Research suggests interventions designed to mitigate influence of low SES on brain and mental health may be most beneficial for children younger than age five
Credit: McDermott et al., JNeurosci (2018)
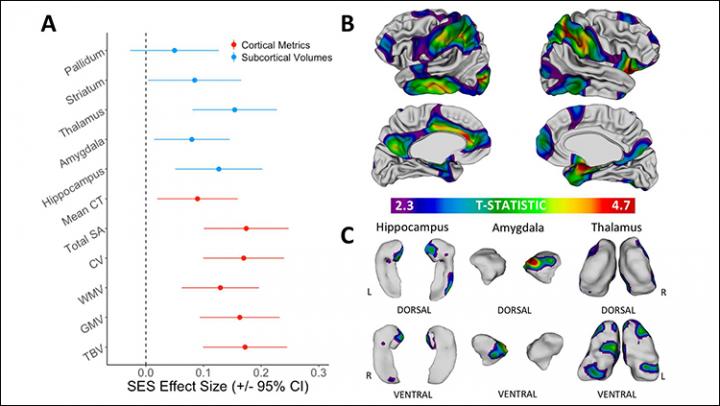
The relationship between socioeconomic status (SES) and brain anatomy is mostly stable from childhood to early adulthood, according to a longitudinal neuroimaging study of more than 600 healthy young people published in JNeurosci. This finding draws attention to the importance of preschool life as a period when associations between SES and brain organization may first develop.
Cassidy McDermott, Armin Raznahan, and colleagues analyzed brain scans of the same individuals collected over time between five and 25 years of age. Comparing this data to parental education and occupation and each participants’ intelligence quotient (IQ) allowed the researchers to demonstrate positive associations between SES and the size and surface area of brain regions involved in cognitive functions such as learning, language, and emotions. In particular, this is the first study to associate greater childhood SES with larger volumes of two subcortical regions – the thalamus and striatum – thereby extending previous SES research that has focused on its relationship to the cortex. Finally, the researchers identify brain regions underlying the relationship between SES and IQ. A better understanding of these relationships could clarify the processes by which SES becomes associated with a range of life outcomes, and ultimately inform efforts to minimize SES-related variation in health and achievement.
###
Article: Longitudinally Mapping Childhood Socioeconomic Status Associations with Cortical and Subcortical Morphology*
DOI: http://www.
Corresponding author: Armin Raznahan (National Institute of Mental Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) [email protected]
*A preprint of this manuscript has been posted on bioRxiv: https:/
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience’s first journal, was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors’ changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world’s largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
Media Contact
David Barnstone
[email protected]
202-962-4000
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




