Credit: Osaka City University
In the 2020 February 25 issue of Scientific Reports, a research group from the Department of Hepatology in Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan reported that levels of a circulating soluble immune checkpoint protein can be used as a potential marker to predict overall survival in patients with advanced HCC. In addition, treatment with an anti-angiogenic agent sorafenib, the current first-line systemic therapy, revealed dynamic changes of soluble checkpoint protein levels in patients with advanced HCC.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, including monoclonal antibodies that target inhibitory immune receptors such as programmed cell death-1 (PD-1), programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4), have emerged as promising treatments for many types of cancer. However, immune checkpoint inhibitors have not been approved for treatment of un-resected, advanced HCC. Some anti-angiogenic agents including sorafenib are currently recommended as first-line or second-line treatments for patients with advanced HCC who have well-preserved liver function. Clinical trials that combine the use of an anti-angiogenic agent with an immune checkpoint inhibitor, such as bevacizumab plus atezolizumab, are ongoing.
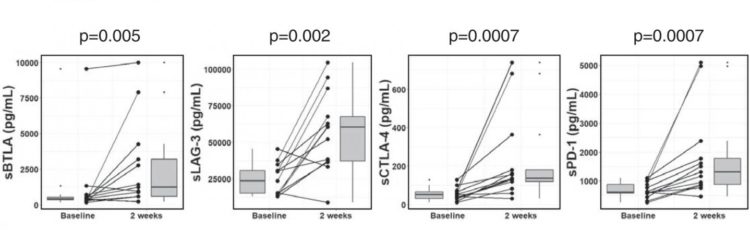
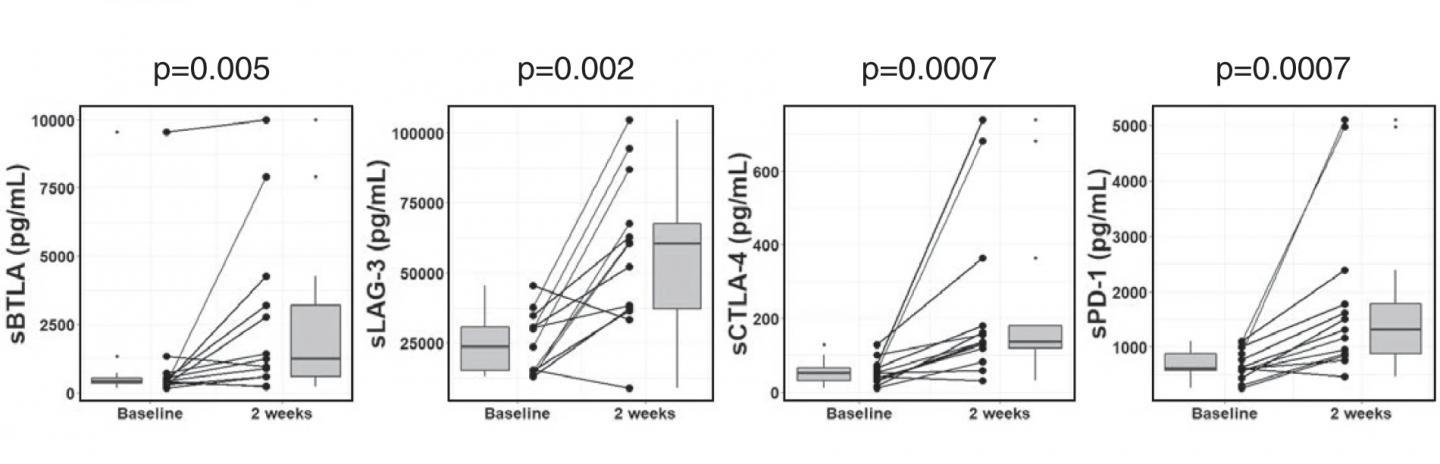
This study profiled the baseline levels of 16 soluble checkpoint proteins and their changes following sorafenib treatment for HCC. Plasma samples were obtained from 53 patients with advanced HCC at baseline, week 1, 2 and 4 of sorafenib treatment, and tested for the concentrations of soluble checkpoint proteins using multiplexed fluorescent bead-based immunoassays. Multivariate analysis showed high soluble B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (sBTLA) levels at baseline were an independent predictor of poor overall survival (Fig. 1). BTLA (indicated by arrows) was highly expressed in T cells and macrophages in peritumoral areas (Fig. 2). At week 2, the concentrations of most inhibitory proteins, including sBTLA, sLAG3, sCTLA-4, and sPD-1, had significantly increased (Fig. 3). The fold-changes of soluble checkpoint receptors and their ligands, including sCTLA-4 with sCD80/sCD86, sPD-1 with sPD-L1; and the fold-changes of sCTLA-4 with sBTLA or sPD-1, were positively correlated (data not shown).
The preparation of molecular-targeted therapies is very costly, and therapeutic responses to treatment only occur in a minority of patients. Furthermore, reliable biomarkers that identify patients who would benefit from immunotherapy have yet to be identified. The research group will conduct further investigations in a large group of patients with HCC to explore potential biomarkers for predicting patient outcomes or therapeutic responses.
The design and rationale of the combinations of anti-angiogenic agents and immune checkpoint inhibitors were based on results of previous in vivo studies, indicating that anti-angiogenic agents might enhance anti-tumor immunity through multiple mechanisms. However, the immunomodulatory effects of anti-angiogenic agents in HCC had yet to be elucidated in a clinical setting. Associate Professor Masaru Enomoto said “it was quite surprising for us that even an anti-angiogenic agent alone resulted in the dynamic changes of the immune systems in patients with HCC. Further investigation is also necessary to determine which anti-angiogenic agents are optimal partners for specific immune checkpoint inhibitors, and how much the optimal doses are when used in combination.”
###
Media Contact
Kaori NISHIMAE
[email protected]
81-666-053-410
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.