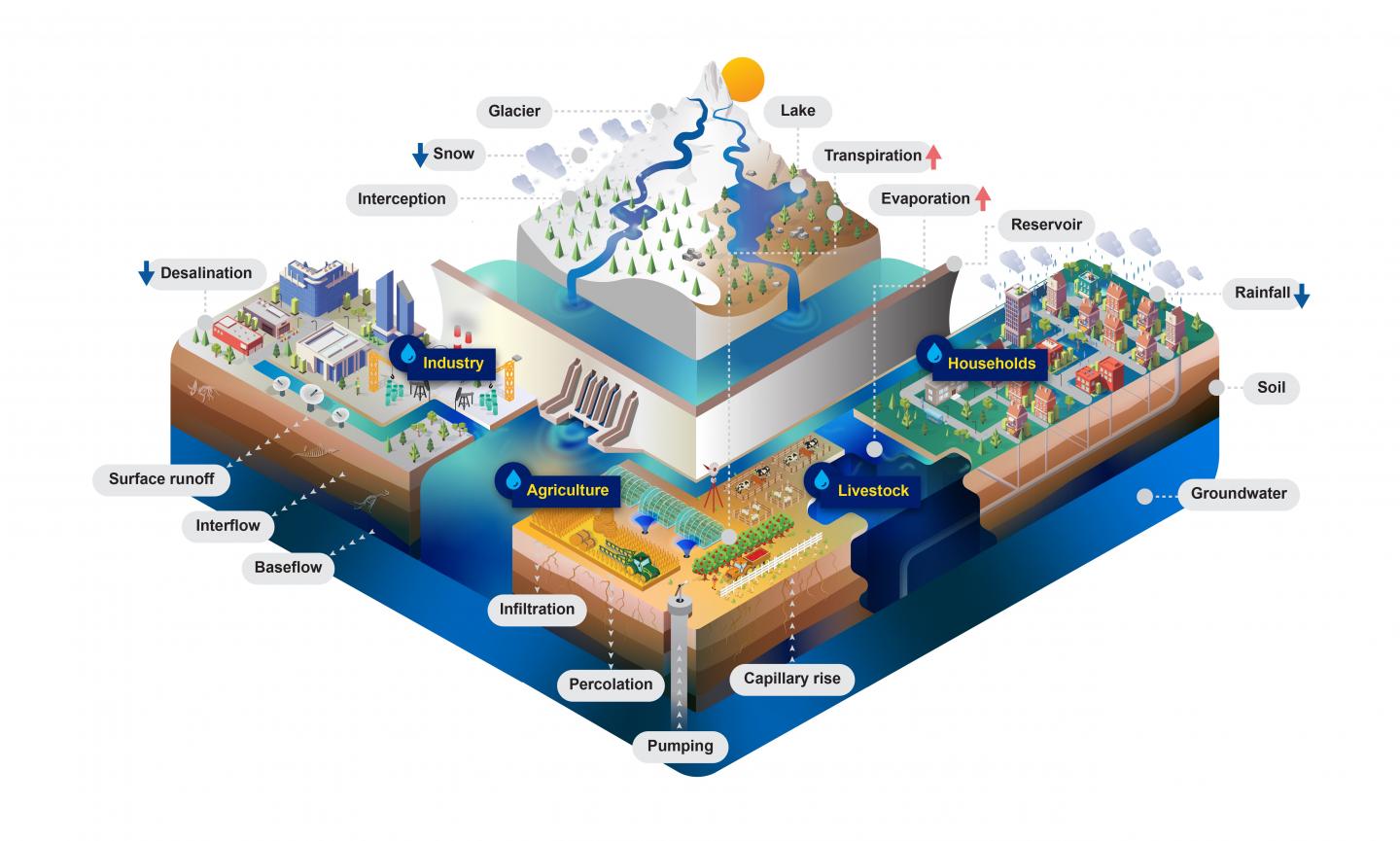
Credit: IIASA
The growing global population and continued economic development will likely require a significant increase in water demand, especially in developing regions. At the same time, climate change is already having global, regional, and local impacts on water availability. Ensuring that the changing supply can meet the continuously growing demand without compromising the sensitive aquatic environments from which it is derived, is clearly a huge challenge that will require strategies and policies informed by science.
In order to aid in the accurate assessment of water supply and the demands of both people and the environment, IIASA researchers have developed a large-scale hydrological and water resources model ? the Community Water Model (CWatM). The model can simulate the movement, distribution, and management of water both globally and regionally to evaluate water availability in terms of water demand and environmental needs. It includes an accounting of how future water demand will evolve in response to socioeconomic change and how water availability will be influenced by climate change. The integrated modeling framework considers water demand from agriculture, domestic needs, energy, industry, and the environment.
The Community Water Model has a modular structure that is open source and uses state-of-the-art data storage protocols as input and output data, while being community-driven to promote the team’s work among the wider water community. It is flexible enough to change between scales, to be integrated with water quality and the hydro-economy, and to be linked with other IIASA models like MESSAGE, the Global Biosphere Management Model (GLOBIOM), BeWhere, and the Environmental Policy Integrated (EPIC) model.
Because the modeling framework is general, it can also be adapted to address new interdisciplinary research questions, which means that it opens the door to many potential applications to explore connections between the nexus aspects of energy, land, and water. According to the researchers, the main novelty of the model is that it combines existing good practice in various scientific communities beyond hydrology itself, rather than provide entirely new concepts for modeling hydrological and socioeconomic processes. Furthermore, the model is customizable to the needs of different users with varying levels of programming skills. This will support and enable different stakeholder groups and scientific communities beyond hydrology and of varying capacities to engage with a hydrological model in support of their investigations
“The Community Water Model represents one of the new key elements of the IIASA Water Program to assess water supply, water demand, and environmental needs at the global and regional level. It is the first step towards developing an integrated modeling framework, that can be used to explore the economic trade-offs between different water management options, encompassing both water supply infrastructure and demand management. With this framework we are able to provide vital information to decision and policymakers,” says Peter Burek, an IIASA researcher and the lead author of a new paper outlining the model’s development published in Geoscientific Model Development.
The Community Water Model will continue to be developed to include more features such as a routing scheme related to reservoirs and canals to better simulate water availability in both agricultural and urban contexts, and the capacity to explore aspects related to groundwater management.
###
The model can be accessed here: https:/
Reference
Burek P, Satoh Y, Kahil T, Tang T, Greve P, Smilovic M, Guillaumot L, Zhao F, & Wada Y (2020). Development of the Community Water Model (CWatM v1.04) – a high-resolution hydrological model for global and regional assessment of integrated water resources management. Geoscientific Model Development 13, 3267-3298 DOI: 10.5194/gmd-13-3267-2020
Contacts:
Researcher contact
Peter Burek
Research Scholar
IIASA Water Program
Tel: +43 2236 807 1090
[email protected]
Press Officer
Ansa Heyl
IIASA Press Office
Tel: +43 2236 807 574
Mob: +43 676 83 807 574
[email protected]
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe. http://www.
Media Contact
Ansa Heyl
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.