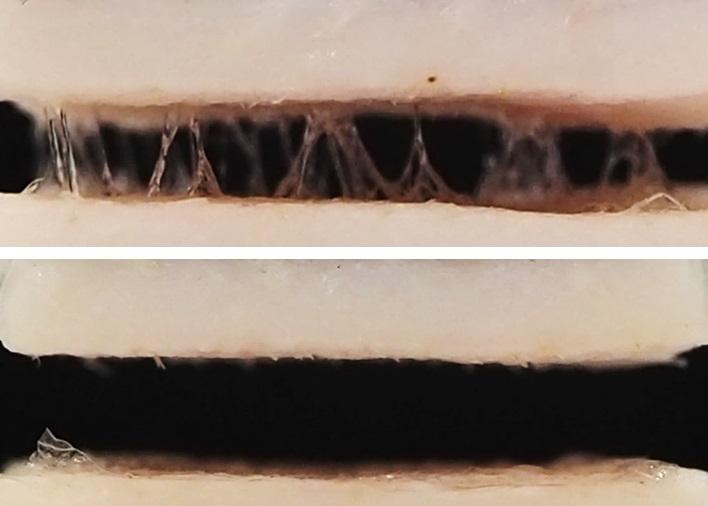
Credit: Adapted from ACS Omega 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03305
By conveniently and painlessly collecting data, wearable sensors create many new possibilities for keeping tabs on the body. In order to work, these devices need to stay next to the skin. In a study described in ACS Omega, researchers tweaked a widely used polymer to create a potential new adhesive to keep these sensors in place.
Wearable devices are making an impact in medicine. For example, they are being used to monitor blood sugar without drawing blood, and some can automatically measure hospital patients’ vital signs. Sensors like these are often put in place using acrylic-based medical bandages. However, the adhesives on these bandages can provoke allergic reactions or cause pain when removed. Another option, silicone-based adhesives, doesn’t cause irritation, but also doesn’t stay put. Other adhesives, including bio-inspired ones that mimic gecko feet and octopus suckers, are not yet practical for mass production. To develop a better alternative, Xi Chen and Tetsushi Taguchi turned to a polymer, poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA), which is not irritating to the skin and is currently used in some wound dressings, contact lenses and other similar items.
Despite its many appealing properties, PVA can come off easily when wet. So, the researchers modified the compound by adding alkyl chains to try to improve its adhesion. They made versions with chains that contained three, six or nine methylene carbons, then tested them to see which performed best. It turned out that films made of longer chain versions were more hydrophobic, but had less tensile strength. Cells best tolerated the short chain known as 4C3-PVA, and in tests with pig skin, they found it bonded most strongly. The researchers conclude that 4C3-PVA is a promising adhesive for wearable devices.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, Sekisui Chemical Company and the Uehara Memorial Foundation.
The study is freely available as an ACS AuthorChoice article here.
For more research news, journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration for the ACS Spring 2020 National Meeting & Exposition in Philadelphia.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us on Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
301-775-8455




