A team of researchers at Duke University and their collaborators have uncovered the atomic mechanisms that make a class of compounds called argyrodites attractive candidates for both solid-state battery electrolytes and thermoelectric energy converters.
Credit: Olivier Delaire, Duke University
A team of researchers at Duke University and their collaborators have uncovered the atomic mechanisms that make a class of compounds called argyrodites attractive candidates for both solid-state battery electrolytes and thermoelectric energy converters.
The discoveries—and the machine learning approach used to make them—could help usher in a new era of energy storage for applications such as household battery walls and fast-charging electric vehicles.
The results appeared online May 18 in the journal Nature Materials.
“This is a puzzle that has not been cracked before because of how big and complex each building block of the material is,” said Olivier Delaire, associate professor of mechanical engineering and materials science at Duke. “We’ve teased out the mechanisms at the atomic level that are causing this entire class of materials to be a hot topic in the field of solid-state battery innovation.”
As the world moves toward a future built on renewable energy, researchers must develop new technologies for storing and distributing energy to homes and electric vehicles. While the standard bearer to this point has been the lithium-ion battery containing liquid electrolytes, it is far from an ideal solution given its relatively low efficiency and the liquid electrolyte’s affinity for occasionally catching fire and exploding.
These limitations stem primarily from the chemically reactive liquid electrolytes inside Li-ion batteries that allow lithium ions to move relatively unencumbered between electrodes. While great for moving electric charges, the liquid component makes them sensitive to high temperatures that can cause degradation and, eventually, a runaway thermal catastrophe.
Many public and private research labs are spending a lot of time and money to develop alternative solid-state batteries out of a variety of materials. If engineered correctly, this approach offers a much safer and more stable device with a higher energy density — at least in theory.
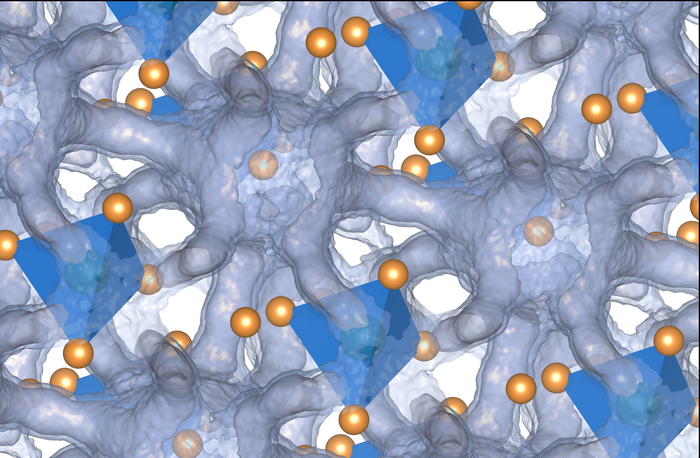
While nobody has yet discovered a commercially viable approach to solid-state batteries, one of the leading contenders relies on a class of compounds called argyrodites, named after a silver containing mineral. These compounds are built from specific, stable crystalline frameworks made of two elements with a third free to move about the chemical structure. While some recipes such as silver, germanium and sulfur are naturally occurring, the general framework is flexible enough for researchers to create a wide array of combinations.
“Every electric vehicle manufacturer is trying to move to new solid-state battery designs, but none of them are disclosing which compositions they’re betting on,” Delaire said. “Winning that race would be a game changer because cars could charge faster, last longer and be safer all at once.”
In the new paper, Delaire and his colleagues look at one promising candidate made of silver, tin and selenium (Ag8SnSe6). Using a combination of neutrons and x-rays, the researchers bounced these extremely fast-moving particles off atoms within samples of Ag8SnSe6 to reveal its molecular behavior in real-time. Team member Mayanak Gupta, a former postdoc in Delaire’s lab who is now a researcher at the Bhabha Atomic Research Center in India, also developed a machine learning approach to make sense of the data and created a computational model to match the observations using first-principles quantum mechanical simulations.
The results showed that while the tin and selenium atoms created a relatively stable scaffolding, it was far from static. The crystalline structure constantly flexes to create windows and channels for the charged silver ions to move freely through the material. The system, Delaire said, is like the tin and selenium lattices remain solid while the silver is in an almost liquid-like state.
“It’s sort of like the silver atoms are marbles rattling around about the bottom of a very shallow well, moving about like the crystalline scaffold isn’t solid,” Delaire said. “That duality of a material living between both a liquid and solid state is what I found most surprising.”
The results and, perhaps more importantly, the approach combining advanced experimental spectroscopy with machine learning, should help researchers make faster progress toward replacing lithium-ion batteries in many crucial applications. According to Delaire, this study is just one of a suite of projects aimed at a variety of promising argyrodite compounds comprising different recipes. One combination that replaces the silver with lithium is of particular interest to the group, given its potential for EV batteries.
“Many of these materials offer very fast conduction for batteries while being good heat insulators for thermoelectric converters, so we’re systematically looking at the entire family of compounds,” Delaire said. “This study serves to benchmark our machine learning approach that has enabled tremendous advances in our ability to simulate these materials in only a couple of years. I believe this will allow us to quickly simulate new compounds virtually to find the best recipes these compounds have to offer.”
This work was supported by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021B1515140014), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52101236, U1732154, T2125008, 52272006), the Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Science (E15154U110), the Open project of Key Laboratory of Artificial Structures and Quantum Control (2021-05), the U.S. National Science Foundation (DMR-2119273), the “Shuguang Program” from the Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, the Australia Research Council (DP210101436).
CITATION: “Extreme Phonon Anharmonicity Underpins Superionic Diffusion and Ultralow Thermal Conductivity in Argyrodite Ag8SnSe6” Qingyong Ren, Mayanak K. Gupta, Min Jin, Jingxuan Ding, Jiangtao Wu, Zhiwei Chen, Siqi Lin, Oscar Fabelo, Jose Alberto Rodríguez-Velamazán, Maiko Kofu, Kenji Nakajima, Marcell Wolf, Fengfeng Zhu, Jianli Wang, Zhenxiang Cheng, Guohua Wang, Xin Tong, Yanzhong Pei, Olivier Delaire, Jie Ma. Nature Materials, May 18, 2023. DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01560-x
Journal
Nature Materials
DOI
10.1038/s41563-023-01560-x
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Extreme Phonon Anharmonicity Underpins Superionic Diffusion and Ultralow Thermal Conductivity in Argyrodite Ag8SnSe6
Article Publication Date
18-May-2023




