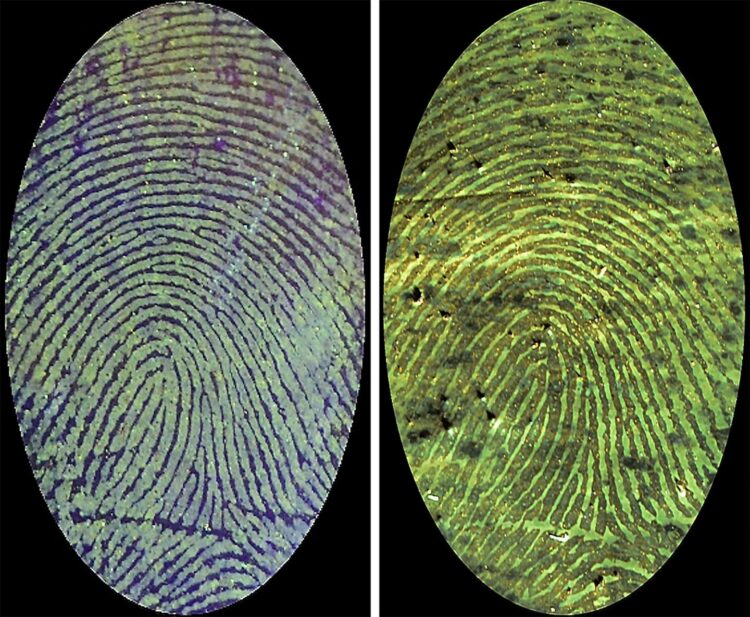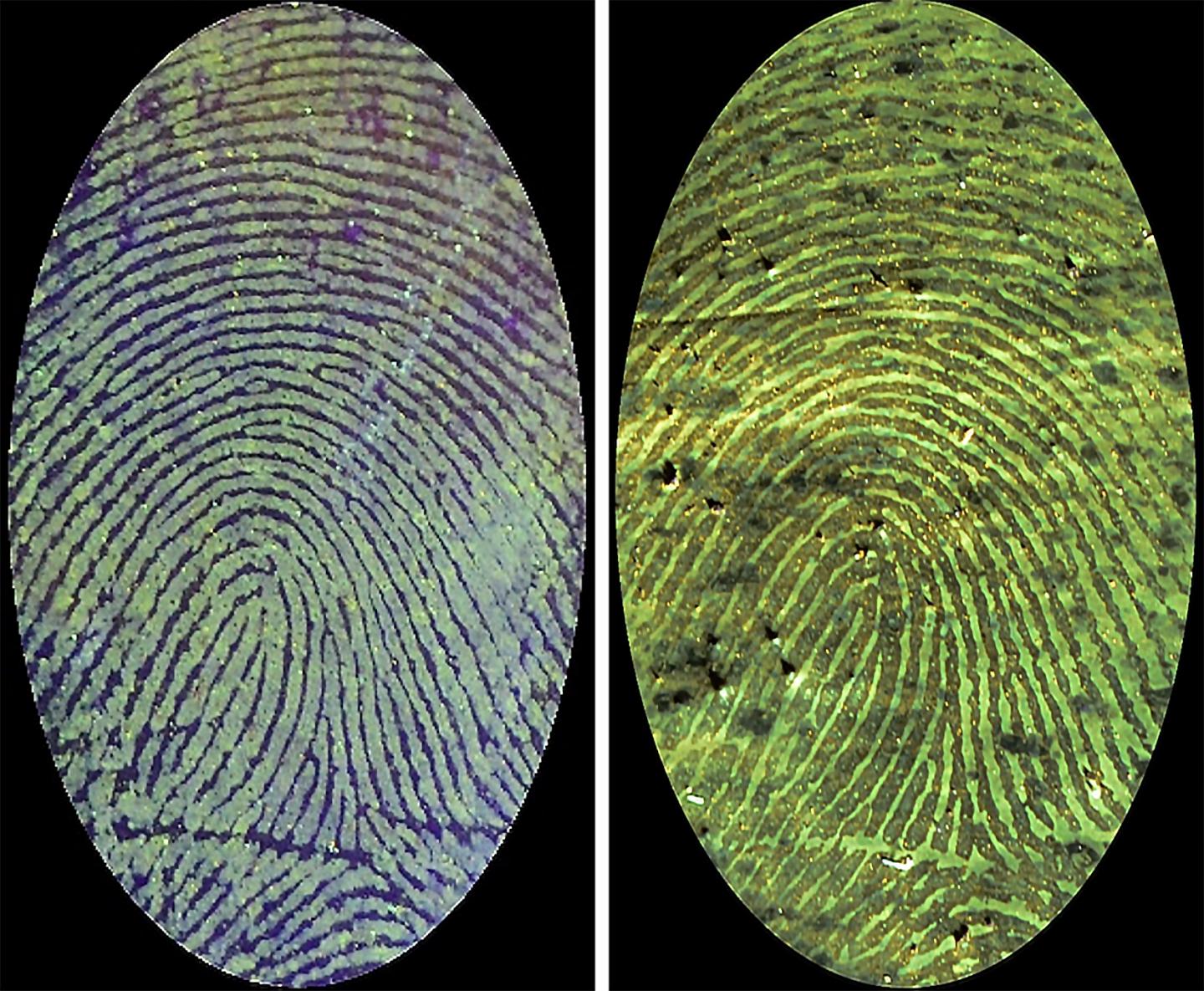
Credit: Adapted from ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2021, DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c00710
Careful criminals usually clean a scene, wiping away visible blood and fingerprints. However, prints made with trace amounts of blood, invisible to the naked eye, could remain. Dyes can detect these hidden prints, but the dyes don’t work well on certain surfaces. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed a fluorescent polymer that binds to blood in a fingerprint — without damaging any DNA also on the surface — to create high-contrast images.
Fingerprints are critical pieces of forensic evidence because their whorls, loops and arches are unique to each person, and these patterns don’t change as people age. When violent crimes are committed, a culprit’s fingerprints inked in blood can be hard to see, especially if they tried to clean the scene. So, scientists usually use dyes to reveal this type of evidence, but some of them require complex techniques to develop the images, and busy backgrounds can complicate the analysis. In addition, some textured surfaces, such as wood, pose challenges for an identification. Fluorescent compounds can enhance the contrast between fingerprints and the surface on which they are deposited. However, to get a good and stable image, these molecules need to form strong bonds with molecules in the blood. So, Li-Juan Fan, Rongliang Ma and colleagues wanted to find a simple way to bind a fluorescent polymer to blood proteins so that they could detect clear fingerprints on many different surfaces.
The researchers modified a yellow-green fluorescent polymer they had previously developed by adding a second amino group, which allowed stable bonds to form between the polymer and blood serum albumin proteins. They dissolved the polymer and absorbed it into a cotton pad, which was placed on top of prints made with chicken blood on various surfaces, such as aluminum foil, multicolored plastic and painted wood. After a few minutes, they peeled off the pad, and then let it air-dry. All of the surfaces showed high contrast between the blood and background under blue-violet light and revealed details, including ridge endings, short ridges, whorls and sweat pores. These intricate patterns were distinguishable when the researchers contaminated the prints with mold and dust, and they lasted for at least 600 days in storage. In another set of experiments, a piece of human DNA remained intact after being mixed with the polymer, suggesting that any genetic material found after processing a print could still be analyzed to further identify a suspect, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from Yao Liu, academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering; the Major Basic Research Project of the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China; the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions; and the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China.
The abstract that accompanies this paper can be viewed here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]