Credit: Waseda University
Tokyo, Feb 21, 2017 — A group of researchers at Waseda University has developed processes and materials for ultrathin stick-on electronic devices using elastomeric "nanosheet" film, achieving ease of production while also preserving high elasticity and flexibility fifty times better than previously reported polymer nanosheets.
This research is published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry C online edition, February 1, 2017.
Smart electronics and wearable devices have several requirements for widespread adoption, especially ease of fabrication and wearing comfort. The materials and processes developed by the Waseda University team represent huge strides forward in both criteria.
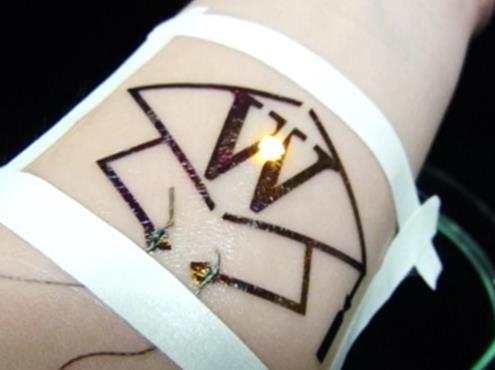
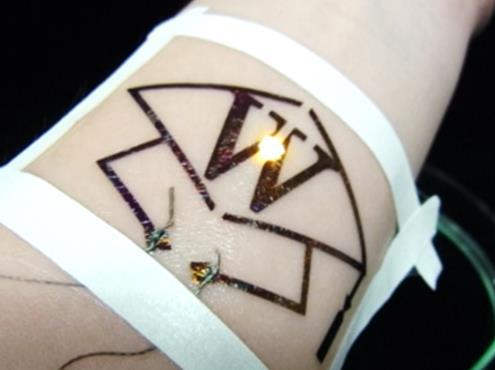
Inkjet printing of circuitry and low-temperature fixing allow production of electronic devices which are durable and functional but also extremely thin and flexible enough for use as a comfortable, skin-fitting appliance, while also maintaining the easy handling properties and protection of elastomeric films. At only 750 nm, the new film is ultra-thin and flexible. These advances could help change the nature of wearable electronics from objects like wristwatches to items less noticeable than a band-aid.
The Waseda team also established a method of joining electronic components without soldering, allowing thinner and more flexible elastomer films (SBS: polystyrene-polybutadiene-polystyrene). Conductive "wiring" is created by inkjet printing, which can be done with a household type printer without the need for clean room conditions. Further, conductive lines and elements such as chips and LEDs are connected by adhesive sandwiching between two elastomeric nanosheets, without using chemical bonding by soldering or special conductive adhesives.
Thanks to the simple, low-temperature processes, the resulting ultrathin structures achieve better adhesion, without using adhesive matter such as tape or glue, better elasticity and comfort for skin-contact applications. The new system was proven functional for several days on an artificial skin model.
These results were achieved through collaboration among three specialties: Molecular assembly and biomaterials science; medical robotics and rehabilitation engineering; and micro-electromechanical systems, thanks to collaborative structures at Waseda University.
Uses for these products are expected to include human-machine interfaces and sensors in the form of electronic tattoos, as radically improved tools for the fields of medicine, healthcare and sports training.
These applications are the subject of further investigation by the Waseda University Institute of Advanced Active Aging Research.
###
Title: Sandwich fixation of electronic elements using free-standing elastomeric nanosheets for low-temperature device processes
Authors: Marin Okamoto, Mizuho Kurotobi, Shinji Takeoka, Junki Sugano, Eiji Iwase, Hiroyasu Iwata and Toshinori Fujie
Journal: Journal of Materials Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1039/c6tc04469g
About Waseda University
Waseda University is a leading private, non-profit institution of higher education based in central Tokyo, with over 50,000 students in 13 undergraduate and 21 graduate schools.
Founded in 1882, Waseda cherishes three guiding principles: academic independence, practical innovation and the education of enlightened citizens. Established to mold future leaders, Waseda continues to fulfill this mission, counting among its alumni seven prime ministers and countless other politicians, business leaders, journalists, diplomats, scholars, scientists, actors, writers, athletes and artists.
Waseda is Japan's most global campus, including number of study abroad students, incoming and outgoing, and international faculty, with the broadest range of degree programs taught fully in English, and exchange partnerships with over 600 top institutions in 84 countries.
Media Contact
Marshall Adams
[email protected]
@waseda_univ
http://www.waseda.jp/top/index-e.html
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag