Exercise increases dopamine signaling in the motor areas of mice, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
Credit: Bastioli et al., JNeurosci 2022
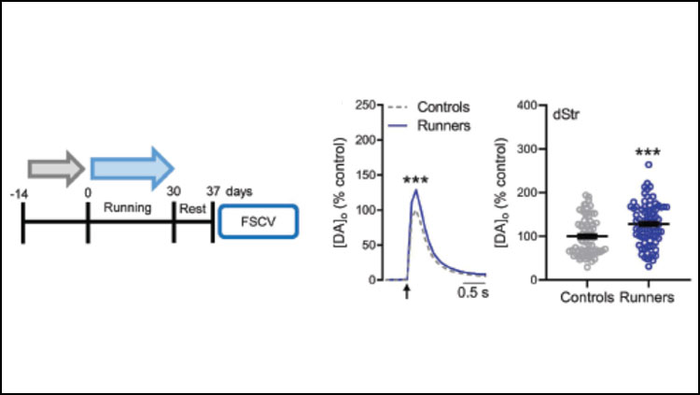
Exercise increases dopamine signaling in the motor areas of mice, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
It’s no secret exercise is good for the brain — working out can improve mood, sharpen memory, and stave off cognitive decline. Exercise even improves motor behavior in people with Parkinson’s disease, but the exact mechanism is not known. One possibility is through an increase in dopamine, a neurotransmitter needed for motor and emotional control that declines as the disease progresses.
Bastioli et al. compared dopamine signaling in mice after 30 days of voluntary wheel running or inactivity. In the runner mice, dopamine release in the striatum (a motor area) increased in response to electrical stimulation, while there was no change in sedentary mice. The increased dopamine release remained even a week after the exercise ended. The researchers also measured increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein involved in neuron health, in the striatum of active mice. When the researchers repeated the experiments in a genetic mouse model lacking BDNF, there was no difference in dopamine release between the active and sedentary mice, suggesting BDNF catalyzes increased dopamine signaling. Future studies will examine if the relationship holds true in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, and if exercise can improve motor outcomes.
###
Paper title: Voluntary Exercise Boosts Striatal Dopamine Release: Evidence for the Necessary and Sufficient Role of BDNF
Please contact [email protected] for the full-text PDF and to join SfN’s journals media list.
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience’s first journal, was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors’ changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world’s largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
Journal
JNeurosci
DOI
10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2273-21.2022
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Voluntary exercise boosts striatal dopamine release: evidence for the necessary and sufficient role of BDNF
Article Publication Date
16-May-2022




