A recent study from the Laxman lab at inStem, Bangalore, elucidates how a small metabolite and amino acid, methionine, acts as a growth signal for cells, by setting into motion a metabolic program for cell proliferation
Credit: Adhish Walvekar and Sunil Laxman, Institute for Stem Cell Science and Regenerative Medicine (inStem), Bangalore, India
A recent study from the Laxman lab elucidates how a small metabolite and amino acid, methionine, acts as a growth signal for cells, by setting into motion a metabolic program for cell proliferation.
For cells to grow and then divide, they must be in an anabolic state, where there is sufficient production of all necessary building blocks. It was earlier thought that as long as enough nutrients are present, cells would continue to grow under the control of different internal signalling programs. However, recent studies show that many small intermediates and products of biological metabolism commonly termed as metabolites can themselves act as signalling molecules and control cell growth programs.
Several studies, particularly from cancer researchers, have hinted that methionine might be a signalling metabolite. Many cancers appear to be dependent on methionine for growth. However, how methionine controls growth is still a mystery. We used a very simple model system (budding yeast cells), to address how methionine might regulate growth. To understand the logic of such a growth program, we analysed gene expression profiles as well as measured the new synthesis of necessary building blocks. By piecing together this network, we constructed the organization of a core anabolic program triggered by methionine. This anabolic program relies on a few specific nodes in metabolism and is sufficient to orchestrate an entire cascade of transcriptional and metabolic events that can sustain growth.
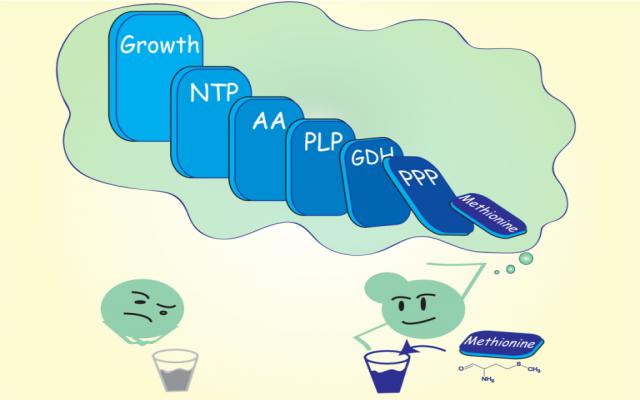
Our findings on how cells perceive methionine as a growth cue are illustrated in the simple cartoon (see banner image). When methionine is limited, cells do not grow (the unhappy cell without a bud, on the left). On the other hand, when methionine is abundant, it acts as a growth signal and triggers a cascade of biochemical events, ultimately leading to cell growth (the happy yeast with a bud, on the right). Analogous to the butterfly effect, methionine leads to a series of larger metabolic events, controlling an entire cellular program. Methionine activates three key nodes in metabolism: the pentose phosphate pathway, the production of glutamine, and the formation of pyridoxal phosphate (the PPP-GDH-PLP node). These nodes produce a set of critical substrates and co-factors that fuel the production of all other amino acids, as well as make nucleotides, which are critical for growth. In the cartoon, the dominoes of increasing size show this chain of events and capture how methionine eventually has a significant impact on cell growth.
This is a fundamental study, which advances our understanding of how some metabolites can act as signalling molecules and play a critical role in controlling cell growth. This study provides a much-awaited explanation on the role of methionine in sustaining cell growth, and it might clarify why cancer cells are addicted to methionine for their growth. However, a long-term methionine study could provide strategies to control the growth of many types of cancer.
###
Media Contact
Sunil Laxman
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




