They were in the first in the world to research the solid-state polymerization of aryl cyanates
Credit: Kazan Federal University
Employees of the Department of Physical Chemistry of Kazan Federal University have found out that the mechanisms of polymerization of aryl cyanates in the solid state and in the melt differ in the number of broken multiple bonds of the monomer at the stage that determines the rate of the process.
Solid phase polymerization is widely used to create polymers with controlled structure, molecular weight, and other parameters. In the industry, a number of polycarbonates, polyamides and polyesters for various purposes are obtained by this method. Aryl cyanates are used to create polymer composite materials used, in particular, in the aerospace industry.
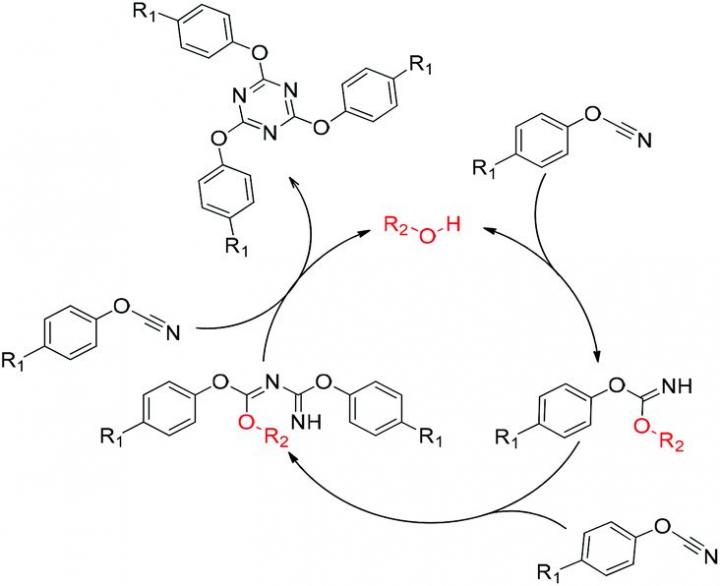
As senior researcher Andrey Galukhin explained, for solid-phase polymerization, it is necessary for the reaction to start at a temperature below the melting point. However, for some monomers this condition is not met, so this type of polymerization is not available for them. These include aryl cyanates, which have high thermal, chemical and radiation resistance. It is thanks to these properties that they have found application in the aerospace industry, where they are used as parts of composite materials. The high stability of aryl cyanates is due to the presence of 1,3,5-triazine aromatic fragments as cross-linking sites of polymer chains.
Kazanian scientists were the first to study the solid phase polymerization of aryl cyanate. They assumed that the solid state polymerization of this substance would be very different from the same process in the melt. The authors synthesized a unique monomer with a high melting point (403°C). Since the polymerization temperature of this substance is below its melting point, this made the solid phase reaction possible. A detailed study with differential scanning calorimetry made it possible to obtain important information about the kinetics of this process. It was possible to find out that the mechanisms of solid-phase polymerization and polymerization in a monomer melt differ in the number of broken multiple bonds of the monomer at the stage that determines the rate of the process. Also, it turned out that the rate of solid-phase polymerization does not depend on the degree of monomer conversion, that is, the kinetics is described by a zero-order reaction. The reason for this behavior lies in the topochemical nature of the process taking place in flat monomer crystals.
“Aryl cyanates play a very important role in the aeronautical and aerospace industries, where they are used as binders in composite materials to create various dimensionally stable structures. Expanding our knowledge of the relationship between the reactivity of these monomers and their structure will open up new possibilities for the targeted design of materials with desired properties,” concluded Galukhin.
###
Media Contact
Yury Nurmeev
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




