Credit: ©Science China Press
The interfacial decomposition products forming the so-called solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) during the first charging/discharging significantly determine the electrochemical performances of lithium (Li) batteries. To date, the dynamic evolutions, chemical compositions, stabilities and the influencing factors of the SEI films have been captured tremendous attentions.
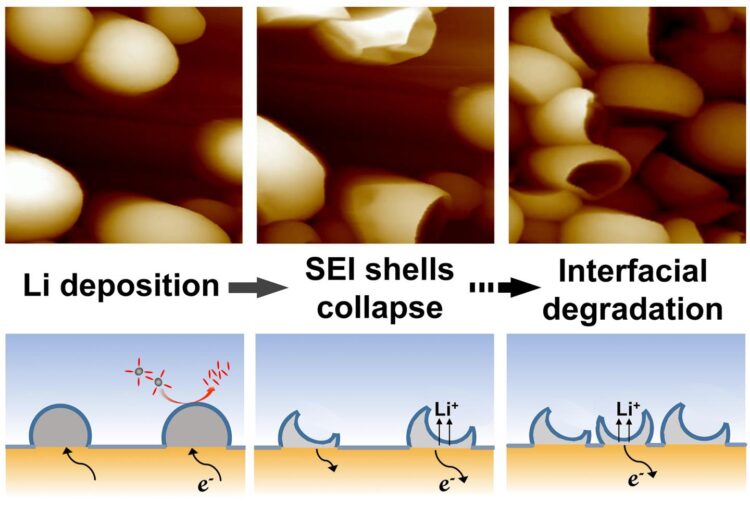
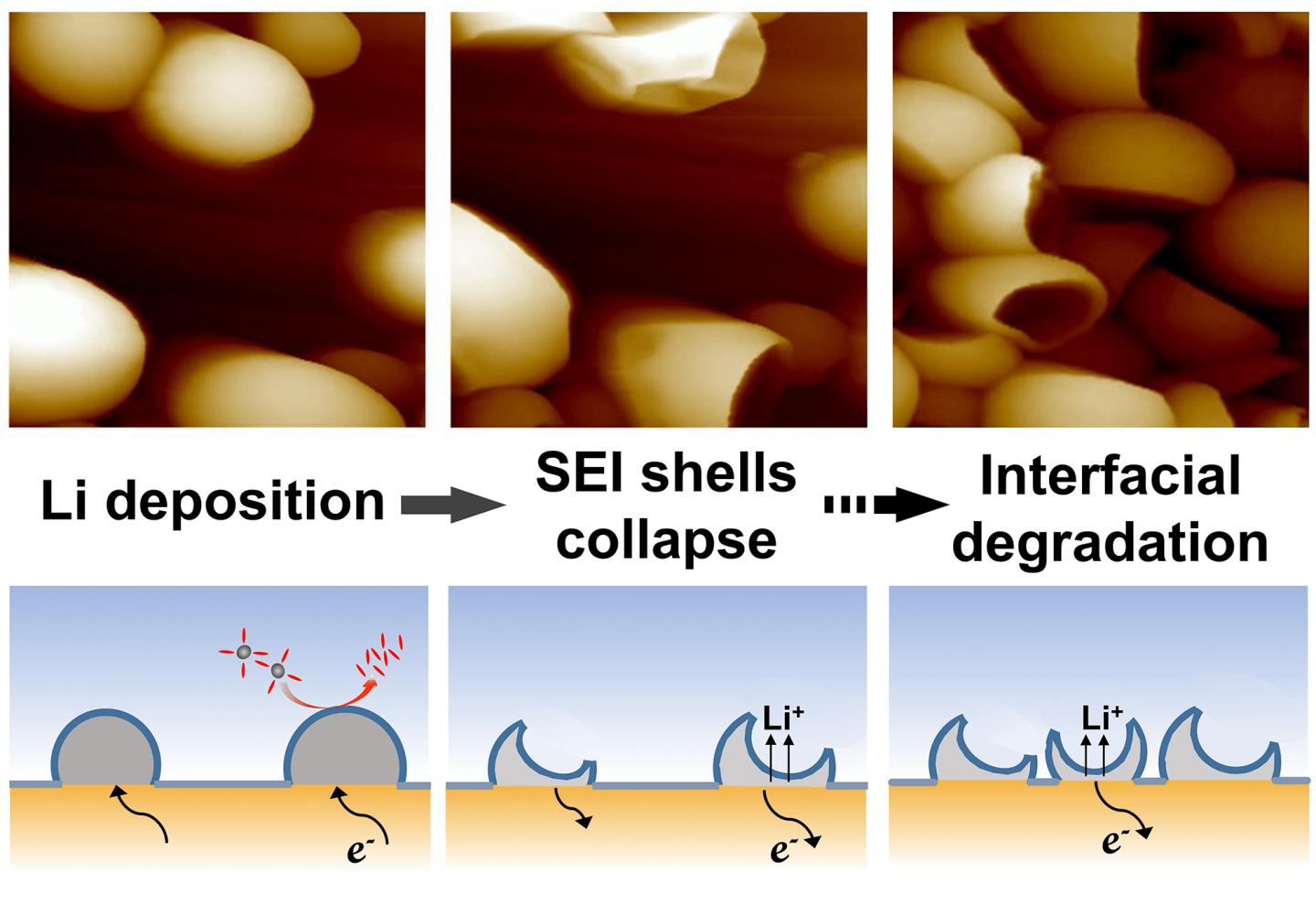
It’s noted that, in contrast to the SEI film formation at the surface of electrodes, a kind of SEI shells usually conformally forms at the outmost layer of the on-site deposited Li once the freshly deposited Li contacts with the electrolyte, which could directly influence Li nucleation, growth behaviors and electrochemical properties at the electrode/electrolyte interface.
Furthermore, the chemical/morphological instabilities of the on-site formed SEI shell pose challenges for the in-situ characterizations. Directly capturing the dynamic evolution of the SEI shells is crucial to interprete their impacts on the anode/elelctrolyte interface and battery performances.
The electrochemical atomic force microscopy (EC-AFM) enables the real-time characterization of the morphology change, mechanical modulus and potential/current distribution at the electrode/electrolyte interface under working conditions, providing an important in-situ analysis method with high spatial resolution for exploring the dynamic evolution of the on-site formed SEI shell on the deposited Li.
Recently, Prof. Li-Jun Wan and Prof. Rui Wen et al. provide the straightforward visualized evidence of SEI shells evolution during Li deposition/stripping to reveal anode degradation via in-situ EC-AFM.
During Li deposition, the quasi-spherical Li particles nucleate and grow on a Cu electrode. Subsequently, the collapse of the SEI shells is distinctly captured with the continuous Li stripping. As the cycling progresses, new Li deposits are prone to renucleating on the deposit-free sites with higher electrochemical activity. The fresh SEI shells form on freshly-deposited Li while the original SEI shells retain their collapsed morphology at the same position. Severe SEI regeneration/collapse along with electrolyte depletion and interfacial impedance increasing take one of the responsiblities for the degradation of anodes.
This work reveals the interfacial evolution at nanoscale, provides deep insights into the fundamental comprehension of SEI properties and further guides improvement strategies of the interface design in Li batteries.
###
See the article: Shi Y, Liu GX, Wan J, Wen R, Wan LJ. In-situ nanoscale insights into the evolution of solid electrolyte interphase shells: revealing interfacial degradation in lithium metal batteries. Sci China Chem, 2021, 64, doi:10.1007/s11426-020-9984-9.
https:/
Media Contact
Rui Wen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.