Credit: (c) Institut Pasteur / Pascal Marseaud
Depression is a mental disorder that affects more than 264 million people of all ages worldwide. Understanding its mechanisms is vital for the development of effective therapeutic strategies. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur, Inserm and the CNRS recently conducted a study showing that an imbalance in the gut bacterial community can cause a reduction in some metabolites, resulting in depressive-like behaviors. These findings, which show that a healthy gut microbiota contributes to normal brain function, were published in Nature Communications on December 11, 2020.
The bacterial population in the gut, known as the gut microbiota, is the largest reservoir of bacteria in the body. Research has increasingly shown that the host and the gut microbiota are an excellent example of systems with mutually beneficial interactions. Recent observations also revealed a link between mood disorders and damage to the gut microbiota. This was demonstrated by a consortium of scientists from the Institut Pasteur, the CNRS and Inserm, who identified a correlation between the gut microbiota and the efficacy of fluoxetine, a molecule frequently used as an antidepressant. But some of the mechanisms governing depression, the leading cause of disability worldwide, remained unknown.
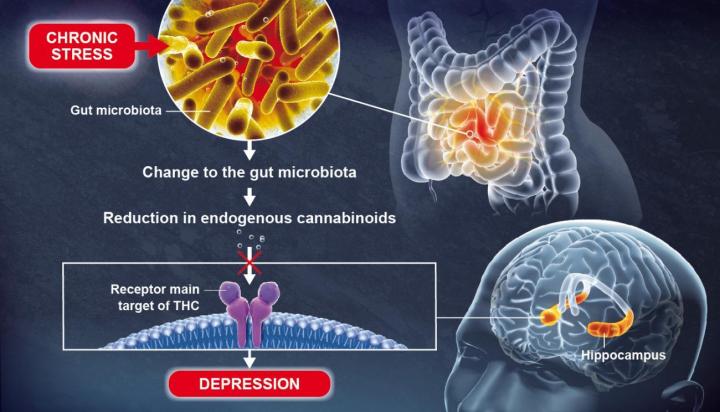
Using animal models, scientists recently discovered that a change to the gut microbiota brought about by chronic stress can lead to depressive-like behaviors, in particular by causing a reduction in lipid metabolites (small molecules resulting from metabolism) in the blood and the brain.
These lipid metabolites, known as endogenous cannabinoids (or endocannabinoids), coordinate a communication system in the body which is significantly hindered by the reduction in metabolites.
Gut microbiota plays a role in brain function and mood regulation
Endocannabinoids bind to receptors that are also the main target of THC, the most widely known active component of cannabis. The scientists discovered that an absence of endocannabinoids in the hippocampus, a key brain region involved in the formation of memories and emotions, resulted in depressive-like behaviors.
The scientists obtained these results by studying the microbiotas of healthy animals and animals with mood disorders. As Pierre-Marie Lledo, Head of the Perception and Memory Unit at the Institut Pasteur (CNRS/Institut Pasteur) and joint last author of the study, explains: “Surprisingly, simply transferring the microbiota from an animal with mood disorders to an animal in good health was enough to bring about biochemical changes and confer depressive-like behaviors in the latter.”
The scientists identified some bacterial species that are significantly reduced in animals with mood disorders. They then demonstrated that an oral treatment with the same bacteria restored normal levels of lipid derivatives, thereby alleviating the depressive-like behaviors. These bacteria could therefore serve as an antidepressant. Such treatments are known as “psychobiotics”.
“This discovery shows the role played by the gut microbiota in normal brain function,” continues Gérard Eberl, Head of the Microenvironment and Immunity Unit (Institut Pasteur/Inserm) and joint last author of the study. If there is an imbalance in the gut bacterial community, some lipids that are vital for brain function disappear, encouraging the emergence of depressive-like behaviors. In this particular case, the use of specific bacteria could be a promising method for restoring a healthy microbiota and treating mood disorders more effectively.
###
Media Contact
Aurelie Perthuison
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




