Quantum entanglement is key for next-generation computing and communications technology, Aalto researchers can now produce it using temperature differences
Credit: Aalto University
A joint group of scientists from Finland, Russia, China and the USA have demonstrated that temperature difference can be used to entangle pairs of electrons in superconducting structures. The experimental discovery, published in Nature Communications, promises powerful applications in quantum devices, bringing us one step closer towards applications of the second quantum revolution.
The team, led by Professor Pertti Hakonen from Aalto University, has shown that the thermoelectric effect provides a new method for producing entangled electrons in a new device. “Quantum entanglement is the cornerstone of the novel quantum technologies. This concept, however, has puzzled many physicists over the years, including Albert Einstein who worried a lot about the spooky interaction at a distance that it causes”, says Prof. Hakonen.
In quantum computing, entanglement is used to fuse individual quantum systems into one, which exponentially increases their total computational capacity. “Entanglement can also be used in quantum cryptography, enabling the secure exchange of information over long distances”, explains Prof. Gordey Lesovik, from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, who has acted several times as a visiting professor at Aalto University School of Science. Given the significance of entanglement to quantum technology, the ability to create entanglement easily and controllably is an important goal for researchers.
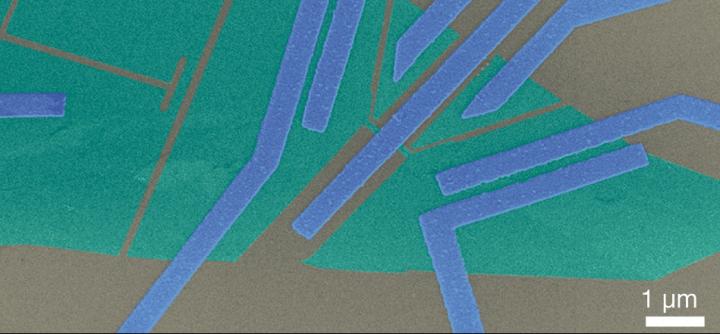
The researchers designed a device where a superconductor was layered withed graphene and metal electrodes. “Superconductivity is caused by entangled pairs of electrons called “cooper pairs”. Using a temperature difference, we cause them to split, with each electron then moving to different normal metal electrode,” explains doctoral candidate Nikita Kirsanov, from Aalto University. “The resulting electrons remain entangled despite being separated for quite long distances.”
Along with the practical implications, the work has significant fundamental importance. The experiment has shown that the process of Cooper pair splitting works as a mechanism for turning temperature difference into correlated electrical signals in superconducting structures. The developed experimental scheme may also become a platform for original quantum thermodynamical experiments.
###
The work was carried out using the OtaNano research infrastructure. OtaNano provides state-of-the-art working environment and equipment for nanoscience and -technology, and quantum technologies research in Finland. OtaNano is operated by Aalto University and VTT, and is available for academic and commercial users internationally. To find out more, visit their website. The work was supported by funded from QTF (Academy of Finland CoE). Gordey Lesovik’s visiting professorship funding came fro Aalto University School of Science and Zhenbing Tan’s post doctoral grant came from the Academy of Finland.
The full paper, Thermoelectric current in a graphene Cooper pair splitter can be read here http://dx.
Contact
Pertti Hakonen
Professor
Aalto University
[email protected]
Media Contact
Pertti Hakonen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




