Slow growth in health sector spending is projected in Sub-Saharan Africa as reported in a study published in the open access journal, PLOS Global Public Health. The decline is expected to continue to 2050, according to Angela E Apeagyei and researchers at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, University of Washington, Seattle, and is driven by tepid growth in the share of government spending that is allocated to health and reductions in development assistance for health.
Slow growth in health sector spending is projected in Sub-Saharan Africa as reported in a study published in the open access journal, PLOS Global Public Health. The decline is expected to continue to 2050, according to Angela E Apeagyei and researchers at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, University of Washington, Seattle, and is driven by tepid growth in the share of government spending that is allocated to health and reductions in development assistance for health.
The research analyses data from databases covering development assistance for health, global health spending and gross domestic spending (GDP) per capita as well as an expected health spending database which provides projected health spending data to 2050. It finds that except for central and eastern Europe and Central Asia, around the world total health spending is expected to rise as a share of GDP, but in Sub-Saharan Africa (except in southern sub-Sahara Africa) it is expected to decrease.
Beyond the challenge of a low prioritization of the health sector in the government budget, another major driver of this decline is a reduction in development assistance for health. The Millennium Development Goals led to a period of growth in health funding, and development assistance for health grew on average 11.1% annually from 2000 until 2015. It has since dropped to just 4.6% and was particularly hit by the global economic issues caused by the COVID pandemic and subsequent economic shocks such as the war in Ukraine. Although government spending on health in Sub-Saharan Africa has increased, and is expected to continue to rise, the gap left by decreases in development assistance will not be met.
Without improvements, this trend will pose a significant challenge to meeting health-related Sustainable Development Goals and the African Union’s Africa Agenda 2063. The authors hope that their analysis will help policymakers understand future health spending patterns and can translate the insights into tangible actions that can help navigate the region’s complex economic and health challenges.
The authors add: “For countries in sub-Saharan Africa, the projected growth in donor and government funding for health is expected to be significantly lower compared to countries in other regions. This worrying trend underscores the need to prioritize innovative financing strategies to strengthen health systems in line with the region’s economic growth and the broader health needs of its population.”
#####
Press-only preview: https://plos.io/3SQcEmu
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Global Public Health: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0003433
Contact: Angela Apeagyei, [email protected]
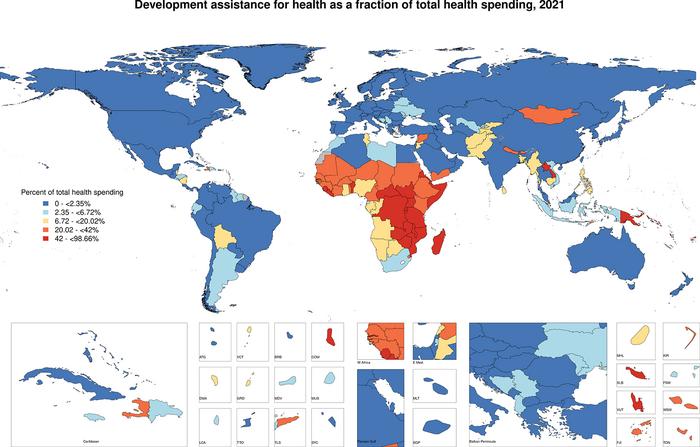
Image Caption: Fig 2. Proportion of health spending that is development assistance, 2021.
Image Credit: Apeagyei et al., 2024, PLOS Global Public Health, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Image Link: https://plos.io/3SV6Tnx
Citation: Apeagyei AE, Lidral-Porter B, Patel N, Solorio J, Tsakalos G, Wang Y, et al. (2024) Financing health in sub-Saharan Africa 1990–2050: Donor dependence and expected domestic health spending. PLOS Glob Public Health 4(7): e0003433. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0003433
Author Countries: Ghana, United Kingdom, United States
Funding: AEA, BLP, NP, JS, GT, YW, WW, AW, and JLD were funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. YZ and JN received no specific funding for this work. The funder of the study had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report.
Journal
PLOS Global Public Health
DOI
10.1371/journal.pgph.0003433
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
COI Statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.