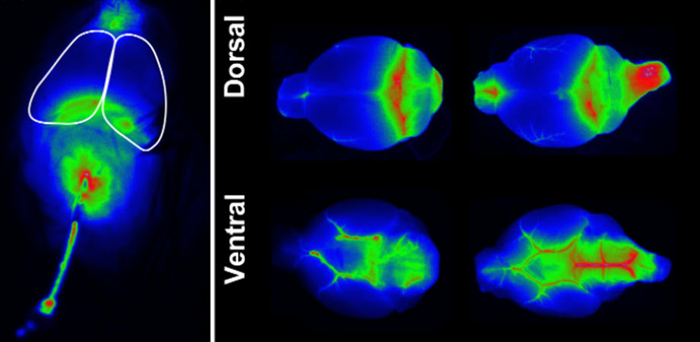
The glymphatic system facilitates fluid exchange in the central nervous system and clears dissolved wastes. This anatomically organized movement occurs primarily during sleep and is supported by astroglial neural cells via water channels called aquaporins. These channels line the perivascular pathways and facilitate cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid exchange throughout the brain.
Credit: Credit: S.A. Keil et al., doi 10.1117/1.NPh.9.2.021915
The glymphatic system facilitates fluid exchange in the central nervous system and clears dissolved wastes. This anatomically organized movement occurs primarily during sleep and is supported by astroglial neural cells via water channels called aquaporins. These channels line the perivascular pathways and facilitate cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid exchange throughout the brain.
Glymphatic dysfunction has been implicated in numerous pathological conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, and stroke. Existing methods for assessing glymphatic function have been challenging. Dynamic methods such as 2-photon microscopy and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) require expensive instrumentation and specific technical skills, yet they have other limitations. For instance, 2-photon microscopy cannot reliably access deeper brain regions. The more readily implemented and widely used method of slice-based fluorescent imaging permits assessment at only a snapshot of a single time point, so obtaining a view across time requires many animals and much effort.
To address the need for combined dynamic imaging and histologic assessment in glymphatic research, a team of researchers at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Puget Sound Health Care System and the University of Washington (UW) in Seattle recently developed a straightforward and novel dynamic imaging paradigm as a surrogate measure of glymphatic flux within the brain. As reported in Neurophotonics, the technique uses a widely available small animal infrared (IR) imaging system (LICOR Pearl) to obtain a sensitive dynamic surrogate measure of glymphatic exchange. It does so by tracking the distribution of an IR tracer in cerebrospinal fluid in real time over the cortical surface of a living mouse brain.
The technique enables measurement of the temporal dynamics of glymphatic functions, as well as the ability to follow up with the gold standard slice-based fluorescence analysis and histological evaluation for concurrent visualization of resolution of deeper structures. This approach allows both dynamic and structural insights to be assessed in parallel. The technique works great for research involving mice, but not for larger animals like rats, due to the size of the imaging platform and the thicker skulls of larger rodents.
The team’s reliance on affordable and widely available equipment readily allows for replication and widespread adoption. According to the study senior author Jeffrey Iliff, Associate Director for Research at the VISN20 Mental Illness, Research, Education, and Clinical Center of the VA Puget Sound Health Care System and the Arthur J. and Marcella McCaffray Professor in Alzheimer’s Disease at the UW School of Medicine, “The glymphatic field is expanding rapidly, both in the clinical and pre-clinical realms. With so much work to do, we hope that this simple, low-cost approach will place rigorous study of glymphatic biology within the reach of a wider, more diverse group of research teams and institutions.”
Read the open access article by S.A. Keil et al., “Dynamic infrared imaging of cerebrospinal fluid tracer influx into the brain,” Neurophotonics 9(3) 031915 (2022), doi 10.1117/1.NPh.9.2.021915.
Journal
Neurophotonics
DOI
10.1117/1.NPh.9.3.031915
Article Title
Dynamic infrared imaging of cerebrospinal fluid tracer influx into the brain
Article Publication Date
17-May-2022




