In a laboratory first, Duke researchers have grown human skeletal muscle that contracts and responds just like native tissue to external stimuli such as electrical pulses, biochemical signals and pharmaceuticals. The lab-grown tissue should soon allow researchers to test new drugs and study diseases in functioning human muscle outside of the human body.
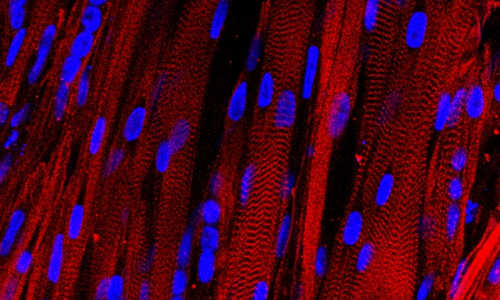
A microscopic view of lab-grown human muscle bundles stained to show patterns made by basic muscle units and their associated proteins (red), which are a hallmark of human muscle.
The study was led by Nenad Bursac, associate professor of biomedical engineering at Duke University, and Lauran Madden, a postdoctoral researcher in Bursac’s laboratory. It appears January 13 in the open-access journal eLife.
“The beauty of this work is that it can serve as a test bed for clinical trials in a dish,” said Bursac. “We are working to test drugs’ efficacy and safety without jeopardizing a patient’s health and also to reproduce the functional and biochemical signals of diseases—especially rare ones and those that make taking muscle biopsies difficult.”
Bursac and Madden started with a small sample of human cells that had already progressed beyond stem cells but hadn’t yet become muscle tissue. They expanded these “myogenic precursors” by more than a 1000-fold, and then put them into a supportive, 3D scaffolding filled with a nourishing gel that allowed them to form aligned and functioning muscle fibers.
“We have a lot of experience making bioartifical muscles from animal cells in the laboratory, and it still took us a year of adjusting variables like cell and gel density and optimizing the culture matrix and media to make this work with human muscle cells,” said Madden.
Madden subjected the new muscle to a barrage of tests to determine how closely it resembled native tissue inside a human body. She found that the muscles robustly contracted in response to electrical stimuli—a first for human muscle grown in a laboratory. She also showed that the signaling pathways allowing nerves to activate the muscle were intact and functional.
To see if the muscle could be used as a proxy for medical tests, Bursac and Madden studied its response to a variety of drugs, including statins used to lower cholesterol and clenbuterol, a drug known to be used off-label as a performance enhancer for athletes.
The effects of the drugs matched those seen in human patients. The statins had a dose-dependent response, causing abnormal fat accumulation at high concentrations. Clenbuterol showed a narrow beneficial window for increased contraction. Both of these effects have been documented in humans. Clenbuterol does not harm muscle tissue in rodents at those doses, showing the lab-grown muscle was giving a truly human response.
“One of our goals is to use this method to provide personalized medicine to patients,” said Bursac. “We can take a biopsy from each patient, grow many new muscles to use as test samples and experiment to see which drugs would work best for each person.”
This goal may not be far away; Bursac is already working on a study with clinicians at Duke Medicine—including Dwight Koeberl, associate professor of pediatrics—to try to correlate efficacy of drugs in patients with the effects on lab-grown muscles. Bursac’s group is also trying to grow contracting human muscles using induced pluripotent stem cells instead of biopsied cells.
“There are a some diseases, like Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy for example, that make taking muscle biopsies difficult,” said Bursac. “If we could grow working, testable muscles from induced pluripotent stem cells, we could take one skin or blood sample and never have to bother the patient again.”
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Duke University.