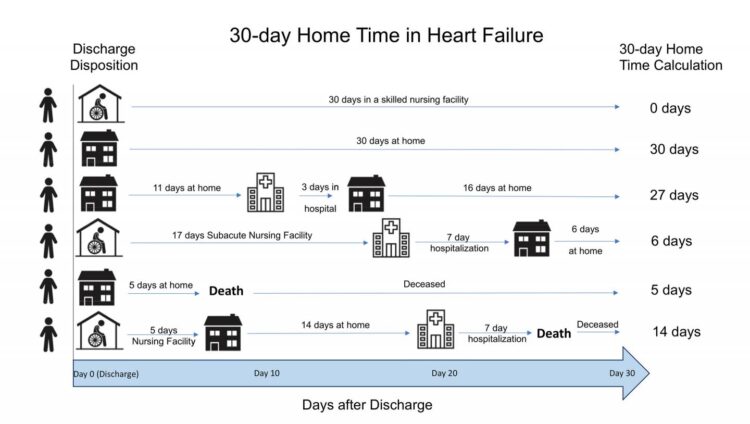
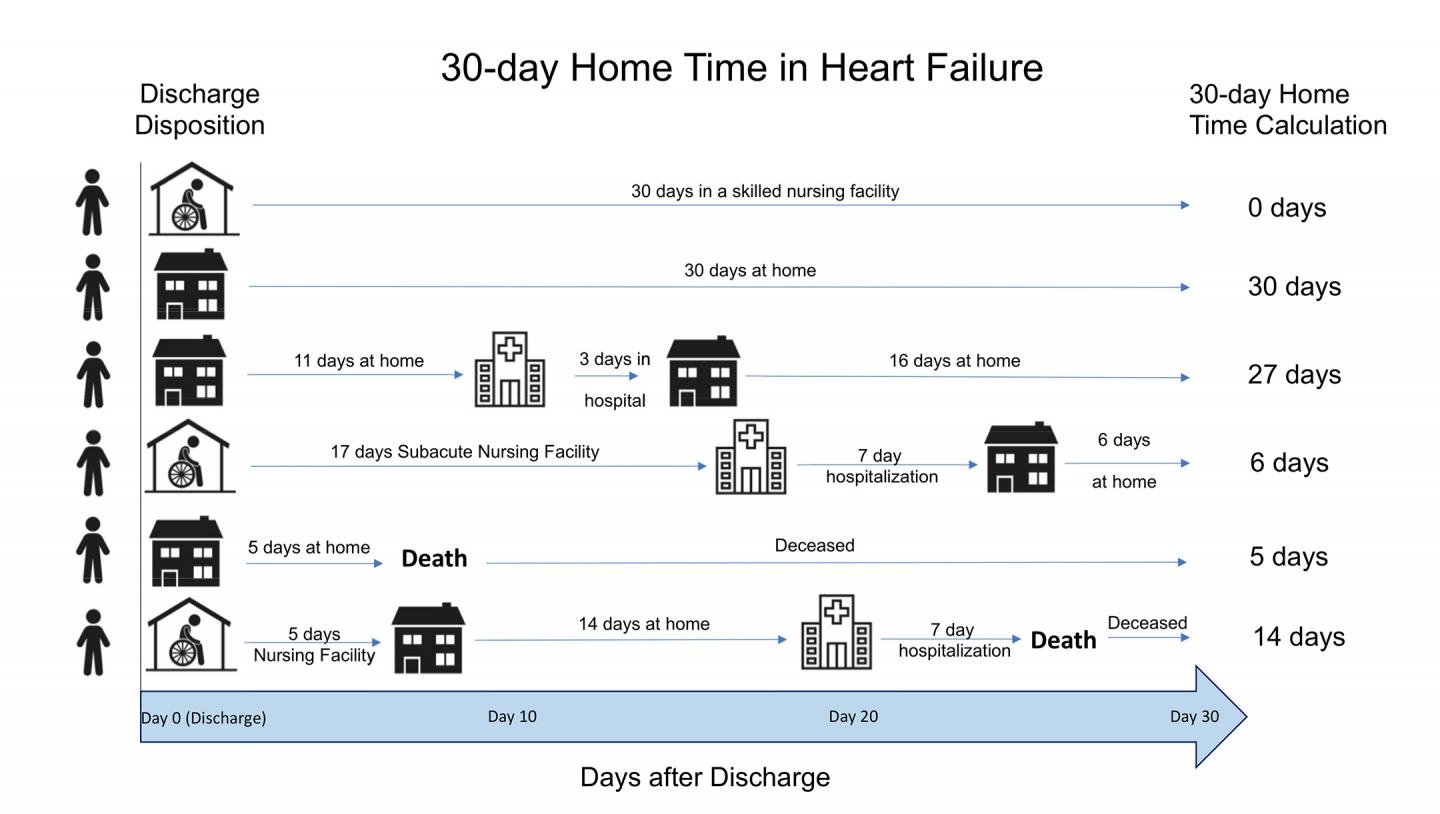
Medicare should look at the number of days spent home after discharge to ensure that low readmission rates don’t reflect patients who needed nursing care or died.
Credit: UT Southwestern Medical Center
DALLAS – Oct. 28, 2020 – Two new studies suggest Medicare’s system of penalizing hospitals if too many patients are readmitted within 30 days should also look at whether the patients were well enough to remain in their home during that time.
The studies propose adding a new metric to examine how many of the initial 30 days following hospitalization are actually spent at home – a “risk-adjusted 30-day home time” test to balance the current “30-day risk-standardized readmission rate” measure.
“The current readmission penalty has been a matter of debate,” says Ambarish Pandey, M.D., first author of the study published today in JAMA Cardiology, as well as of an earlier study published in Circulation in July.
“Some hospitals that have had lower readmission rates were actually having high mortality rates,” says Pandey, assistant professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern. “If you die, you’re not going to be readmitted.”
In addition, the current focus on hospital readmissions does not take into account patients who wind up in a skilled nursing facility or intermediate/long-term care facility after hospital discharge, Pandey points out.
A “30-day home time” metric, he says, would paint a more comprehensive picture and be more patient-centered.
The federal Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) tracks readmissions as part of its effort to improve the quality of care in the nation’s hospitals. In 2019, CMS penalized almost 2,600 U.S. hospitals by withholding an estimated $563 million in Medicare payments after determining they exceeded the expected number of patient readmissions, according to the Circulation study.
CMS focuses its readmissions standard on cases involving heart failure, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and pneumonia.
The studies examined how applying a 30-day home-time metric would have affected the quality rankings of hospitals treating heart failure (the JAMA Cardiology study) and acute myocardial infarction (Circulation), based on Medicare claims data. In both studies, the researchers found that using the 30-day home-time metric changed the quality ranking a hospital had received under the readmission standard about 30 percent of the time.
The JAMA Cardiology study found that heart failure patients spent a risk-adjusted median of 21.77 days at home in the 30 days after discharge. However, 6.61 days were spent in an intermediate/long-term or skilled nursing facility, and another 1.37 days were lost to death. Readmission accounted for only 1.25 of the days lost.
Similarly, in the Circulation study, patients stayed home a risk-adjusted median of 24.0 days, with 4.7 days subtracted for nursing facilities, 2.5 days for death, and 1.0 days for readmission.
Hospitals with higher 30-day home time were larger and more likely to be academic medical centers, according to the studies.
The findings suggest that the 30-day home-time metric complements the existing readmission rate metric “by not only accounting for post-discharge mortality but also the variability in the post-acute care utilization of intermediate/long-term care facility and [skilled nursing facilities],” according to today’s JAMA Cardiology study.
In addition, “a home time metric may be more easily understood by patients and clinicians,” the study says.
###
Neil Keshvani, M.D., UTSW Division of Cardiology, was co-first author on both studies.
Researchers at the University of Iowa, Iowa City Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Northwestern University, and Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center participated in the JAMA Cardiology study.
Researchers at the University of Iowa and the Iowa City Veterans Affairs Medical Center participated in the Circulation study.
About UT Southwestern Medical Center
UT Southwestern, one of the premier academic medical centers in the nation, integrates pioneering biomedical research with exceptional clinical care and education. The institution’s faculty has received six Nobel Prizes, and includes 23 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 17 members of the National Academy of Medicine, and 13 Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigators. The full-time faculty of more than 2,500 is responsible for groundbreaking medical advances and is committed to translating science-driven research quickly to new clinical treatments. UT Southwestern physicians provide care in about 80 specialties to more than 105,000 hospitalized patients, nearly 370,000 emergency room cases, and oversee approximately 3 million outpatient visits a year.
Media Contact
UT Southwestern Medical Center
[email protected]