A UC Riverside genetic discovery could turn disease-carrying mosquitoes into insect Peter Pans, preventing them from ever maturing or multiplying.
Credit: Lewis Hun/UCR
A UC Riverside genetic discovery could turn disease-carrying mosquitoes into insect Peter Pans, preventing them from ever maturing or multiplying.
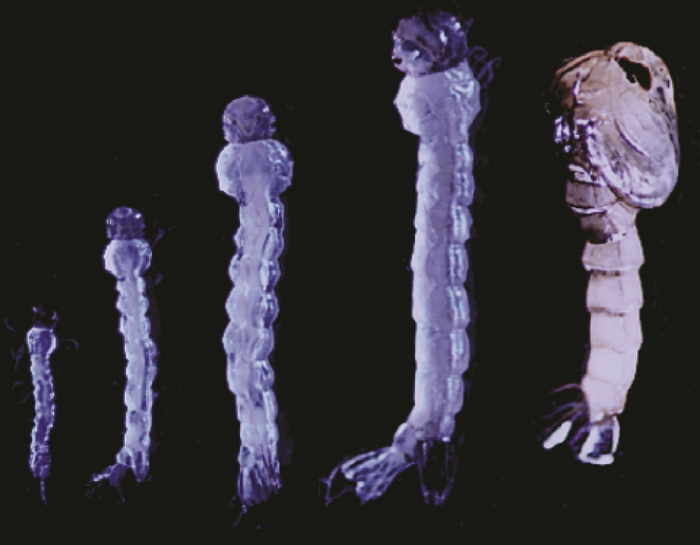
In 2018, UCR entomologist Naoki Yamanaka found, contrary to accepted scientific wisdom, that an important steroid hormone requires transporter proteins to enter or exit fruit fly cells. The hormone, ecdysone, is called the “molting hormone.” Without it, flies will never mature, or reproduce.
Before his discovery, textbooks taught that ecdysone travels freely across cell membranes, slipping past them with ease. “We now know that’s not true,” Yamanaka said.
Every insect species requires ecdysone for some aspect of their journey from egg to offspring-producing adult. And every insect that Yamanaka has tested also possesses the ecdysone transporter that he found in 2018, plus a few more found in a new study. But in this new study, he found mosquitoes to be different.
Mosquitoes have only three of the four transporter proteins that fruit flies possess. They lack the most important, primary ecdysone transporter.
“This primary one is somehow, mysteriously, missing in mosquitoes,” Yamanaka said.
These findings have now been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The discovery opens the door to a mosquito-specific insecticide that would not harm beneficial bees or other pollinators. It would, however, affect mosquitoes like the ones used in the study, Aedes aegypti, which spread Zika, dengue, yellow fever, chikungunya and other viruses.
“We can develop chemicals to block the functions of these ecdysone transporters but do not affect the original transporter that is so key for other insects,” Yamanaka said. “The chances for off-target effects would be low.”
A related UC Riverside study, led by cell biologist Sachiko Haga-Yamanaka, is attempting to locate similar hormone transporting machinery in humans.
“Textbooks say that steroid hormones transport freely into and out of human cells, but based on our insect research, we doubt that to be the case,” Yamanaka said.
Yamanaka’s research has been funded by the National Institutes of Health. His laboratory is now screening for chemicals that can block mosquitoes’ ecdysone importers. He is also investigating ecdysone transporters in other animals.
Other methods do exist of ensuring local populations of mosquitoes cannot breed. Releasing sterile, irradiated male mosquitoes into the wild to mate with females results in eggs that do not hatch, a technique that eliminates the need for insecticides.
Though there are effective methods like this for controlling local populations of mosquitoes, Yamanaka feels it is important to develop additional tools so we can handle mosquito-related issues in many different scenarios.
“It is impossible to make mosquitoes go extinct,” Yamanaka said. “Depending on one tool to control them is dangerous. As the climate heats up, it creates even more favorable conditions for them to multiply, and they’re only likely to become a bigger problem, especially in Southern California.”
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2202932119
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Essential functions of mosquito ecdysone importers in development and reproduction
Article Publication Date
13-Jun-2022




