Protein could lead to new treatments for epileptic seizures
Credit: UIC/Jeffrey Loeb
Epileptic seizures often originate in small, localized areas of the brain where neurons abnormally fire in unison. These electrical impulses disrupt proper brain functioning and cause seizures. But what makes regions where seizures start different from parts of the brain where electrical impulses remain normal? More importantly, what prevents these epileptic centers from growing?
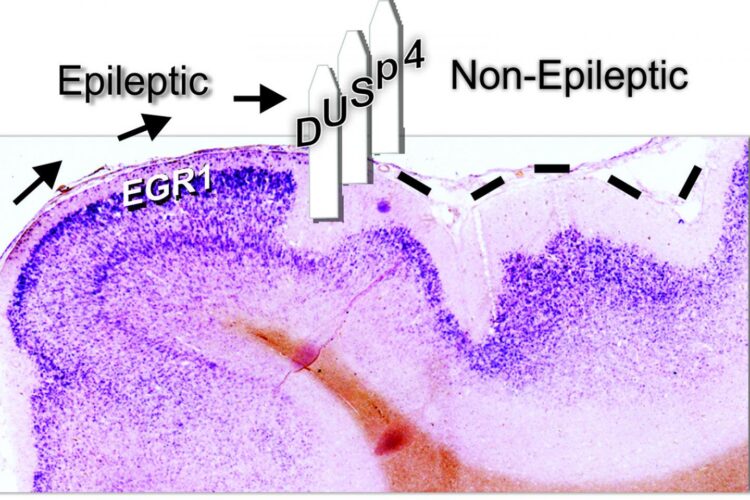
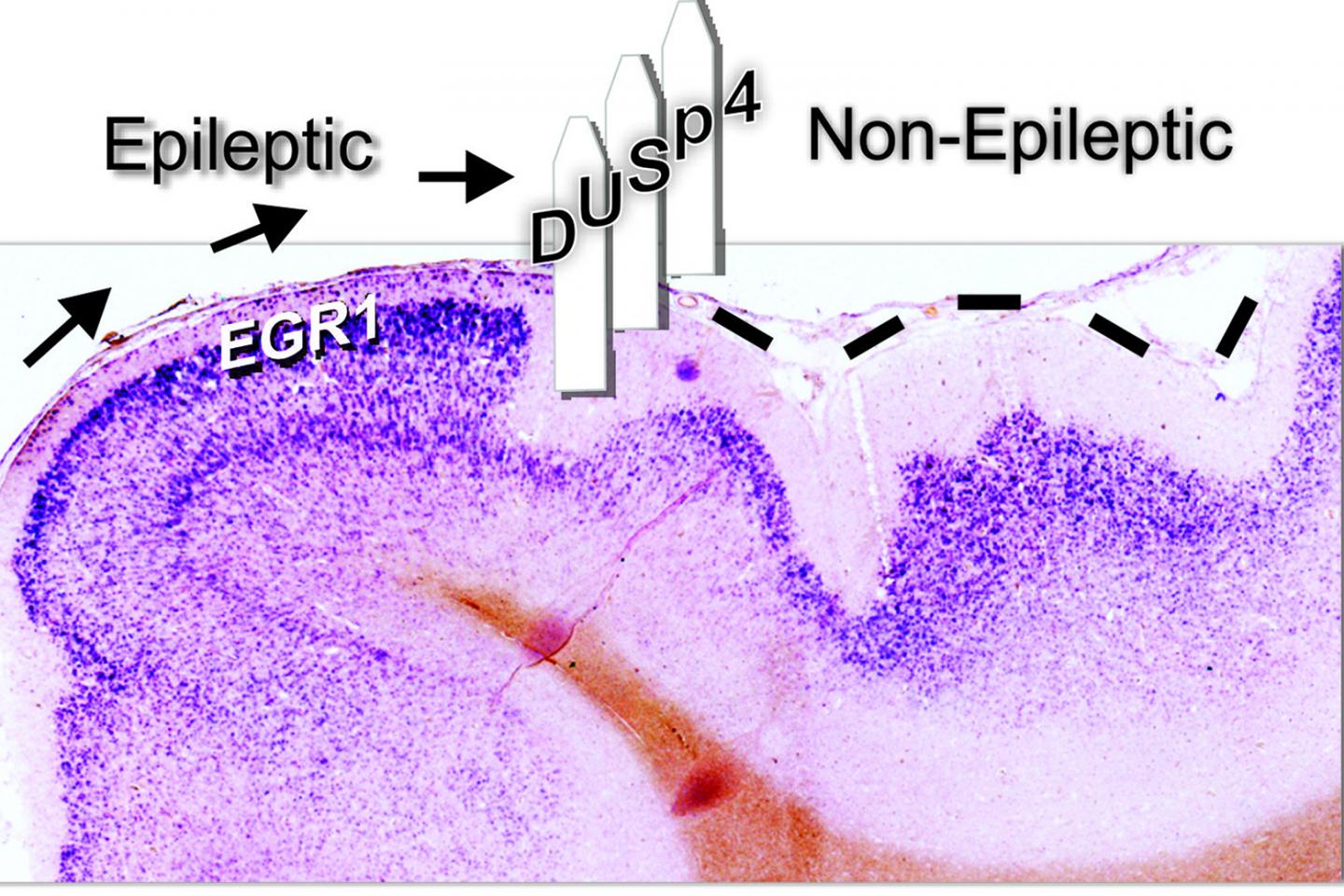
The answer to these questions may lie in a new discovery by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago. Dr. Jeffrey Loeb and his colleagues found that a protein — called DUSP4 — was increased in healthy brain tissue directly adjacent to epileptic tissue. Their research suggests that boosting levels of DUSP4 could be a novel way of preventing or treating epilepsy.
Their findings are reported in the journal Neurobiology of Disease.
“If epileptic brain regions spread throughout the brain with nothing to stop them, the seizures would overwhelm the brain, it would not be survivable,” said Loeb, UIC professor and head of neurology and rehabilitation at the College of Medicine and corresponding author on the study. “We wondered if there were natural ways that epileptic brain areas are quarantined. We searched for genes at the border between epileptic and normal brain tissue that may help prevent the spread of epilepsy.”
Loeb and colleagues analyzed thousands of genes in tissues from 20 patients who underwent surgery to treat their epilepsy. During these surgical procedures, brain tissue from epileptic areas and directly adjacent, non-epileptic tissue was removed. Tissue not required for pathological evaluation was stored in the University of Illinois NeuroRepository — a human brain tissue bank and research database that links clinical, radiological, physiological, histological and molecular/genomic data to thousands of human tissue samples.
The researchers used a mathematical modeling technique called cluster analysis to sort through huge numbers of genes from the epileptic versus the nonepileptic tissue. They identified a number of genes that were increased — or “upregulated” — in or near epileptic tissues and the observed that DUSP4 fell into a different cluster than most of the pro-epileptic genes.
In previous research, Loeb and colleagues identified a signaling pathway that was highly upregulated in areas of the brain where epileptic seizures started. In an animal model, suppression of the pathway –known as the mitogen-activated protein kinase, or MAPK, pathway — reduced epileptic electrical activity in the brain.
“We were excited about DUSP4 because it is known to be a potent MAPK pathway inhibitor in cancer cells,” Loeb said. “Seeing this gene activated at the borders and shutting off MAPK signaling genes in the human brain led us to believe that the protein cordons off epileptic regions so that they don’t enlarge or spread, similar to how in a ship you might get a leak in one area, but you can close and seal off doors to keep the leak isolated. That’s how we think DUSP4 is working to keep epileptic focal points from enlarging.”
In addition to the gene, when the researchers went back to look at the protein’s levels in their tissue samples, they found that tissue from brain regions with lower epileptic activity had lower MAPK activity and higher levels of the DUSP4 protein.
Loeb and colleagues currently are investigating potential drugs that can upregulate or augment the activity of DUSP4 to help treat or even prevent epilepsy.
“These DUSP4-targeting drugs would represent a new kind of ‘disease-modifying’ treatment for epilepsy, which currently does not exist,” Loeb said.
###
Allison Kirchner and Fabien Dachet of UIC and Shruti Bagla of Wayne State University are co-authors on the paper.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NS109515, NS083527) and an American Epilepsy Society Predoctoral Fellowship.
Media Contact
Jackie Carey
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.