By identifying the role of a specific protein in the development of obesity-related liver diseases, UNIGE researchers pave the way for better diagnosis, and potentially better treatment.
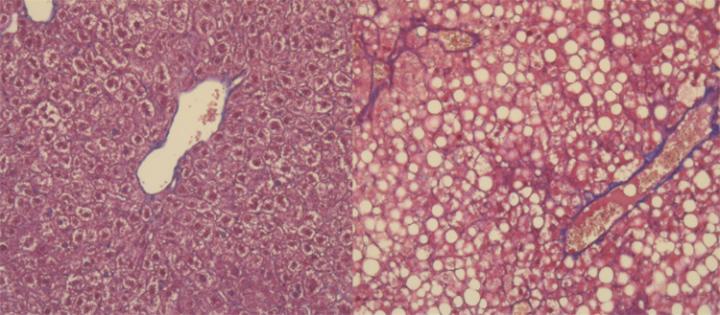
Credit: © UNIGE
Hepatocellular carcinoma, a very common liver cancer linked to the presence of fat in the liver, is one of the leading causes of cancer death worldwide. With the increase in our sedentary lifestyle and in the sugar and fat content of our diet, the number of individuals at risk is on the rise. Scientists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have discovered a protein involved in the progression of a “fatty liver” towards cancer. This protein, S100A11, could not only allow early detection of the risk of developing liver cancer, but also open the way to new targeted therapies. These results, published in the journal Gut, highlight the close links between our diet and cancer development.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common liver cancer. It can occur in the context of a chronic liver inflammation caused by excessive fat accumulation. Obesity is therefore an important risk factor for the development of this cancer. The difficulty in detecting it and the lack of targeted treatment contribute to the severity of this disease, which causes the death of more than 700,000 people per year worldwide. Moreover, with almost 41% of the Swiss population being overweight or obese, the extent of this cancer is likely to alarmingly increase in the next decades.
When fat triggers liver sickness
Among the largest organs in our body, the liver performs essential functions and is involved in the storage of sugars and fats from food. If the diet is too caloric, liver cells accumulate the excess of energy under the form of fat, a pathological condition called fatty liver disease. Inflammation and build-up of fibrous tissue can then develop and even lead to cirrhosis or cancer. These dysfunctions, initially asymptomatic, often go unnoticed or are considered benign. “We already know that a fatty liver can become inflamed and progress into cancer, but very little is known about the molecular mechanisms responsible for these pathologies”, explains Michelangelo Foti, Professor and Director of the Department of Cell Physiology and Metabolism at UNIGE Faculty of Medicine, who supervised this work. “Fatty liver disease already affects nearly 30% of the world’s population and will very quickly become a major public health problem.”
A protein network involved
The aim of UNIGE researchers was to detect changes in the expression of specific proteins that could promote cancer development. “To date, studies have focused mainly on genetic mutations associated with liver cancer, but this has not led to effective treatments”, adds Michelangelo Foti. “That is why we have been looking for other alterations that could explain the progression of a fatty liver towards an inflammatory state and cancer.”
It turns out that a whole network of proteins becomes deregulated, in the absence of any genetic alterations, thereby creating an amenable environment to the development of cancer. Among this network, the protein S100A11 particularly caught the attention of scientists. “We first discovered that S100A11 promotes inflammation and build-up of fibrous tissue in the liver”, explains Cyril Sobolewski, researcher at the Department of Cell Physiology and Metabolism and first author of this work. “Additional tests showed that the more S100A11 was expressed, the greater the severity of the cancer.”
A therapeutic target?
The discrete symptoms of liver inflammation and cancer play an important role in their dangerousness, but the presence of S100A11 in the blood raises the possibility of an early detection by simple blood sampling. “The earlier the patient is treated, the greater the chances of survival”, highlights Michelangelo Foti. “In addition, S100A11 may be a promising therapeutic target, says Cyril Sobolewski. The next step would be to generate specific antibodies able to neutralize the protein and prevent its carcinogenic effect.” This type of approach, called immunotherapy, has already shown promising results in the fight against several cancers.
###
Media Contact
Michelangelo Foti
[email protected]
41-223-795-204
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




