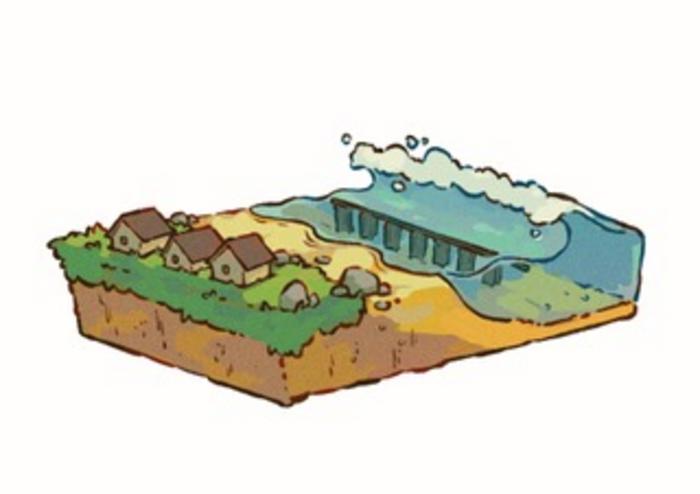
Engineers have designed a modular artificial reef that can dissipate wave energy far better than natural coral reefs, according to a study. Sixty percent of the world’s coral reefs are under threat from rising ocean temperatures, overfishing, or coastal development. At the same time, climate change is leading to sea level rise, frequent high-tide flooding, and powerful storm surges. Artificial reefs can help protect coastal infrastructure from storms as well as provide habitat for marine organisms. Michael Triantafyllou and colleagues proposed and tested an architected cellular reef structure designed to dissipate wave energy at higher rates than natural reefs. The structure is made of concrete and is designed as a modular unit, many of which can be combined like building blocks. Each unit, known as a voxel, is a truncated pyramid. The shape of the structure was optimized through hydrodynamic modeling and experimental testing. Tests of scale models of reefs made of miniaturized version of the modules at the MIT Towing Tank confirm its effectiveness at dissipating wave energy. According to the authors, coastal communities can help protect themselves and provide shelter for marine life by installing artificial reefs made of concrete voxels at a sufficient depth such that waves would encounter the reef before breaking.
Credit: Melissa Wen
Engineers have designed a modular artificial reef that can dissipate wave energy far better than natural coral reefs, according to a study. Sixty percent of the world’s coral reefs are under threat from rising ocean temperatures, overfishing, or coastal development. At the same time, climate change is leading to sea level rise, frequent high-tide flooding, and powerful storm surges. Artificial reefs can help protect coastal infrastructure from storms as well as provide habitat for marine organisms. Michael Triantafyllou and colleagues proposed and tested an architected cellular reef structure designed to dissipate wave energy at higher rates than natural reefs. The structure is made of concrete and is designed as a modular unit, many of which can be combined like building blocks. Each unit, known as a voxel, is a truncated pyramid. The shape of the structure was optimized through hydrodynamic modeling and experimental testing. Tests of scale models of reefs made of miniaturized version of the modules at the MIT Towing Tank confirm its effectiveness at dissipating wave energy. According to the authors, coastal communities can help protect themselves and provide shelter for marine life by installing artificial reefs made of concrete voxels at a sufficient depth such that waves would encounter the reef before breaking.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
Architected materials for artificial reefs to increase storm energy dissipation
Article Publication Date
26-Mar-2024




