Large-scale study with more than 4000 participants at ZIEL – Institute for Food & Health
Credit: A. Heddergott / TUM
The microbial composition of the intestines is complex and varies widely from one individual to another. Many factors such as environmental factors, lifestyle, genetics or illnesses affect the intestinal ecosystem of helpful gut bacteria.
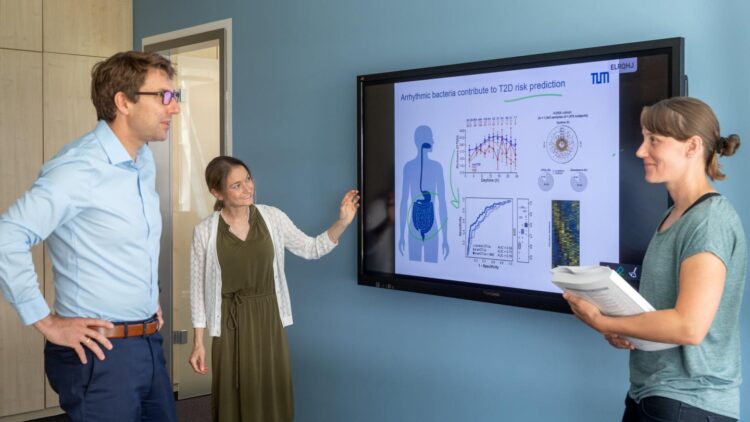
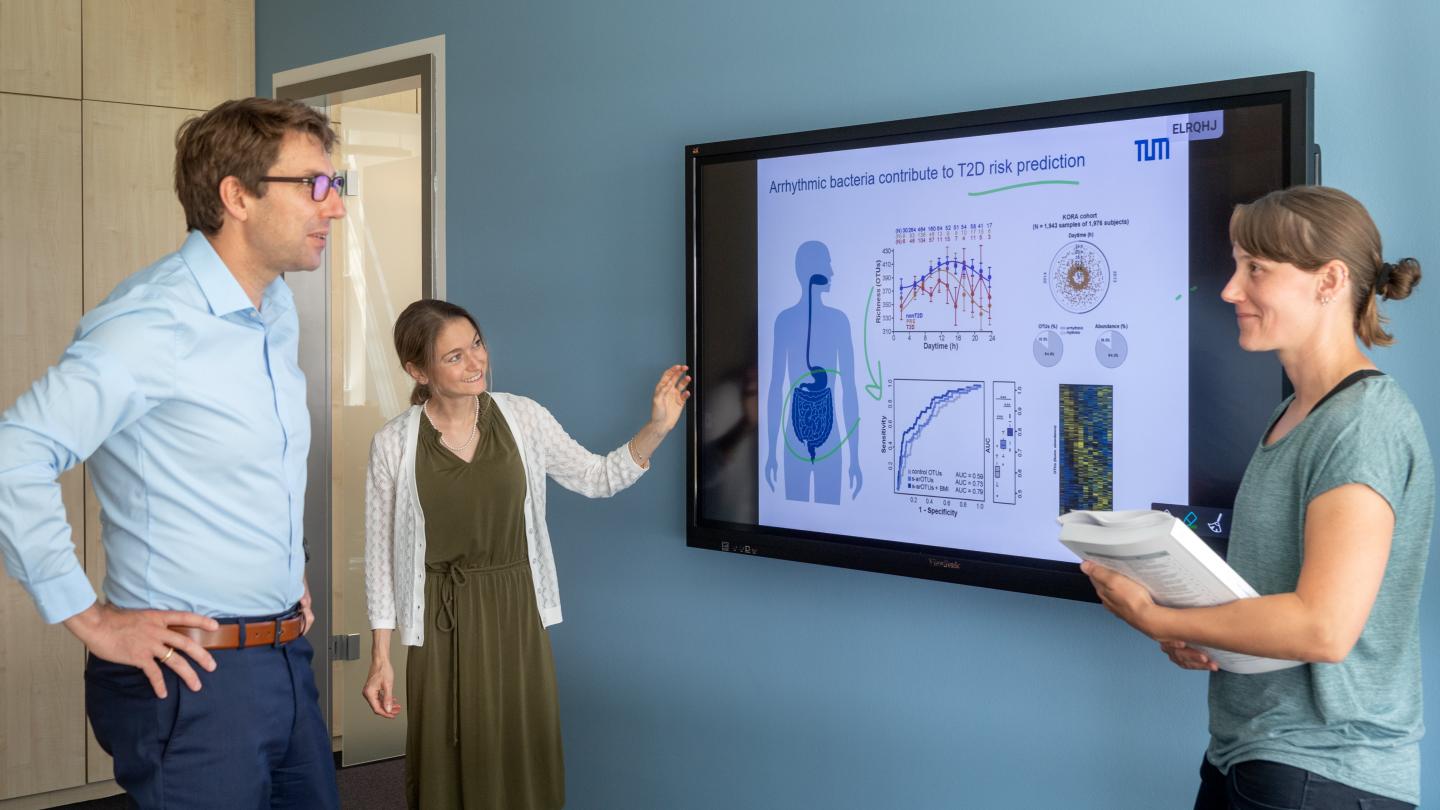
Dirk Haller, Professor for Nutrition and Immunology at TUM, and his team have examined the importance of daytime-dependent fluctuations of the gut microbiome in relation to type 2 diabetes; they present their study encompassing more than 4000 people and it is the first study in this field based on a large prospective human cohort.
The relationship between gut bacteria and medical conditions
“In order to see whether changes in the gut microbiome allow conclusions about medical conditions, so-called prospective cohort studies are required,” explained Prof. Haller.
In these prospective cohort studies, a cross section of the population is being observed; however, none of the participants showed any signs of disease. This population is being re-examined over time. This way, researchers can find out whether a certain observation may be typical for future occurrences of diseases.
Diagnosis and outlook of type 2 diabetes may be improved
“When certain gut bacteria do not follow a day-night rhythm, so if their number and function does not change over the course of the day, this can be an indicator for a potential type 2 diabetes disease. Knowing this can improve diagnosis and outlook of type 2 diabetes,” said Chronobiologist Dr. Silke Kiessling, another contributor to the study.
These arrhythmic bacteria – those that are not changing between day and night – are a marker for potential disease. Researchers refer to this as a risk signature. “Mathematical models also show that this microbial risk signature consisting of arrhythmic bacteria helps diagnosing diabetes,” explained Sandra Reitmeier, first author on the study.
Primarily, the scientists analyzed data from an existing independent cohort by Helmholtz Zentrum München. The diabetes-related results were validated using additional cohorts from Germany. “By comparing our data to cohorts in England, we could confirm that there is – among other things – a strong regional factor affecting the microbial ecosystem. Therefore, there is a demand for finding locally specified arrhythmic risk signatures,” elaborated Haller.
Nutritionist Haller emphasizes that “apart from bacteria and their variations over the course of the day, other parameters such as the body mass index play a role in being able to better predict a person’s future medical conditions.”
Intestinal bacteria’s day and night rhythm as starting point for further research
Registering the time of day when taking human fecal samples for research purposes can heavily influence disease diagnostics. “Documenting these timestamps is essential for improving risk markers,” Prof. Haller emphasizes.
This research substantiates the hypothesis that changes in the microbiome have an effect of nutrition-related diseases. How gut bacteria changing (or not changing) during the day affect other microbiome-associated diseases such as Crohn’s disease or intestinal cancer may be subject to further scientific examination.
The results of this study are of particular importance for further work in the Collaborative Research Center of “Microbiome Signatures” (https:/
###
Media Contact
Dirk Haller
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.