Over the last few decades, antimicrobial resistance has become a major public health concern globally. This has led to a search for alternative methods of treating microbial infections. One such innovation is the discovery of antimicrobial properties of certain peptides. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are short peptides found in most animals, plants, and microorganisms as a natural defense against infections. AMPs combat harmful bacteria via a nonspecific mechanism that prevents them from developing antimicrobial resistance. Despite these exceptional abilities, research on AMPs is being hindered because the existing systems for identifying candidate AMPs are like a black box, where the outputs are not easily interpretable for further analysis.
Credit: Hojung Nam from Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
Over the last few decades, antimicrobial resistance has become a major public health concern globally. This has led to a search for alternative methods of treating microbial infections. One such innovation is the discovery of antimicrobial properties of certain peptides. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are short peptides found in most animals, plants, and microorganisms as a natural defense against infections. AMPs combat harmful bacteria via a nonspecific mechanism that prevents them from developing antimicrobial resistance. Despite these exceptional abilities, research on AMPs is being hindered because the existing systems for identifying candidate AMPs are like a black box, where the outputs are not easily interpretable for further analysis.
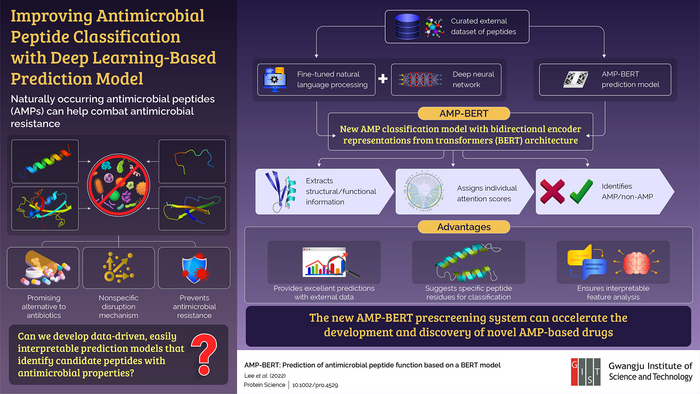
Now, in a recent breakthrough published in Protein Science, a team of researchers from Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, including Prof. Hojung Nam and Mr. Hansol Lee, proposed an AMP-BERT classification system that uses AI-based bidirectional encoder representation from transformers (BERT) architecture to improve upon the existing AMP classification models. Their findings were published online on 3 December 2022 and in print in Volume 32, Issue 1 of the journal in January 2023.
When asked about the motivation behind developing the classification system, Prof. Nam explains: “The misuse and overuse of antibiotics have resulted in the development of bacteria that cannot be effectively treated with these antibiotics. This has resulted in an increased health risk not only in humans but also agriculture. So, we wanted to develop an AMP pre-screening platform that isn’t a black box of algorithms but can be easily interpreted for further research.”
The team incorporated a natural language processing (NLP)-based deep neural network that was pre-trained with billions of protein sequences then fine-tuned with thousands of peptide sequences from a benchmark AMP database. This enabled the AMP-BERT model to not only extract the structural and functional information from the input peptide sequences but also differentiate AMPs from non-AMPs. This enhanced the prediction power allowed the model to make better classifications even with external data.
The team also designed the model to assign individual attention scores to each amino acid from the input peptide sequence. The attention feature then revealed the important subregions of AMPs that play a major role in deciding whether a peptide has antimicrobial properties or not. Furthermore, the prediction results indicated the AMP-BERT model’s applicability extends even to unseen peptide data and that it can learn meaningful functional and structural information from those peptides.
The novel AMP-BERT peptide pre-screening model can open new doors for the discovery and development of AMP-based drug candidates for treating antimicrobial-resistant illnesses. The important peptide subregion information provided by this prediction platform can also be used to optimize the antibiotic efficiency of peptides. “As more AMPs are experimentally validated and new structural information is uncovered using computational methods, we will be able to make more effective antibiotic drugs and potentially stop a new pandemic from spreading across the world in near future” concludes Prof Nam.
AMP-BERT will certainly be a powerful weapon in our war against antimicrobial resistance!
***
Reference
Authors: Hansol Lee1, Songyeon Lee1, Ingoo Lee1, Hojung Nam1,2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4529
Affiliations:
1 School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Gwangju Institute of
Science and Technology (GIST)
2 AI Graduate School, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
About the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST)
The Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) is a research-oriented university situated in Gwangju, South Korea. Founded in 1993, GIST has become one of the most prestigious schools in South Korea. The university aims to create a strong research environment to spur advancements in science and technology and to promote collaboration between international and domestic research programs. With its motto of “A Proud Creator of Future Science and Technology,” GIST has consistently received one of the highest university rankings in Korea.
Website: http://www.gist.ac.kr/
About the author
Hojung Nam is an Associate Professor in the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, and the AI Graduate School at Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST). She received her Ph.D. in the Dept. of Bio and Brain Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and completed her postdoctoral training in the Dept. of Bioengineering at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Currently, her research group is working on the development of various computational tools for drug discovery, development, and models for the prediction of drug side effects.
Hansol Lee is a Ph.D. candidate at GIST under Prof. Hojung Nam’s instruction. During his Ph.D. course, he has carried out research on AMP-related deep learning models, including AMP class prediction and AMP sequence generation.
Journal
Protein Science
DOI
10.1002/pro.4529
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
AMP-BERT: Prediction of antimicrobial peptide function based on a BERT model
Article Publication Date
3-Dec-2022
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests




