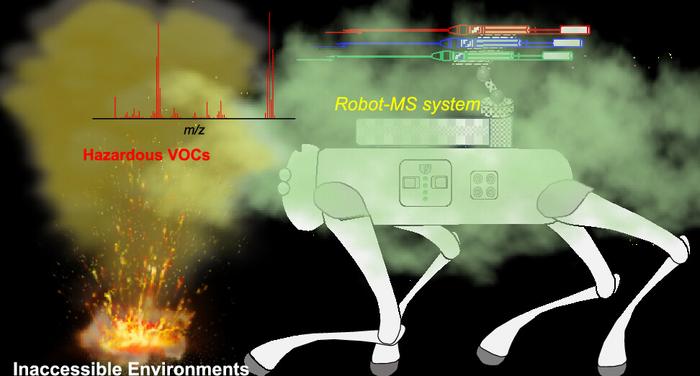
Nightmare material or truly man’s best friend? A team of researchers equipped a dog-like quadruped robot with a mechanized arm that takes air samples from potentially treacherous situations, such as an abandoned building or fire. The robot dog walks samples to a person who screens them for potentially hazardous compounds, says the team that published its study in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry. While the system needs further refinement, demonstrations show its potential value in dangerous conditions.
Credit: Adapted from Analytical Chemistry 2024, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c01555
Nightmare material or truly man’s best friend? A team of researchers equipped a dog-like quadruped robot with a mechanized arm that takes air samples from potentially treacherous situations, such as an abandoned building or fire. The robot dog walks samples to a person who screens them for potentially hazardous compounds, says the team that published its study in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry. While the system needs further refinement, demonstrations show its potential value in dangerous conditions.
Testing the air for dangerous chemicals in risky workplaces or after an accident, such as a fire, is an important but very dangerous task for scientists and technicians. To keep humans out of harm’s way, Bin Hu and colleagues are developing mobile detection systems for hazardous gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by building remote-controlled sampling devices like aerial drones and tiny remotely operated ships. The team’s latest entry into this mechanical menagerie is a dog-like robot with an articulated testing arm mounted on its back. The independently controlled arm is loaded with three needle trap devices (NTDs) that can collect air samples at any point during the robot’s terrestrial mission.
The researchers test-drove their four-legged “lab” through a variety of inaccessible environments, including a garbage disposal plant, sewer system, gasoline fireground and chemical warehouse, to sample the air for hazardous VOCs. While the robot had trouble navigating effectively in rainy and snowy weather, it collected air samples and returned them to the portable mass spectrometer (MS) for onsite analysis in less time than it would take to transfer the samples to an off-site laboratory — and without putting a technician in a dangerous environment. The researchers say the robot-MS system represents a “smart” and safer approach for detecting potentially harmful compounds.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Guangzhou Science and Technology Program and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Journal
Analytical Chemistry
DOI
10.1021/acs.analchem.4c01555
Article Title
“Portable Mass Spectrometry for On-site Detection of Hazardous Volatile Organic Compounds via Robotic Extractive Sampling”
Article Publication Date
17-May-2024




