Credit: by Gebhardt, M., Heuermann, T., Klas, R. et al.
Bright, coherent soft X-ray radiation (SXR) is used in many scientific applications such as advanced absorption spectroscopy or lens-less imaging, and in fundamental research e.g. to produce extremely short isolated optical pulses. Therefore, the generation, control, and detection of this type of short-wavelength light is highly important in fields like fundamental atomic physics, solid-state physics, the semiconductor industry, material science and biology.
To date, high photon flux in the soft X-ray spectral region is mostly delivered by large-scale facilities like synchrotrons or free electron lasers. An alternative is to use high-order harmonic generation (HHG) sources, which are currently driven by pulsed laser systems with very high peak powers. It is highly desired to increase the repetition rate of such sources beyond 1000 shots per second (e.g. to allow for a faster data acquisition/increase the signal-to-noise ratio) and to make them simpler, more compact and easier to operate.
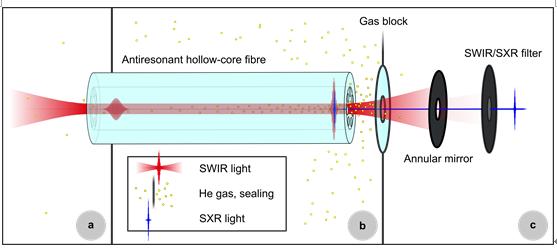
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Jens Limpert from the Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena, and co-workers have developed a laser-driven soft X-ray source, which is based on high-order harmonic generation inside of an antiresonant gas-filled hollow core fibre (ARHCF). They designed the source such that the intensity of the driving laser pulses is enhanced by temporal self-compression inside of the hollow fibre before the soft X-rays are generated. The integration of laser enhancement and high-order harmonic generation in a single gas-filled hollow core fibre allows “compact, high repetition rate laser technology, including commercially available systems, to drive simple and cost-effective, coherent high-flux SXR sources”, the scientists state in their paper. In their work, they have optimized the input laser parameters and the gas particle density inside of the fibre such that a macroscopic HHG signal builds up towards the fibre end. This soft X-ray light emerges directly from the output of a potentially flexible hollow-core fibre. The reported method opens new avenues for simple and powerful laser-driven soft X-ray sources based on fibre technology. This allows moderate peak power laser systems with high repetition rates to drive HHG directly.
The authors state, “This enables the first 100 kHz-class repetition rate, table-top SXR source, that delivers an application-relevant flux of 2.8×106 Photons/s/eV around 300 eV.”. They go on to demonstrate a proof-of-principle spectroscopy measurement at the carbon K-edge. Furthermore, they show a long term run of the source over more than 20 minutes. While this source is based on a high repetition rate 2 μm wavelength fibre laser, it is applicable to any laser technology in the short-wavelength infrared.
The scientists forecast that their results are “most interesting for a variety of applications, which significantly benefit from compact and easy-to-use high repetition rate SXR sources”. They add: “These sources could use ARHCFs for beam delivery, self-compression and HHG in a single apparatus, making them more affordable, and available to a much broader community in fundamental and applied sciences with medical applications in reach.”
###
Media Contact
Martin Gebhardt
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




