Lung-on-a-chip technology used to study toxic agents, develop treatments
Credit: WFIRM
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, – Oct. 8, 2019 – The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) is the recipient of a major research funding award from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to support its lung-on-a-chip technology as a model to develop chemical injury treatments.
The five-year $24 million program has been approved with an initial contracting commitment of $13.5 million for the first 2 years.
Specifically, the funding from the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), part of the HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, awarded over a five-year period, will validate how WFIRM’s lung-on-a-chip technology works in modeling the effects of chlorine gas ¬- deemed a potential national security threat – on human lungs and to develop treatments.
Currently, the study of respiratory health, disease and biomedical interventions is primarily performed in animal models or 2D cell culture models using human or animal cells. This funding will help the WFIRM research team advance the development of its micro-tissue engineered lung organ tissue equivalent platform. This model can be engineered to reflect both normal and diseased tissue and includes innate immune system responsiveness, and accurate and reproducible response to drugs and toxins.
“Our lung-on-a-chip technology has grown out of our body-on-a-chip research, a system of miniature human organs created in the laboratory that can be used to further our understanding of the effects of inhaled chlorine gas and other toxins, as well as potential treatments,” said WFIRM Director, Anthony Atala, M.D.
WFIRM experts in regenerative medicine will work with Precision Medicine colleagues with expertise in genomics to identify the effects of chlorine gas and other toxic agents on the lungs and to determine the usefulness of the organoid in developing treatments for the resulting lung injuries.
According to BARDA, chlorine gas was used as a weapon during World War I and has been used repeatedly during the ongoing Syrian civil war. In addition, the amount of chlorine manufactured, along with its ready availability, makes this chemical a potential national security threat to the United States. Further, chlorine is one of the most-used industrial gases in the United States and causes multiple deaths and injuries due to accidents. In 2005, a train accident in Graniteville, South Carolina caused a tank car containing chlorine gas to leak, causing nine deaths and at least 250 injuries.
How Lung-on-a-Platform Works
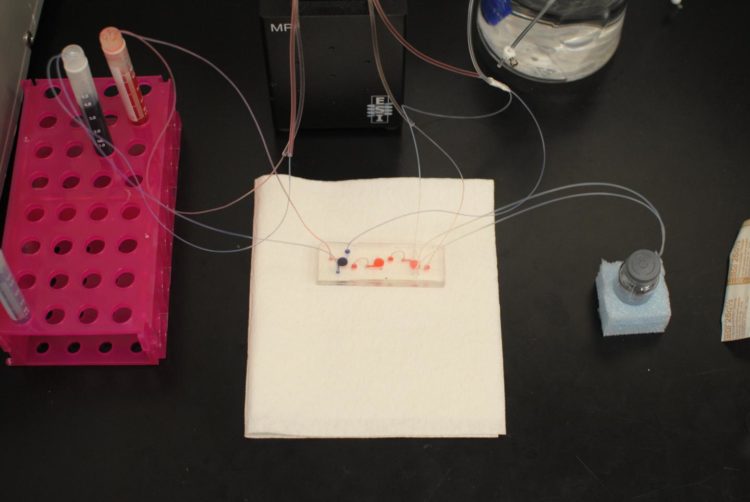
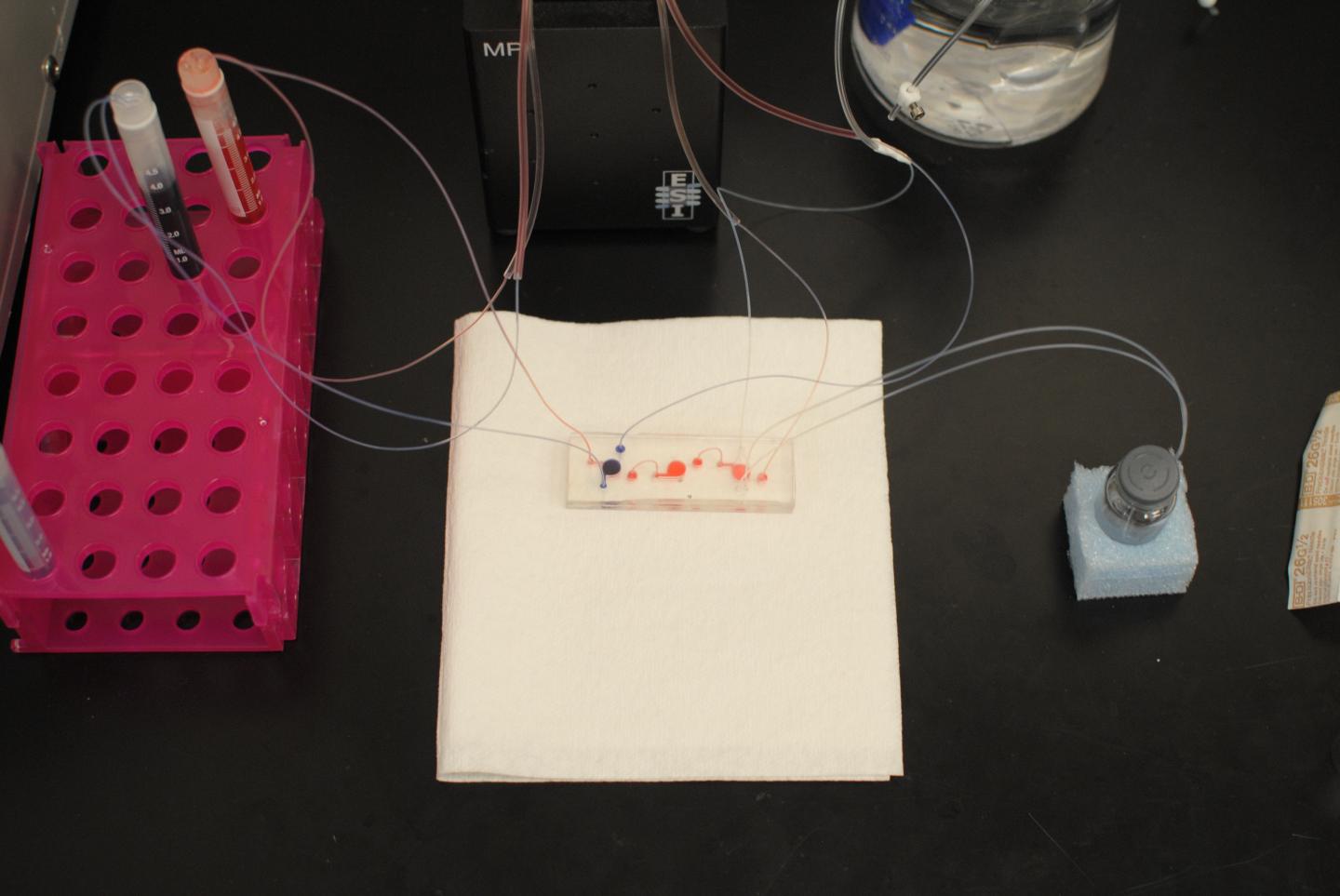
The lung-on-a-chip platform is part of WFIRM’s overall Body-on-a-Chip program, a miniaturized system of human organs that can model the body’s response to harmful agents, can test the effects of new agents during drug discovery, or can help to develop potential therapies. The system can also be used for personalized medicine; for example, it can screen chemotherapy agents on a patient’s own cancer, so the most effective treatment can be given from the start. The Body-on-a-chip system overcomes the substantial limitations of animal models and 2D cell culture models for studying mechanisms of disease and treatment efficacy.
To create the system, human cells are used to create tiny 3D organ-like structures called tissue equivalents, that mimic the function of the heart, liver, lung, blood vessels, etc. Placed on a 2-inch chip, these structures are connected to a system of fluid channels and sensors to provide online monitoring of individual organs and the overall organ system. The circulating blood substitute keeps the cells alive and can be used to introduce chemical or biological agents, as well as potential therapies, into the system. Hollow channels automatically guide toxins or therapies that are being evaluated from one tissue to the next, and sensors measure real-time temperature, oxygen levels, pH and other factors.
“We look forward to pursuing the long-term goal of this research with BARDA, which is to reduce the overall burden of in vivo testing in the development and management of products for human clinical use and to speed up the development of treatments,” Atala said.
###
Media Contact: Bonnie Davis, [email protected], 336-713-1597(o) or 336-493-6184 (m).
About WFIRM
The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine is recognized as an international leader in translating scientific discovery into clinical therapies, with many world firsts, including the development and implantation of the first engineered organ in a patient. More than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. WFIRM has led the world in clinical scale tissue engineering and a number of the basic principles of tissue engineering were first developed at the institute. WFIRM researchers have successfully engineered replacement tissues and organs in all four categories – flat structures, tubular tissues, hollow organs and solid organs – and nine different cell/tissue therapies, such as skin, urethras, cartilage, bladders, muscle, and vaginal organs have been successfully implanted into human patients.
About HHS, ASPR, and BARDA
HHS works to enhance and protect the health and well-being of all Americans, providing for effective health and human services and fostering advances in medicine, public health, and social services. The mission of the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR) is to save lives and protect Americans from 21st century health security threats. Within ASPR, BARDA invests in the advanced research and development, acquisition, and manufacturing of medical countermeasures – vaccines, drugs, therapeutics, devices, diagnostic tools, and non-pharmaceutical products needed to combat health security threats. For more about ASPR and BARDA, visit http://www.
Media Contact
Bonnie Davis
[email protected]
336-713-1597
Original Source
https:/