Credit: Jolyon Troscianko
Changes in the colour and intensity of light pollution over the past few decades result in complex and unpredictable effects on animal vision, new research shows.
Insect attraction to light is a well-known phenomenon, but artificial lighting can also have more subtle consequences for species that rely on night-time vision for their behaviour.
To explore these effects, University of Exeter researchers examined the impact of more than 20 kinds of lighting on the vision of moths, and birds that eat them.
The study found that elephant hawkmoth vision was enhanced by some types of lighting and disrupted by others, while the vision of birds that hunt moths was improved by almost any lighting.
Night-time lighting is increasing rapidly worldwide, and has changed dramatically in the last 20 years, as amber (low-pressure sodium) streetlights are replaced with a diverse range of modern lights such as LEDs.
“Modern broad-spectrum lighting allows humans to see colour more easily at night,” said Dr Jolyon Troscianko, of the Centre for Ecology and Conservation on Exeter’s Penryn Campus in Cornwall.
“However, it is difficult to know how these modern light sources affect the vision of other animals.
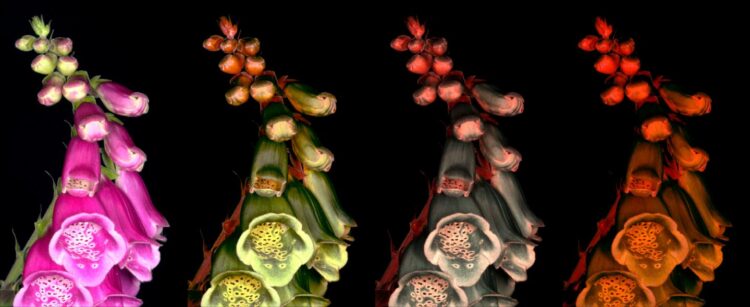
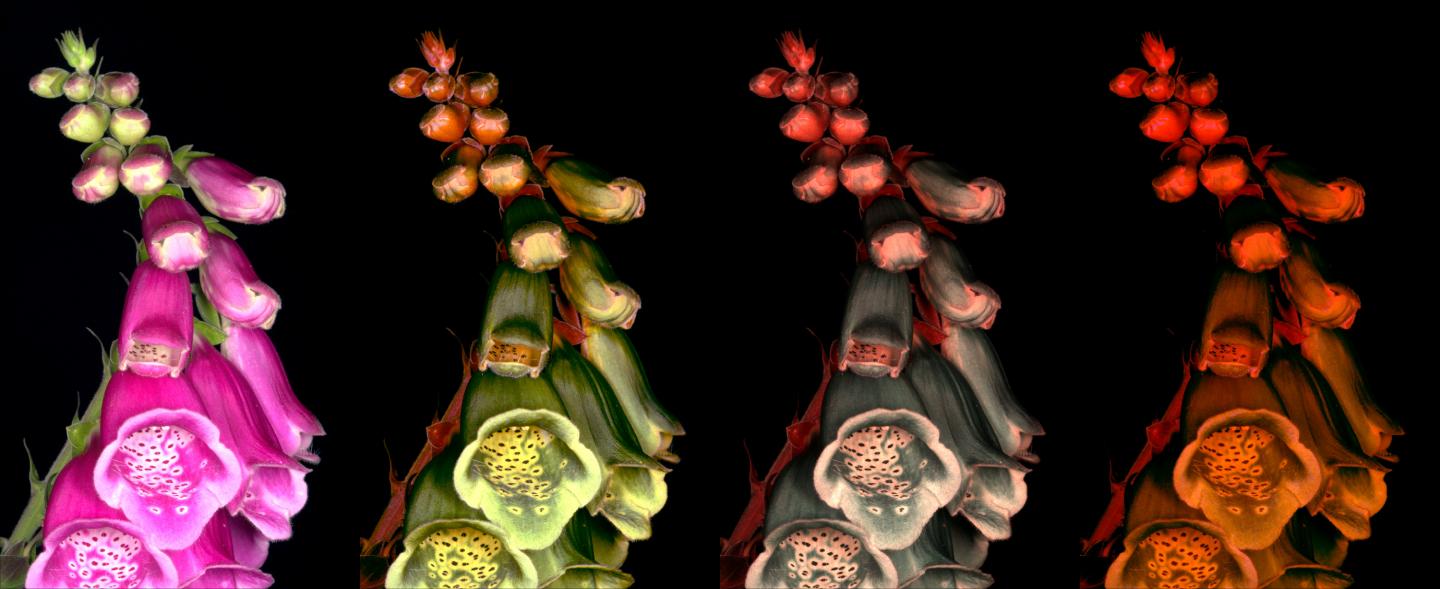
“Hawkmoth eyes are sensitive to blue, green and ultraviolet, and they use this colour vision to help find flowers just like bees, but at incredibly low light levels – even under starlight.
“Moths are also vitally important pollinators – accounting for a similar proportion of pollination as bees – so we urgently need to investigate how lighting affects them.
“We used animal vision modelling to calculate the ability of moths to see flower colours, and of birds to see camouflaged moths under a wide range of natural and artificial lighting.
“Artificial lights designed for human vision lack the blue and ultraviolet ranges that are key to moth colour vision, and under many conditions will block the moth’s ability to see any colours at all.
“This could make it more difficult for them to find and pollinate wildflowers, and for them to find suitable spots to camouflage them from predators.
“Conversely, bird vision is much more robust, meaning artificial light will help them to find camouflaged moth prey, and will allow them to hunt later into the evening and earlier in the morning.”
The study finds that phosphor converted amber LED lighting – often suggested to be less harmful to nocturnal insects – has unpredictable consequences for insect vision depending on distance from the light source and the colour of the objects viewed.
White lights (with a greater blue component), allow for more natural colour vision in moths, but these light sources are known to be harmful for other species.
Moth numbers are declining across Europe, but this is particularly true of nocturnal species, with growing evidence for a link with light pollution.
The researchers call for a “nuanced approach” to lighting, beyond general efforts to limit the amount and intensity of light where possible.
###
The study was funded by the Natural Environment Research Council.
The paper, published in the journal Nature Communications, is entitled: “Artificial nighttime lighting impacts visual ecology links between flowers, pollinators and predators.”
Media Contact
Alex Morrison
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.