Credit: Takhistov et. al.
What is the origin of black holes and how is that question connected with another mystery, the nature of dark matter? Dark matter comprises the majority of matter in the Universe, but its nature remains unknown.
Multiple gravitational wave detections of merging black holes have been identified within the last few years by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), commemorated with the 2017 physics Nobel Prize to Kip Thorne, Barry Barish, and Rainer Weiss. A definitive confirmation of the existence of black holes was celebrated with the 2020 physics Nobel Prize awarded to Andrea Ghez, Reinhard Genzel and Roger Penrose. Understanding the origin of black holes has thus emerged as a central issue in physics.
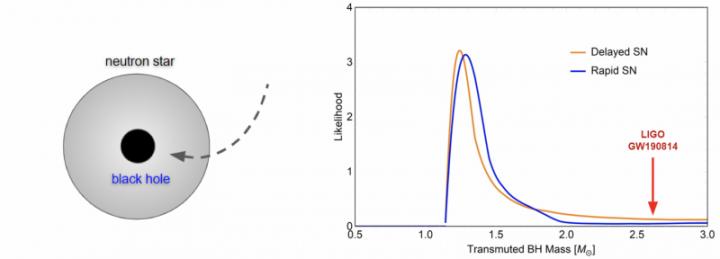
Surprisingly, LIGO has recently observed a 2.6 solar-mass black hole candidate (event GW190814, reported in Astrophysical Journal Letters 896 (2020) 2, L44). Assuming this is a black hole, and not an unusually massive neutron star, where does it come from?
Solar-mass black holes are particularly intriguing, since they are not expected from conventional stellar evolution astrophysics. Such black holes might arise in the early Universe (primordial black holes) or be “transmuted” from existing neutron stars. Some black holes could have formed in the early universe long before the stars and galaxies formed. Such primordial black holes could make up some part or all of dark matter. If a neutron star captures a primordial black hole, the black hole consumes the neutron star from the inside, turning it into a solar-mass black hole. This process can produce a population of solar mass black holes, regardless of how small the primordial black holes are. Other forms of dark matter can accumulate inside a neutron star causing its eventual collapse into a solar-mass black hole.
A new study, published in Physical Review Letters, advances a decisive test to investigate the origin of solar-mass black holes. This work was led by the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU) Fellow Volodymyr Takhistov and the international team included George M. Fuller, Distinguished Professor of Physics and Director of the Center for Astrophysics and Space Science at the University of California, San Diego, as well as Alexander Kusenko, Professor of Physics and Astronomy at the University of California, Los Angeles and a Kavli IPMU Visiting Senior Scientist.
As the study discusses (see Fig. 1), “transmuted” solar-mass black holes remaining from neutron stars being devoured by dark matter (either tiny primordial black holes or particle dark matter accumulation) should follow the mass-distribution of the original host neutron stars. Since the neutron star mass distribution is expected to peak around 1.5 solar masses, it is unlikely that heavier solar-mass black holes have originated from dark matter interacting with neutron stars. This suggests that such events as the candidate detected by LIGO, if they indeed constitute black holes, could be of primordial origin from the early Universe and thus drastically affect our understanding of astronomy. Future observations will use this test to investigate and identify the origin of black holes.
Previously (see Fuller, Kusenko, Takhistov, Physical Review Letters 119 (2017) 6, 061101), the same international team of researchers also demonstrated that disruption of neutron stars by small primordial black holes can lead to a rich variety of observational signatures and can help us understand such long-standing astronomical puzzles as the origin of heavy elements (e.g. gold and uranium) and the 511 keV gamma-ray excess observed from the center of our Galaxy.
###
Media Contact
John Amari
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




