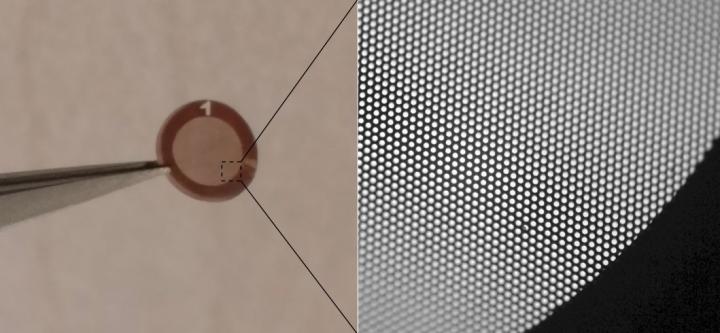
Credit: Dr. Santiago Jose Cartamil-Bueno
Overseas exploration and trade during the Age of Discovery (15th-17th centuries) were possible by sail technology, and deep-space exploration will require the same for the coming Age of NewSpace. This time, however, the new sails shall move with light instead of wind, for which these light sails need to be extremely large, thin, lightweight, reflective and strong.
In a light-hearted leap for humankind, ESA-backed researchers demonstrate the laser-propulsion of graphene sails in microgravity.
Let me play among the stars
Physical exploration of deep space became a reality when NASA’s Voyager 1 left our Solar System in 2012, after a trip of 35 years and 121 AU (18,100,000,000 Km, 11,250,000,000 mi). Were Voyager 1 traveling to Alpha Centauri Cb, the exoplanet of our closest neighboring star system at 260,000 AU, humanity would have to wait dozens of millennia and hope that the shuttle kept some power to reach us then.
As demonstrated first by JAXA’s mission IKAROS (2010) and recently by The Planetary Society’s LightSail 2 (2019), using light sails as propulsion system is among the most promising ideas to enable fast and affordable space trips. Not only sails do not require fuel to move, but they save its corresponding costly weight and that of its containing tanks. Unfortunately, the light radiation pressure (momentum transfer of photons) only confers relevant acceleration when the sails are sufficiently large (from few to thousands of squared meters) with a minimal mass, and currently used materials are limited when scaling up their size.
“Graphene is part of the solution”, says Dr. Santiago J. Cartamil-Bueno, SCALE Nanotech’s director and leader of GrapheneSail team. “We demonstrate a novel sail design that reduces the overall sail mass by using perforated films. By covering the holes with CVD graphene, the full area of the sail is again available for optical performance at minimal mass cost. The fabrication is relatively simple and could be easily scaled up to squared kilometers, although the in-space deployment of such a giant sail will be a serious challenge”.
Völlig losgelöst, von der Erde
With the support of ESA, the researchers gained access to the ZARM Drop Tower in Bremen (Germany), in order to test the graphene sails in space-like conditions. Here, experiments are performed in a free-fall capsule that ensures a high-quality microgravity environment (2.
Dr. Thorben Könemann, Dep. Scientific Director, ZARM Drop Tower Operation and Service Company, remarked: “It is always a great pleasure for us to support visionary and promising experiment concepts. The success of the GrapheneSail team underlines again the capabilities of the Bremen Drop Tower – offering not only an excellent microgravity environment for fundamental research, but also being a first stepping stone and testbed for space technology without the complexity of in-orbit operations”.
Accessing this type of facilities is not trivial, even for such a breakthrough initiative. Luckily, Dr. Astrid Orr, ESA’s Physical Sciences Coordinator at ESTEC, saw it different: “this project is a wonderful example of scientific research that can be performed with the support of ESA on a ground-based space-analogue platform – in this case microgravity – and which also has high potential for ESA’s future spaceflight and exploration programs”.
“We want to set sails to Mars before SpaceX,” jokes Dr. Santiago J. Cartamil-Bueno, “but for now we keep our feet on the ground. Currently, the graphene sails are being developed through the European Space Agency Business Incubator Center Hessen & Baden-Württemberg and we look for more strategic partners that allow us to scale the technology up for an eventual test in space”. Maybe it’s the final countdown for graphene to take off.
###
Media Contact
Gabi Predikant
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




