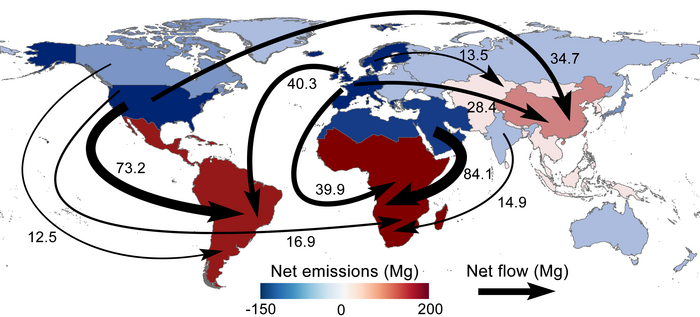
Almost half of mercury exposure comes from mercury embedded in global trade, according to an analysis of the global flows of the toxic metal. Mercury is a neurotoxin that harms human health in even very small doses. Zhencheng Xing, Ruirong Chang, and their colleagues traced the element through international trade routes from sites of pollution to exposure in the environment, and accounted for the resulting human health impacts. The authors linked a mercury emission inventory, a global multi-regional input-output model, a coupled atmosphere-land-ocean-ecosystem model, and an exposure-risk-valuation model to investigate the global biogeochemical mercury cycle. The world emits about 1,800 megagrams of mercury annually. Most of these global emissions are linked to the smelting and pressing of non-ferrous metals, particularly during artisanal and small-scale gold mining. Mercury used in these processes can wash downstream and become airborne, polluting soil, rivers and parts of the ocean. People are then exposed through eating seafood, freshwater fish, or rice—sometimes many thousands of miles away from the mercury’s source. Many developed countries, including the United States and Japan, can be classified as outsourcers of mercury because developed countries are the ultimate consumers of gold, electric equipment, machinery, and other products whose production produces mercury pollution but such countries are spared exposure. According to the authors, strategies to tackle mercury exposure should include both production-side controls and demand-side measures, including consumption taxes to influence consumer behavior.
Credit: Xing et al.
Almost half of mercury exposure comes from mercury embedded in global trade, according to an analysis of the global flows of the toxic metal. Mercury is a neurotoxin that harms human health in even very small doses. Zhencheng Xing, Ruirong Chang, and their colleagues traced the element through international trade routes from sites of pollution to exposure in the environment, and accounted for the resulting human health impacts. The authors linked a mercury emission inventory, a global multi-regional input-output model, a coupled atmosphere-land-ocean-ecosystem model, and an exposure-risk-valuation model to investigate the global biogeochemical mercury cycle. The world emits about 1,800 megagrams of mercury annually. Most of these global emissions are linked to the smelting and pressing of non-ferrous metals, particularly during artisanal and small-scale gold mining. Mercury used in these processes can wash downstream and become airborne, polluting soil, rivers and parts of the ocean. People are then exposed through eating seafood, freshwater fish, or rice—sometimes many thousands of miles away from the mercury’s source. Many developed countries, including the United States and Japan, can be classified as outsourcers of mercury because developed countries are the ultimate consumers of gold, electric equipment, machinery, and other products whose production produces mercury pollution but such countries are spared exposure. According to the authors, strategies to tackle mercury exposure should include both production-side controls and demand-side measures, including consumption taxes to influence consumer behavior.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
DOI
10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad128
Article Title
International trade shapes global mercury-related health impacts
Article Publication Date
23-May-2023




