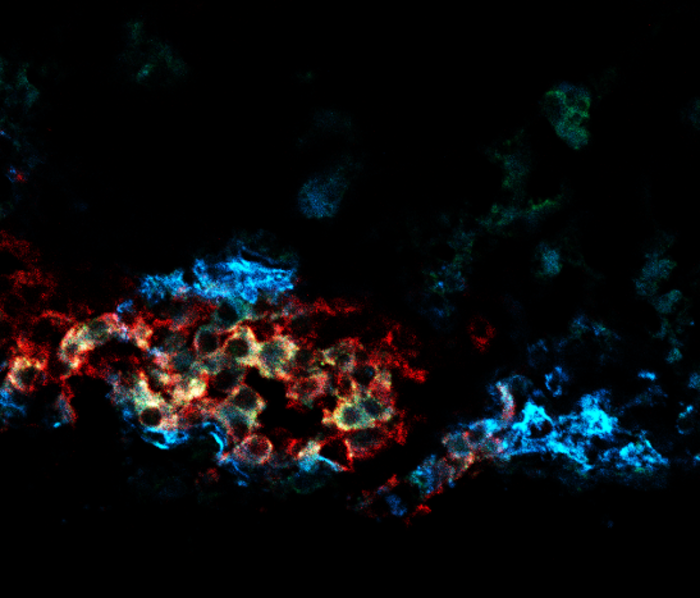
Multiple types of beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas, helping to balance blood sugar levels. Losing a particularly productive type of beta cell may contribute to the development of diabetes, according to a new study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
Credit: Weill Cornell Medicine
Multiple types of beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas, helping to balance blood sugar levels. Losing a particularly productive type of beta cell may contribute to the development of diabetes, according to a new study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
In the study, published March 16 in Nature Cell Biology, Dr. James Lo, associate professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, and colleagues measured gene expression in individual beta cells collected from mice to determine how many different types of beta cells exist in the pancreas. The team discovered four distinct beta cell types, including one that stood out. The cluster 1 group of beta cells produced more insulin than other beta cells and appeared better able to metabolize sugar. The study also showed that loss of this beta cell type might contribute to type 2 diabetes.
“Before this, people thought a beta cell was a beta cell, and they just counted total beta cells,” said Dr. Lo, who is also a member of the Weill Center for Metabolic Health and the Cardiovascular Research Institute at Weill Cornell Medicine and a cardiologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “But this study tells us it might be important to subtype the beta cells and that we need study the role of these special cluster 1 beta cells in diabetes.”
Drs. Doron Betel, Jingli Cao, Geoffrey Pitt and Shuibing Chen at Weill Cornell Medicine teamed up with Dr. Lo to carry out the study.
The investigators used a technique called single-cell transcriptomics to measure all the genes expressed in individual mouse beta cells and then used that information to group them into four types. The cluster 1 beta cells had a unique gene expression signature that included high expression of genes that help cellular powerhouses called mitochondria to break down sugar and power them to secrete more insulin. Additionally, they could distinguish the cluster 1 beta cells from the other beta cell types by its high expression of the CD63 gene, which enabled them to use the CD63 protein as a marker for this specific beta cell type.
“CD63 expression provided us a way to identify the cells without destroying them and allowed us to study the live cells,” he said.
When the team looked at both human and mouse beta cells, they found that cluster 1 beta cells with high CD63 gene expression produce more insulin in response to sugar than the three other types of beta cells with low CD63 expression.
“They are very high-functioning beta cells,” Dr. Lo said. “We think they may carry the bulk of the workload of producing insulin, so their loss might have profound impacts.”
In mice fed an obesity-inducing, high-fat diet and mice with type 2 diabetes, the numbers of these insulin-producing-powerhouse beta cells decreased.
“Because the numbers of cluster 1/high CD63 cells went down, you may have less insulin production, which may play a major role in diabetes development,” he said.
Transplanting beta cells with high CD63 production into mice with type 2 diabetes restored their blood sugar levels to normal. But removing the transplanted cells caused high blood sugar levels to return. Transplanting low CD63 production beta cells into the mice didn’t restore blood sugar to normal levels. The transplanted low CD63 beta cells instead appeared dysfunctional.
The discovery may have important implications for the use of beta cell transplants to treat diabetes, Dr. Lo said. For example, it may be better to transplant only high CD63- beta cells. He noted that it might also be possible to transplant fewer of these highly productive cells. Dr. Lo’s team also found that humans with type 2 diabetes had lower levels of high CD63 beta cells compared to those without diabetes.
Next, Dr. Lo and his colleagues would like to find out what happens to the high CD63-producing beta cells in mice with diabetes and how to keep them from disappearing.
“If we can figure out how to keep them around longer, surviving and functional, that could lead to better ways to treat or prevent type 2 diabetes,” he said.
They would also like to study how existing diabetes treatments affect all types of beta cells. GLP-1 agonists, which help increase the release of insulin in people with diabetes, interact with high and low CD63-producing beta cells.
“Our study also shows that GLP-1 agonists might also be a way to get the low CD63-producing beta cells to work better,” Dr. Lo said.
Many Weill Cornell Medicine physicians and scientists maintain relationships and collaborate with external organizations to foster scientific innovation and provide expert guidance. The institution makes these disclosures public to ensure transparency. For this information, see profile for Dr. Lo.
Journal
Nature Cell Biology
Article Publication Date
16-Mar-2023




