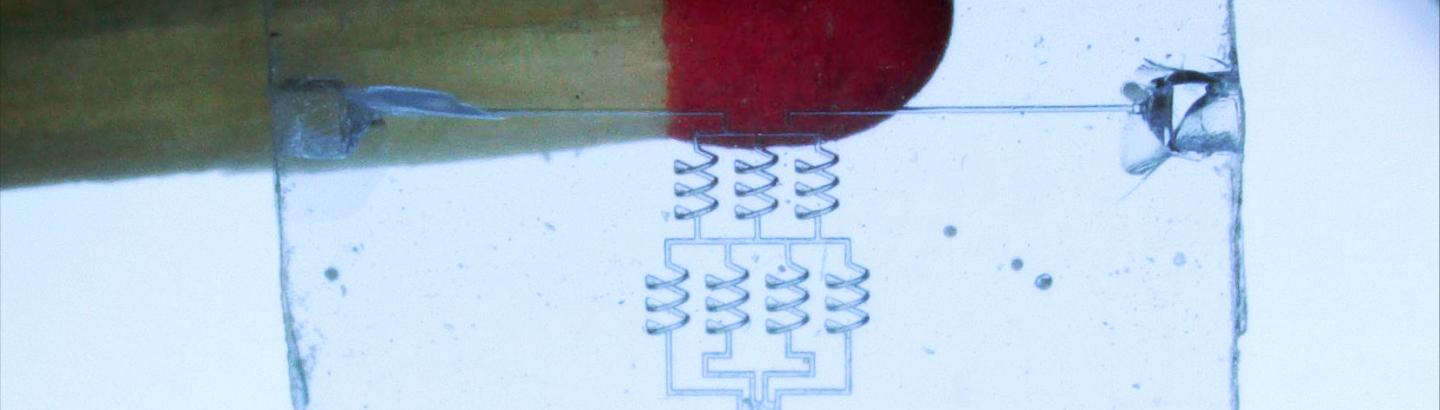
Credit: AG Rapp
Quartz glass is the preferred material for applications that require long-term use because of its high chemical and mechanical stability and excellent optical properties. The engineer Prof. Dr. Bastian E. Rapp from the Department of Microsystems Engineering (IMTEK) at the University of Freiburg and his team have developed the Glassomer process, a method that enables scientists to shape glass like plastic. In the scientific journal Nature Communications, they recently presented a new application: They are now able to produce three-dimensional hollow structures in quartz glass.
Glass is chemically very resistant, which is why cavities such as optical waveguides or microfluidic channels are difficult to produce in it, especially if they have to be three-dimensional. The Glassomer process developed by Rapp and his team simplified this process. Glassomer is a mixture in which high-purity silicon oxide is added in fine powder form to a liquid plastic. As long as this mixture is liquid, it can be processed like a plastic. When exposed to light, it hardens so that it can, for example, be drilled or milled. During the final heat treatment step in the process, the plastic is decomposed leaving leaving a dense glass component. Until now, channel structures could not be manufactures because the researchers had to remove the liquid material from the cavities which is not possible for long channels.
The Freiburg scientists are therefore taking a different approach by first creating the desired cavity as a polymeric component in the 3D printer: A later channel is printed as a polymer thread and then encapsulated with Glassomer. The finished printed product is then heated to 1,300 degrees Celsius so that the plastic – including the polymer thread – is decomposed. The result is a channel surrounded by real glass.
###
Original publication:
Kotz, F., Risch, P., Arnold, K. et al., Rapp, B.E. (2019): Fabrication of arbitrary three-dimensional suspended hollow microstructures in transparent fused silica glass. In: Nature Communications. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09497-z
Contact:
Department of Microsystems Engineering
University of Freiburg
Media Contact
Bastian E. Rapp
[email protected]



