The drug minocycline, an antibiotic that also decreases inflammation, failed to slow vision loss or expansion of geographic atrophy in people with dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD), according to a phase II clinical study at the National Eye Institute (NEI), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Credit: National Eye Institute
The drug minocycline, an antibiotic that also decreases inflammation, failed to slow vision loss or expansion of geographic atrophy in people with dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD), according to a phase II clinical study at the National Eye Institute (NEI), part of the National Institutes of Health.
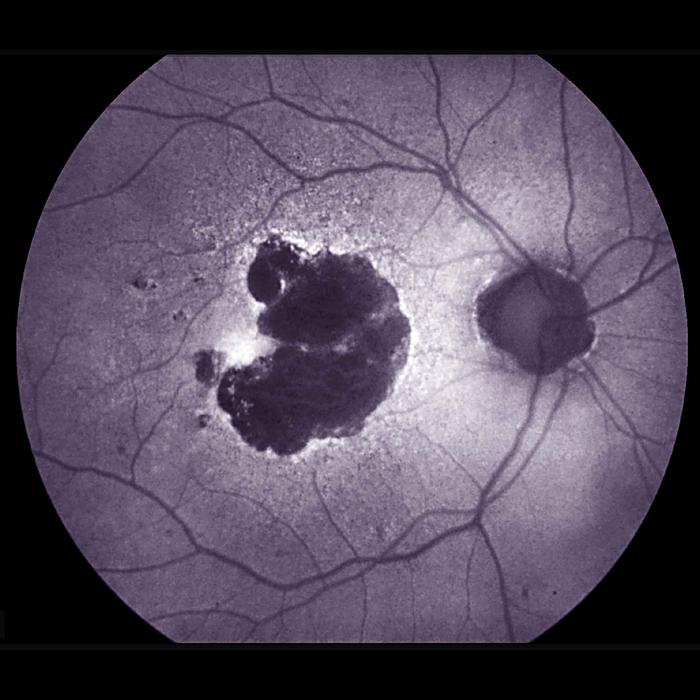
Dry AMD affects the macula, the part of the eye’s retina that allows for clear central vision. In people with dry AMD, patches of light-sensing photoreceptors and their nearby support cells begin to die off, leaving regions known as geographic atrophy. Over time, these regions expand, causing people to lose more and more of their central vision. Microglia, immune cells that help maintain tissue and clear up debris, are present at higher levels around damaged retinal regions in people with dry AMD than in people without AMD. Scientists have suggested that inflammation – and particularly microglia – may be driving the expansion of geographic atrophy regions.
This study, led by Tiarnan Keenan, M.D., Ph.D., a Stadtman Tenure-Track Investigator at the NEI’s Division of Epidemiology and Clinical Applications, tested whether inhibiting microglia with minocycline might help slow geographic atrophy expansion and its corresponding vision loss. The trial enrolled 37 participants at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, and at the Bristol Eye Hospital, United Kingdom. After a nine-month period where the researchers tracked each participant’s rate of geographic atrophy expansion, the participants took twice-daily doses of minocycline for two years. The researchers compared each participant’s rate of geographic atrophy expansion while taking minocycline to their baseline rate, and found there was no difference in geographic atrophy expansion rate or vision loss with minocycline.
Previous studies have shown that minocycline can help reduce inflammation and microglial activity in the eye, including the retina. The drug has shown beneficial effects for conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, but has not previously been tested for dry AMD.
The clinical study was funded by the NEI Intramural Program, and took place in part at the NIH Clinical Center. Clinical trial number NCT02564978.
REFERENCE: Keenan TDL, Bailey C, Abraham M, Orndahl C, Menezes S, Bellur S, Arunachalam T, Kangale-Whitney C, Srinivas S, Karamat A, Nittala M, Cunningham D, Jeffrey BG, Wiley HE, Thavikulwat AT, Sadda S, Cukras CA, Chew EY, Wong WT. Phase 2 Trial Evaluating Minocycline for Geographic Atrophy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024 Mar 14. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.0118.
NEI leads the federal government’s efforts to eliminate vision loss and improve quality of life through vision research…driving innovation, fostering collaboration, expanding the vision workforce, and educating the public and key stakeholders. NEI supports basic and clinical science programs to develop sight-saving treatments and to broaden opportunities for people with vision impairment. For more information, visit https://www.nei.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov/.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Journal
JAMA Ophthalmology
DOI
10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.0118
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Phase 2 Trial Evaluating Minocycline for Geographic Atrophy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
Article Publication Date
14-Mar-2024




