Credit: Yubo Wang, Takuya Yamamoto
Hokkaido University scientists have found a way to prevent gold nanoparticles from clumping, which could help towards their use as an anti-cancer therapy.
Attaching ring-shaped synthetic compounds to gold nanoparticles helps them retain their essential light-absorbing properties, Hokkaido University researchers report in the journal Nature Communications.
Metal nanoparticles have unique light-absorbing properties, making them interesting for a wide range of optical, electronic and biomedical applications. For example, if delivered to a tumour, they could react with applied light to kill cancerous tissue. A problem with this approach, though, is that they easily clump together in solution, losing their ability to absorb light. This clumping happens in response to a variety of factors, including temperature, salt concentration and acidity.
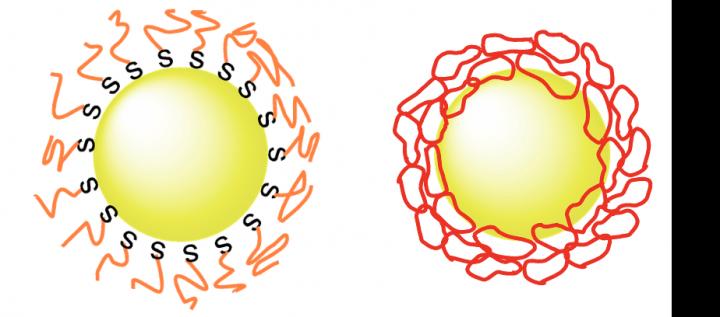
Scientists have been trying to find ways to ensure nanoparticles stay dispersed in their target environments. Covering them with polyethylene glycol, otherwise known as PEG, has been relatively successful at this in the case of gold nanoparticles. PEG is biocompatible and can prevent gold surfaces from clumping together in the laboratory and in living organisms, but improvements are still needed.
Applied chemist Takuya Yamamoto and colleagues at Hokkaido University, The University of Tokyo, and Tokyo Institute of Technology found that mixing gold nanoparticles with ring-shaped PEG, rather than the normally linear PEG, significantly improved dispersion. The ‘cyclic-PEG’ (c-PEG) attaches to the surfaces of the nanoparticles without forming chemical bonds with them, a process called physisorption. The coated nanoparticles remained dispersed when frozen, freeze-dried and heated.
The team tested the c-PEG-covered gold nanoparticles in mice and found that they cleared slowly from the blood and accumulated better in tumours compared to gold nanoparticles coated with linear PEG. However, accumulation was lower than desired levels, so the researchers recommend further investigations to fine-tune the nanoparticles for this purpose.
Associate Professor Takuya Yamamoto is part of the Laboratory of Chemistry of Molecular Assemblies at Hokkaido University, where he studies the properties and applications of various cyclic chemical compounds.
###
Media Contact
Sohail Keegan Pinto
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




