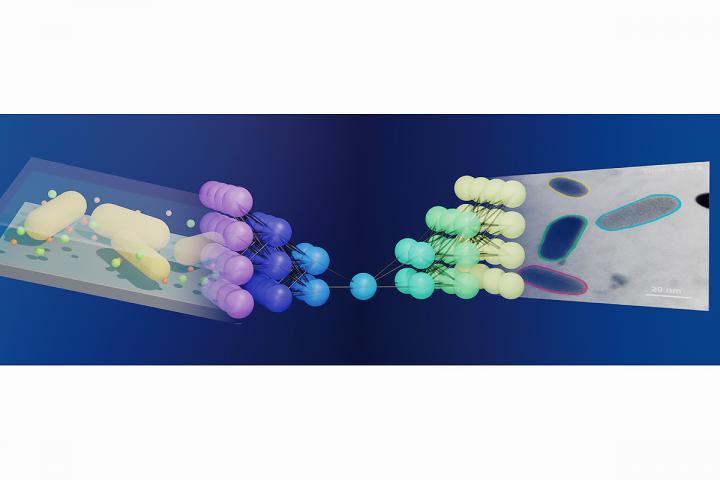
Credit: Graphic courtesy ACS and the Qian Chen group
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In the nanoworld, tiny particles such as proteins appear to dance as they transform and assemble to perform various tasks while suspended in a liquid. Recently developed methods have made it possible to watch and record these otherwise-elusive tiny motions, and researchers now take a step forward by developing a machine learning workflow to streamline the process.
The new study, led by Qian Chen, a professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, builds upon her past work with liquid-phase electron microscopy and is published in the journal ACS Central Science.
Being able to see – and record – the motions of nanoparticles is essential for understanding a variety of engineering challenges. Liquid-phase electron microscopy, which allows researchers to watch nanoparticles interact inside tiny aquariumlike sample containers, is useful for research in medicine, energy and environmental sustainability and in fabrication of metamaterials, to name a few. However, it is difficult to interpret the dataset, the researchers said. The video files produced are large, filled with temporal and spatial information, and are noisy due to background signals – in other words, they require a lot of tedious image processing and analysis.
“Developing a method even to see these particles was a huge challenge,” Chen said. “Figuring out how to efficiently get the useful data pieces from a sea of outliers and noise has become the new challenge.”
To confront this problem, the team developed a machine learning workflow that is based upon an artificial neural network that mimics, in part, the learning potency of the human brain. The program builds off of an existing neural network, known as U-Net, that does not require handcrafted features or predetermined input and has yielded significant breakthroughs in identifying irregular cellular features using other types of microscopy, the study reports.
“Our new program processed information for three types of nanoscale dynamics including motion, chemical reaction and self-assembly of nanoparticles,” said lead author and graduate student Lehan Yao. “These represent the scenarios and challenges we have encountered in the analysis of liquid-phase electron microscopy videos.”
The researchers collected measurements from approximately 300,000 pairs of interacting nanoparticles, the study reports.
Click here to see liquid-phase electron microscopy with combined machine learning in action.
As found in past studies by Chen’s group, contrast continues to be a problem while imaging certain types of nanoparticles. In their experimental work, the team used particles made out of gold, which is easy to see with an electron microscope. However, particles with lower elemental or molecular weights like proteins, plastic polymers and other organic nanoparticles show very low contrast when viewed under an electron beam, Chen said.
“Biological applications, like the search for vaccines and drugs, underscore the urgency in our push to have our technique available for imaging biomolecules,” she said. “There are critical nanoscale interactions between viruses and our immune systems, between the drugs and the immune system, and between the drug and the virus itself that must be understood. The fact that our new processing method allows us to extract information from samples as demonstrated here gets us ready for the next step of application and model systems.”
The team has made the source code for the machine learning program used in this study publicly available through the supplemental information section of the new paper. “We feel that making the code available to other researchers can benefit the whole nanomaterials research community,” Chen said.
###
Chen also is affiliated with chemistry, the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology and the Materials Research Laboratory at the U. of I.
The National Science Foundation and Air Force Office of Scientific Research supported this study.
Editor’s notes:
To reach Qian Chen, call 217-300-1137; [email protected].
The paper “Machine learning to reveal nanoparticle dynamics from liquid-phase TEM videos” is available online and from the U. of I. News Bureau. DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c00430.
Media Contact
Lois Yoksoulian
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




