Credit: Tokyo Institute of Technology
In nature, proteins are assembled into sophisticated and highly ordered structures, which enable them to execute numerous functions supporting different forms of life. The exquisite design of natural proteins prompted scientists to exploit it in synthetic biology to engineer molecules that can self-assemble into nanoparticles with desired structure and that may be used for various purposes such as gas storage, enzyme catalysis, intracellular drug delivery, etc.
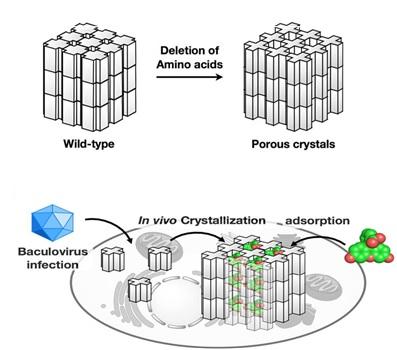
Cytoplasmic polyhedrosis viruses (cypoviruses) infecting insects are embedded in protein crystals called polyhedra which shield the virus from damage. The structure of polyhedra crystals (PhCs) suggests that they can serve as robust containers which can incorporate and protect foreign molecules from degradation, ensuring their compositional and functional stability.
Overview of Research Achievement
Extreme stability of polyhedra under harsh conditions is provided by dense packing of polyhedrin monomers in crystals with solvent channels of very low porosity, which, however, limits the incorporation of foreign particles. Research group led by Satoshi Abe and Takafumi Ueno at Tokyo Institute of Technology hypothesized that if a porous framework inside PhCs is extended without compromising crystal stability, PhCs can be used for accumulation and storage of exogenous molecules in living cells. As in natural PhCs, polyhedrin monomers form a trimer, the scientists assumed that if amino acid residues at the contact interface of each trimer are deleted, the porosity of the resulting crystals would be increased. To achieve this goal, they genetically engineered polyhedrin monomers, which were then expressed and self-assembled in Spodoptera frugiperda IPLB-Sf21AE, the larva of an armyworm moth, infected with baculovirus. The mutant PhCs maintained crystal lattice of the wild-type PhC but had significantly extended porosity (Figure) due to the deletion of amino acid residues with the rearrangement of intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds. As a result, the engineered crystals could adsorb 2-4 times more exogenous molecules (fluorescent dyes) compared to the wild type PhC, with up to 5,000-fold condensation of the dyes from the 10 uM solution.
As a next step, the scientists examined the performance of the mutant crystals in living insect cells. PhCs showed high stability in the intracellular environment. Most importantly, the mutant crystals could accumulate and retain the dyes in live cells, while the natural crystals could not.
Rationale crystal design used by scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology provides a powerful tool for structural manipulation of self-assembled protein crystals to obtain porous nanomaterials with regulated adsorption properties. The engineered porous PhCs can be used as protein containers for in vivo crystal structure analysis of the cellular molecules and bioorthogonal chemistry in various types of living cells.
Structural analysis of microcrystals
Since tiny crystals with only a few microns size were obtained, the structure analyses were performed at beamlines BL32XU and BL41XU at SPring-8, a large synchrotron radiation facility which delivers the most powerful synchrotron radiation. The high-resolution structures were rapidly analyzed with the help of an automated data collection system developed in RIKEN.
###
Media Contact
Emiko Kawaguchi
[email protected]
81-357-342-975
http://www.titech.ac.jp/english/index.html
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag