Device designed for security systems can be built smaller, without the need for an active, energy-extensive doorway

Credit: Huan Liu
WASHINGTON, January 21, 2020 — Most traditional electromagnetic methods for detecting hidden metal objects involve systems that are heavy, bulky and require lots of electricity.
Recent studies have shown metallic objects have their own magnetic fingerprints based on size, shape and physical composition. In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, scientists look to leverage these observations to potentially create a smaller and cheaper system that is just as effective as their larger counterparts.
Researchers demonstrated the use of a new type of magnetic-based metal detection security system using magnetic fingerprinting to identify hidden metal objects more efficiently. By using materials in an emerging field known as weak magnetic detection, the device identified a wide variety of metallic objects, ranging from cellphones to hammers.
The early results helped establish magnetic fingerprinting as a feasible path forward in security detection.
“The achievement of applying magnetic anomaly detection technology in magnetic sensor arrays promises smart public security sensing systems with low cost, small size and low power budgets,” said Huan Liu, an author on the paper. “Unlike other electromagnetic detection methods, it doesn’t require someone to walk through a door framework and can be built in a compact size.”
Most of today’s security metal detectors only function when the user is actively searching for a metallic object, often by using some form of radiation. Such active screening requires machines to be bulky and demand a lot of energy.
In contrast, the group’s device can operate in a passive mode, significantly reducing the energy required for operation. This also potentially allows the technology to be portable and not need to rely on the constrained, threshold type of metal detectors that the public are most familiar.
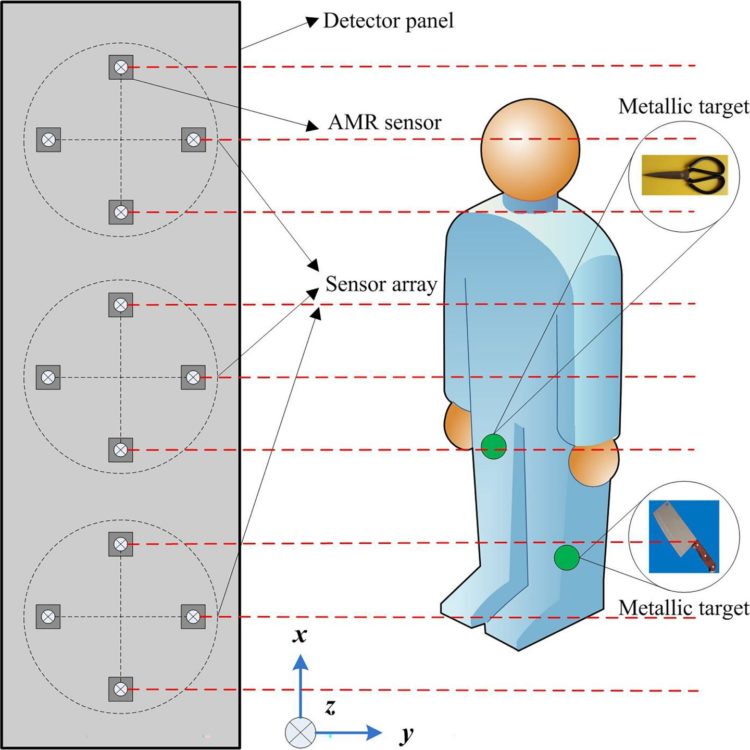
The approach integrates three arrays of anisotropic magnetoresistance sensors with a microcontroller, computer and battery. After 2D magnetic data is gleaned from the advice, the researchers developed a computer workflow that processes the data and its fingerprint, removing noise.
The approach was able to identify fingerprints for objects larger than 16 inches and identify multiple objects separated by less than 8 inches.
“The major challenge in designing a weak magnetic detection-based public security system may lie in the difficulty to distinguish the weak object signals, like scissors and hammers, from unknown interference, which would decrease the signal-to-noise ratio and the range of the detection zone,” Liu said.
The group next hopes to better optimize the device’s ability to accurately identify fingerprints from farther distances.
###
The article, “Magnetic gradient full-tensor fingerprints for metallic objects detection of a security system based on anisotropic magnetoresistance sensor arrays,” is authored by Huan Liu, Xiaobin Wang, Junchi Bin, Haobin Dong, Jian Ge, Zheng Liu, Zhiwen Yuan, Jun Zhu, and Xinqun Luan. The article will appear in the journal AIP Advances on Jan. 21, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5133857). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
301-209-3090
Related Journal Article
http://dx.