Credit: © KU Leuven – Wenzhi Ruan
Plasma astrophysicists at KU Leuven have created the first self-consistent simulation of the physical processes that occur during a solar flare. The researchers used Flemish supercomputers and a new combination of physical models.
Solar flares are explosions on the surface of the Sun that release an enormous amount of energy, equivalent to a trillion ‘Little Boy’ atomic bombs exploding at the same time. In extreme cases, solar flares can disable radio connections and power stations on Earth, but they are also at the basis of stunning space weather phenomena. The Northern Lights, for instance, are linked to a solar flare that disturbs the magnetic field of the Sun to such an extent that a bubble of solar plasma can escape from the atmosphere of the Sun.
Unique simulation
Thanks to satellites and solar telescopes, we already understand quite a lot about the physical processes that take place during a solar flare. For one thing, we know that solar flares convert energy from magnetic fields into heat, light and motion energy very efficiently.
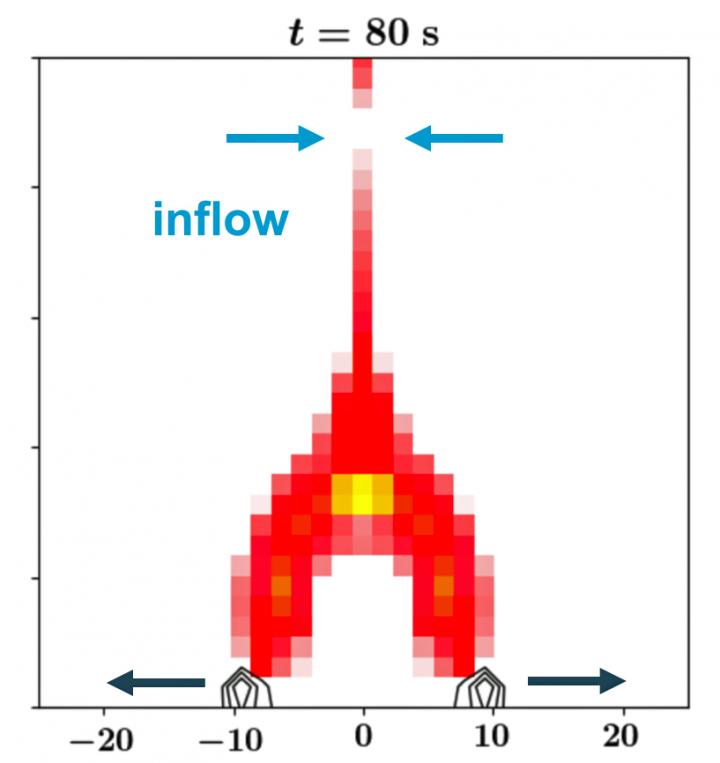
In science textbooks, these processes are commonly visualised as the standard 2-D solar flare model. The details of this illustration, however, have never been confirmed. This is because creating a fully consistent simulation is a huge challenge, given that both macroscopic effects (we’re talking several tens of thousands of kilometres here: larger than Earth) and microscopic particle physics have to be taken into account.
Researchers at KU Leuven have now been able to create such a simulation. As part of his doctoral research, Wenzhi Ruan worked on the simulation with his colleagues in the team of Professor Rony Keppens at the KU Leuven Department of Plasma Astrophysics. The researchers used the computational power of Flemish supercomputers as well as a new combination of physical models in which the microscopic effects of accelerated charged particles were taken into account in a macroscopic model.
From textbook illustration to self-consistent model
“Our work also makes it possible to calculate the energy conversion efficiency of a solar flare,” Professor Rony Keppens explains. “We can calculate this efficiency by combining the strength of the Sun’s magnetic field at the feet of the flare with the speed at which those feet move. If we can complete our observations in time, that is, because everything happens within a time span of tens of seconds to a few minutes.”
“We converted the results of the numerical simulation into virtual observations of a solar flare, whereby we imitated telescopes in all relevant wavelengths. This allowed us to upgrade the standard solar flare model from a textbook illustration to an actual model.”
###
Media Contact
Rony Keppens
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




