Credit: Illustration: Hedyeh Rezaei
Selective communication among different brain regions is crucial for brain function. But the weak and sparse connectivity of the brain is a big hurdle. During the last decade neuroscientists have identified various means by which this limitation can be counteracted. Now scientists from Iran, Germany and Sweden have identified a new role of bi-directional connections in accelerating the communication between brain regions. They have now presented their results in the scientific journal PLoS Computational Biology.
There are essentially two ways by which weak and sparse connectivity can be countered: either by synchrony or by oscillations. In synchrony mode, many neurons spike together (synchronously) when they transmit stimulation. Together they have a stronger combined effect in the downstream network than they do individually. By contrast, in oscillation mode, network oscillations increase the effective connectivity periodically by modulating the membrane potentials of downstream neurons that are receiving the stimulation.
But the oscillations need to be synchronized in the sender and receiver networks. “It is an open question how such synchronous oscillations may occur in the brain. Some time back we proposed that the resonance property of neuronal networks can be used to generate synchronized oscillations,” says Ad Aertsen from the Bernstein Center Freiburg (BCF) of the University of Freiburg. Resonance in a neuronal network means that when this network is stimulated at a specific frequency, the network starts to oscillate and the input has a much bigger impact. This idea is referred to as “communication through resonance (CTR).”
However, CTR posed another problem. It takes several oscillation cycles to build up the resonance in the network. Moreover, such resonance needs to be created at every downstream stage. This means that communication across networks is quite slow. “We thought that synchrony and oscillations provide fast and slow communication modes, respectively. And both can be used in different situations. But we remained wary of this issue,” explains Arvind Kumar from the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) in Stockholm, Sweden.
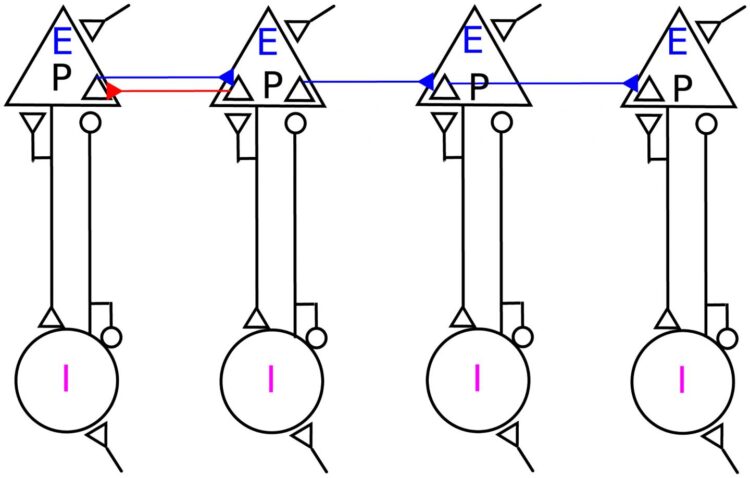
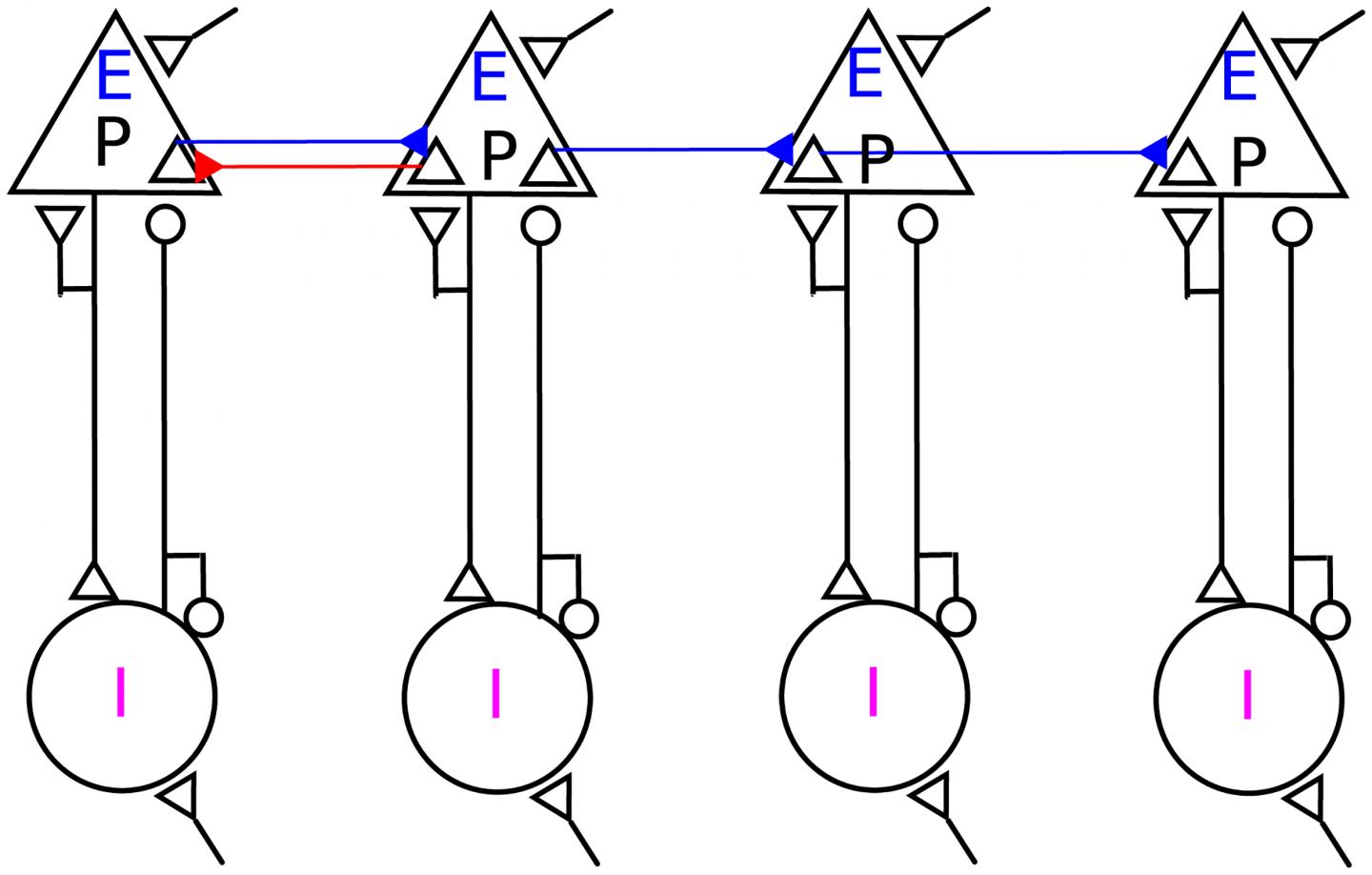
A possible way to speed up the communication is to reduce the time it takes to build-up the resonance. To this end, the group focused on the anatomical observation of bi-directional connections among brain areas. That is, not only do neurons from the sender network project to receiver neurons, but some neurons from the receiver network also project back to the sender network. “Such bi-directional connections are few, but they are sufficient to support a loop between sender and receiver networks,” explains Alireza Valizadeh of Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences in Zanjan, Iran. An important consequence of such a loop is that resonance can be established in fewer cycles. More importantly even, the loop can amplify the signal and there is no need to build-up resonance in subsequent layers. Hedyeh Rezaei, a PhD-student at Zanjan University and visiting student at the BCF under the auspices of her research project says: “It is remarkable that such a loop of connections between just one resonance pair of sender and receiver networks can speed up the network communication by at least a factor of two.”
Ad Aertsen sums up: “These new findings provide support for the idea of ‘communication through resonance.’ What is important is that these results implicate bi-directional connections between brain regions in a novel function, namely, in shaping more rapid and reliable communication between them.”
###
Original Publication:
Rezaei H, Aertsen A, Kumar A, Valizadeh A (2020). Facilitating the propagation of spiking activity in feedforward networks by including feedback. PLOS Computational Biology. 16(8): e1008033. https:/
Further reading:
Hahn G, Bujan AF, Frégnac Y, Aertsen A, Kumar A (2014). Communication through resonance in spiking neuronal networks. PLoS Computational Biology 10(8): e1003811.
Hahn G, Ponce-Alvarez A, Deco G, Aertsen A, Kumar A (2019) Portraits of communication in neuronal networks. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 20(2): 117-27.
Contact:
Bernstein Center Freiburg
University of Freiburg
Prof. Dr. Arvind Kumar
Department of Computational Science and Technology
KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm
[email protected]
Media Contact
Ad Aertsen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.