Marine vehicles can reduce friction by mimicking the way aquatic creatures secrete mucus
Credit: Hyung Jin Sung
WASHINGTON, September 15, 2020 — Long-distance cargo ships lose a significant amount of energy due to fluid friction. Looking to the drag reduction mechanisms employed by aquatic life can provide inspiration on how to improve efficiency.
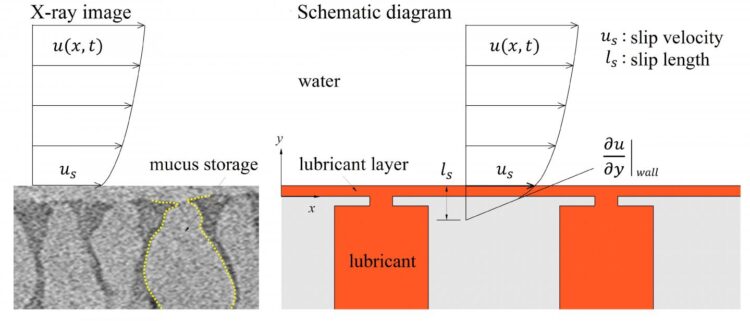
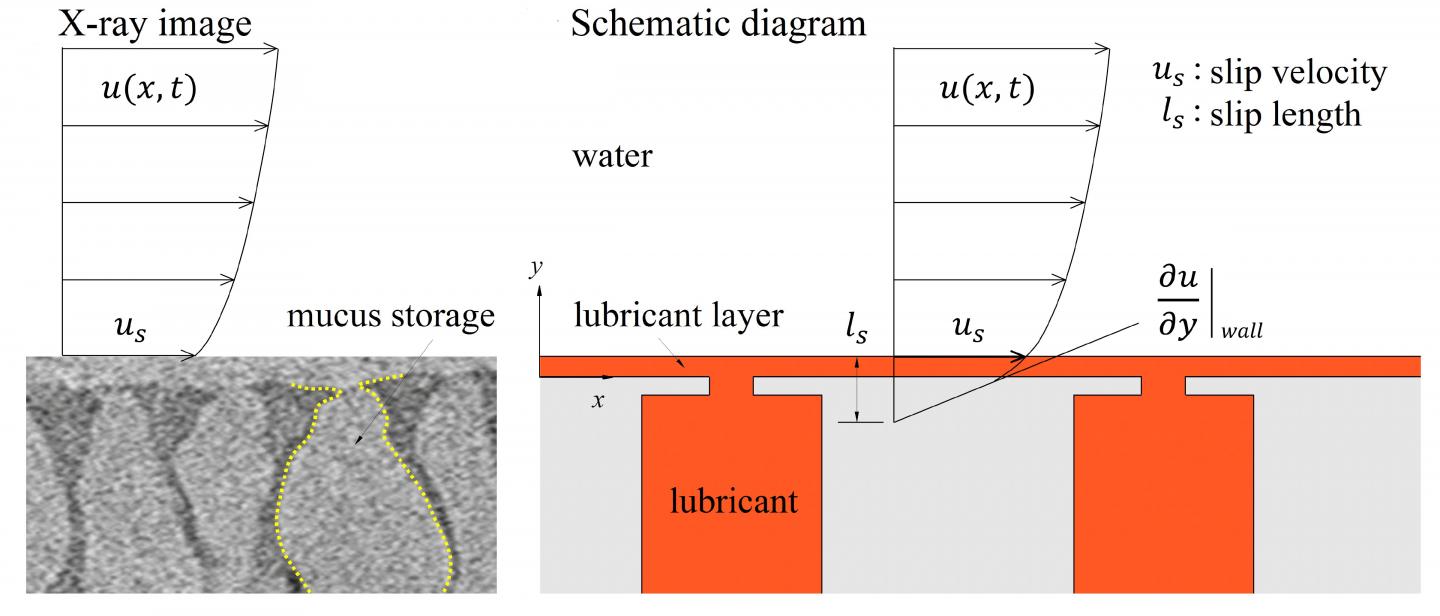
Fish and seaweed secrete a layer of mucus to create a slippery surface, reducing their friction as they travel through water. A potential way to mimic this is by creating lubricant-infused surfaces covered with cavities. As the cavities are continuously filled with the lubricant, a layer is formed over the surface.
Though this method has previously been shown to work, reducing drag by up to 18%, the underlying physics is not fully understood. In the journal Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology and Pohang University of Science and Technology conducted simulations of this process to help explain the effects.
The group looked at the average speed of a cargo ship with realistic material properties and simulated how it behaves under various lubrication setups. Specifically, they monitored the effects of the open area of the lubricant-filled cavities, as well as the thickness of the cavity lids.
They found that for larger open areas, the lubricant spreads more than it does with smaller open areas, leading to a slipperier surface. On the other hand, the lid thickness does not have much of an effect on the slip, though a thicker lid does create a thicker lubricant buildup layer.
“Our investigation of the hydrodynamics of a lubricant layer and how it results in drag reduction with a slippery surface in a basic configuration has provided significant insight into the benefits of a lubricant-infused surface,” said Hyung Jin Sung, an author on the paper.
Now that they have worked on optimizing the lubricant secretion design, the authors hope it can be implemented in real-life marine vehicles.
“If the present design parameters are adopted, the drag reduction rate will increase significantly,” Sung said.
###
The article, “A lubricant-infused slip surface for drag reduction,” is authored by Seung Joong Kim, Hae Nyeok Kim, Sang Joon Lee, and Hyung Jin Sung. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on September 15, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0018460). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex or multiphase fluids. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.