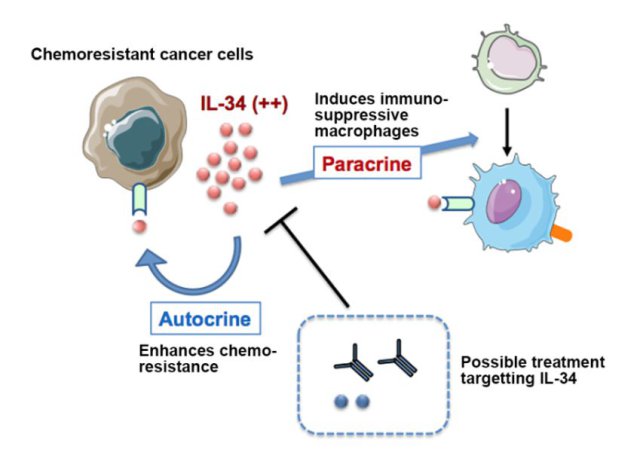
A team of researchers has discovered that chemoresistant lung cancer cells suppress immune functions and strengthen resistance to chemotherapy by producing interleukin-34 (IL-34) — a type of cytokine.
Credit: Image courtesy of Hokkaido University
Chemotherapy is one of the most important treatments for many cancer patients. In recent years, chemotherapies that target the immune system have been developed, resulting in remarkable advances in cancer treatments. However, the ability of tumor cells to escape immune destruction and acquire resistance to chemotherapy remain major obstacles to effective cancer therapy.
It is known that immunosuppressive macrophages accumulate at tumor sites where the tumor cells have become resistant to chemotherapy. Assistant Professor Muhammad Baghdadi, Lecturer Haruka Wada and Professor Ken-ichiro Seino of the Division of Immunobiology at Hokkaido University’s Institute for Genetic Medicine, conducted research with collaborators based on a theory that chemoresistant tumor cells produce an unidentified substance that increases tumor-associated macrophages, thus enhancing their resistance to chemotherapy.
In the latest research, the team cultivated chemosensitive A549-DS, made from A549 lung cancer cells, together with the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin, to create doxorubicin-resistant A549-DR. The researchers examined the two cells, finding a large amount of IL-34 was produced in the A549-DR, but not in the A549-DS. They also found that the IL-34 produced by A549-DR contributed to the production of immunosuppressive macrophages. Furthermore, their experiment showed that IL-34 enhanced the chemoresistance of A549-DR.
In experiments using mice, researchers found that A549-DR was resistant to the chemotherapeutic drug when transplanted in mice, while A549-DR with depleted IL-34 became sensitive to the same drug, suggesting that IL-34 enhanced chemoresistance in the animal body.
Furthermore, researchers discovered high levels of IL-34 in tumors removed from several lung cancer patients. They also examined the prognoses of post-operative patients — studying those with, and those without IL-34 in their tumors, finding that the former’s prognoses were poorer than the latter’s.
“Currently, there are only a few options to treat chemoresistant tumors.,” Professor Seino said. “This latest finding could make it possible to develop a new therapy, which targets IL-34, to treat chemoresistant cancer cells.”
Web Source:
Materials provided by Hokkaido University.
Journal Reference:
Baghdadi M. et. al. Chemotherapy-induced IL-34 enhances immunosuppression by tumor-associated macrophages and mediates survival of chemoresistant lung cancer cells. Cancer Research, October 2016 DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472
The post IL-34: New, possible target to tackle drug-resistant cancer cells appeared first on Scienmag.