Credit: (Graphics: KIT)
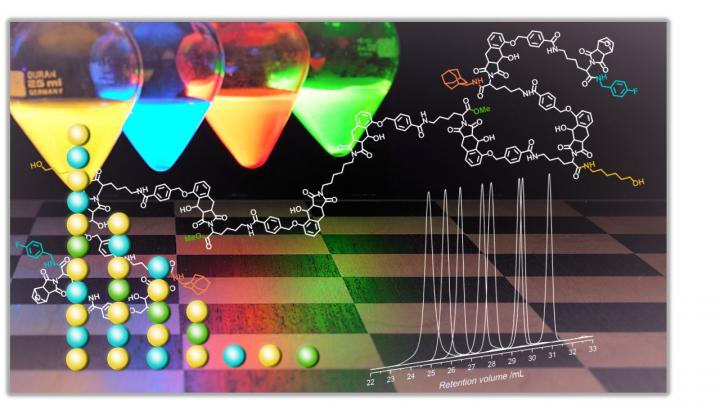
Chemists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have succeeded in specifically controlling the setup of precision polymers by light-induced chemical reactions. The new method allows for the precise, planned arrangement of the chain links, i.e. monomers, along polymer chains of standard length. The precisely structured macromolecules develop defined properties and may possibly be suited for use as storage systems of information or synthetic biomolecules. This novel synthesis reaction is now reported in open-access Nature Communications. (DOI: 10.1038/NCOMMS13672)
Chemical reactions may be triggered by light at room temperature. This effect was used by KIT scientists to specifically link molecules to defined polymer chains under light. "In many conventional processes, polymer chains of variable length are produced. The building blocks are arranged randomly along the chain," says Professor Christopher Barner-Kowollik of the KIT Institute for Chemical Technology and Polymer Chemistry (ITCP). "We wanted to develop a light-induced method for polymer structuring, which reaches the precision of nature," the Holder of the Chair for Preparative Macromolecular Chemistry adds. The models in nature, e.g. proteins, have an exactly defined structure. The new, light-induced synthesis method allows for customized molecule design, with the building blocks being arranged at the positions desired similar to a string of colored pearls.
"By controlling the structure of the molecule, the so-called sequence, properties of macromolecules can be controlled," Barner-Kowollik says. "Sequence-defined polymers might also be used as molecular data and information storage systems." Information might be encoded by the sequence of monomers, similar to the genetic information of the DNA.
The team of Barner-Kowollik now presents the new light-induced and highly precise polymerization method in Nature Communications under the heading of "Coding and Decoding Libraries of Sequence Defined Functional Copolymers Synthesized via Photoligation." The developers expect the fundamental method to become a tool for chemists, biologists, and materials scientists and to be the key to future macromolecular chemistry.
The new method was developed under the Collaborative Research Center 1176 "Molecular Structuring of Soft Matter" which is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and coordinated by KIT. For the first four years, a budget of EUR 9 million is available to the Collaborative Research Center that started in January 2016.
###
Nicolas Zydziak, Waldemar Konrad, Florian Feist, Sergii Afonin, Steffen Weidner, and Christopher Barner-Kowollik: Coding and Decoding Libraries of Sequence Defined Functional Copolymers Synthesized via Photoligation. DOI: 10.1038/NCOMMS13672
More information:
https://www.kit.edu/kit/english/pi_2015_143_specifically-controlling-the-structure-of-macromolecules.php
https://www.kit.edu/kit/english/pi_2016_091_switching-chemical-reactions-with-light.php
Kosta Schinarakis, PKM – Science Scout, Phone: +49 721 608 41956, Fax: +49 721 608 43658, Email: [email protected]
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,300 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
Since 2010, the KIT has been certified as a family-friendly university.
Media Contact
Monika Landgraf
[email protected]
49-721-608-47414
@KITKarlsruhe
http://www.kit.edu/index.php
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag





