Proteins tend to fold wrongly and become defective when exposed to stressors such as heat, oxidation, and pH changes. Accumulation of abnormal proteins contributes to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Credit: Eisuke Itakura from Chiba University
Proteins tend to fold wrongly and become defective when exposed to stressors such as heat, oxidation, and pH changes. Accumulation of abnormal proteins contributes to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
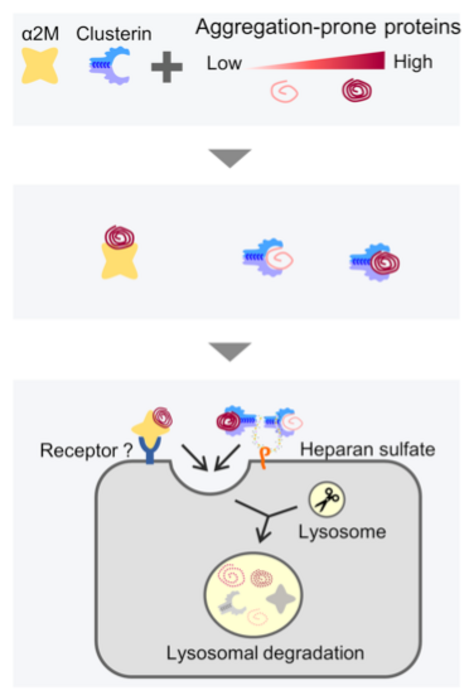
So, how does the human body deal with such misfolded or defective proteins? It regulates protein networks via a process called ‘proteostasis,’ which prevents protein aggregation and any damage that may result from misfolded protein accumulation inside (intracellular) or outside (extracellular) cells. A set of unique proteins—molecular chaperones—play an essential role in proteostasis: they target and interact with misfolded proteins, maintain their solubility, and designate them for refolding or degradation. And, while intracellular proteostasis is well understood, extracellular conditions are harsher. Mediating proteostasis in this environment requires specific extracellular molecular chaperones, and the specifics of extracellular proteostasis are yet to be fully understood. Take, for example, an extracellular chaperone, alpha 2-macroglobulin (ɑ2M), an abundant plasma protein. ɑ2M targets defective proteins and is speculated to facilitate the clearance of defective proteins. However, the exact mechanism of how this happens is unknown.
Now, a team of researchers led by Dr. Eisuke Itakura, Associate Professor in the Department of Biology at Chiba University—also including Dr. Ayaka Tomihari and Dr. Mako Kiyota from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Chiba University, and Dr. Akira Matsuura from the Graduate School of Science, Chiba University—has identified the substrates that ɑ2M targets for degradation. They also developed a novel assay that detects how ɑ2M mediates the lysosomal degradation of targeted proteins. The group’s findings were published online on March 28, 2023, in Volume 13 of Scientific Reports.
“Thus far, no quantitative method has been available to detect the lysosomal degradation of extracellular proteins. Therefore, we established a fluorescence internalization assay to measure α2M-mediated lysosomal degradation,” says Dr. Itakura.
To devise the assay, the chaperone α2M was tagged with red and green fluorescence proteins (RFP and GFP, or RG) that could be visually detected inside cells. When α2M-RG was internalized into lysosomes, the fluorescence of RFP, but not GFP, was detected. This is because GFP is prone to lysosomal degradation, but RFP is quite resistant. “So, in this assay, if α2M is inducing degradation of misfolded proteins, RFP should accumulate in the cell, producing a red fluorescence,” Dr. Itakura explains. These results were also validated in red blood cell lysates.
The group also probed the significance of why multiple extracellular chaperones exist inside our body by comparing the substrate specificities of α2M and clusterin, another extracellular chaperone. Previously, the group had reported that clusterin also plays a part in the extracellular degradation of proteins like amyloid-beta, the extracellular aggregation of which has been implicated in Alzheimer’s disease. The group found that while α2M and clusterin had overlapping functions, their pathways were not redundant. α2M was seen to recognize the defective proteins more prone to aggregation. According to the researchers, this finding lends credence to the theory that an array of extracellular chaperones cooperates to protect us from the spectrum of misfolded proteins likely to be found in the body.
But what are the long-term implications of this work? Dr. Itakura says, “In the future, elucidating the molecular mechanism of protein degradation by extracellular chaperones may prove useful in treating related diseases, like Alzheimer’s disease. By degrading and removing abnormal proteins that accumulate outside cells, extracellular chaperones have the potential to be a valuable therapeutic tool.”
“If a more detailed relationship between extracellular chaperones and disease can be determined, it may be possible to predict an individual’s condition and the likelihood of developing a particular disease through blood tests,” he concludes.
About Associate Professor Eisuke Itakura
Dr. Eisuke Itakura earned his Ph.D. in 2009 from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering at Saitama University. He has been at Chiba University since 2015, where he is an Associate Professor in the Department of Biology. His research interests span the role of autophagy, lysosomes, endocytosis, and the extracellular environment in the accumulation and clearance of defective proteins. He has published over 35 peer-reviewed articles since 2004.
Journal
Scientific Reports
DOI
10.1038/s41598-023-31104-x
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Alpha 2-macroglobulin acts as a clearance factor in the lysosomal degradation of extracellular misfolded proteins
Article Publication Date
28-Mar-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.




