Education saves lives regardless of age, sex, location, and social and demographic backgrounds. That’s according to the latest and largest study of its kind published today in The Lancet Public Health.
Credit: eurohealthnet.eu
Education saves lives regardless of age, sex, location, and social and demographic backgrounds. That’s according to the latest and largest study of its kind published today in The Lancet Public Health.
Researchers have known that those who reach higher levels of schooling live longer than others, but they didn’t know to what extent until now. What they found was that the risk of death drops by two per cent with every additional year of education. That means those who completed six years of primary school had a lower risk of death by an average of 13 per cent. After graduating from secondary school, the risk of dying was cut by nearly 25 per cent, and 18 years of education lowered the risk by 34 per cent.
Researchers also compared the effects of education to other risk factors such as eating a healthy diet, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol, and they found the health outcome to be similar. For example, the benefit of 18 years of education can be compared to that of eating the ideal amount of vegetables, as opposed to not eating vegetables at all. Not going to school at all is as bad for you as drinking five or more alcoholic drinks per day or smoking ten cigarettes a day for 10 years.
“Education is important in its own right, not just for its benefits on health, but now being able to quantify the magnitude of this benefit is a significant development,” said Dr. Terje Andreas Eikemo, co-author and head of Centre for Global Health Inequalities Research (CHAIN) at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
While the benefits of education are greatest for young people, those older than 50 and even 70 years still benefit from the protective effects of education.
Researchers found no significant difference in the effects of education between countries that have reached different stages of development. This means that more years of education is just as effective in rich countries as in poor countries.
“We need to increase social investments to enable access to better and more education around the globe to stop the persistent inequalities that are costing lives,” said Mirza Balaj, co-lead author and postdoctoral fellow at NTNU’s Department of Sociology and Political Science. “More education leads to better employment and higher income, better access to healthcare, and helps us take care of our own health. Highly educated people also tend to develop a larger set of social and psychological resources that contribute to their health and the length of their lives.”
“Closing the education gap means closing the mortality gap, and we need to interrupt the cycle of poverty and preventable deaths with the help of international commitment,” said Claire Henson, co-lead author and researcher at Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington’s School of Medicine. “In order to reduce inequalities in mortality, it’s important to invest in areas that promote people’s opportunities to get an education. This can have a positive effect on population health in all countries.”
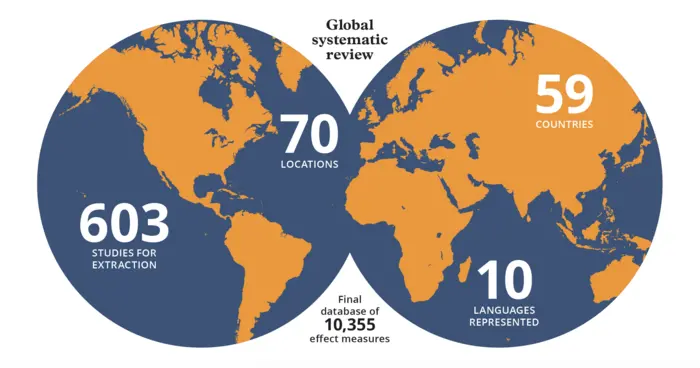
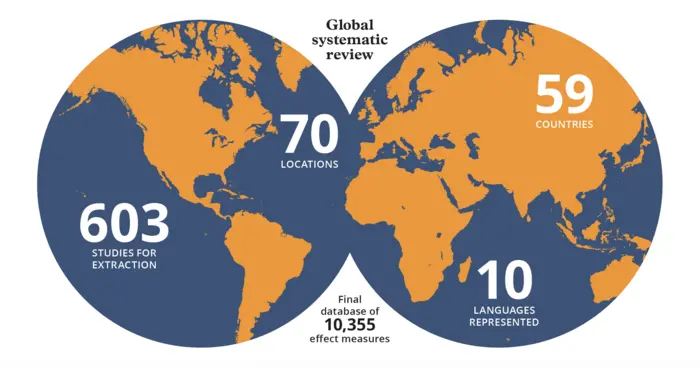
The study identified data from 59 countries and included over 10,000 data points collected from over 600 published articles. Most of the studies reviewed for this study were from high-income settings, highlighting the need for more research in low- and middle-income countries, particularly from sub-Saharan and north Africa where data are scarce.
“Our focus now should be on regions of the world where we know access to schooling is low, and where there is also limited research on education as a determinant of health,” said Dr. Emmanuela Gakidou, co-author and professor at IHME.
Journal
The Lancet Public Health
DOI
10.1016/S2468-2667(23)00306-7
Method of Research
Meta-analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Effects of education on adult mortality: a global systematic review and meta-analysis
Article Publication Date
23-Jan-2024