Understanding complex biological and biomedical systems is greatly aided by 3D imaging, which provides much more detailed information than traditional two-dimensional methods. However, live cell and tissue imaging remain challenging due to factors like limited imaging speed and significant scattering in turbid environments.
Credit: Wang and Huang, doi 10.1117/1.AP.6.2.026001.
Understanding complex biological and biomedical systems is greatly aided by 3D imaging, which provides much more detailed information than traditional two-dimensional methods. However, live cell and tissue imaging remain challenging due to factors like limited imaging speed and significant scattering in turbid environments.
In this context, multimodal microscopy techniques are notable. Specifically, nonlinear techniques like CRS (coherent Raman scattering) use optical vibrational spectroscopy, providing precise chemical imaging in tissues and cells in a label-free way. Furthermore, stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy, a CRS method, can accurately capture images of biomolecules due to the linear relationship between stimulated Raman intensity and the concentration of target molecules. It does so with high sensitivity and without interference from unwanted nonresonant background.
In a recent study published in Advanced Photonics, Professor Zhiwei Huang, Director of the Optical Bioimaging Laboratory in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at the College of Design and Engineering at National University of Singapore, worked with his team to develop a new technique called phase-modulated stimulated Raman scattering tomography (PM-SRST) for the label-free 3D chemical imaging of cells and tissues.
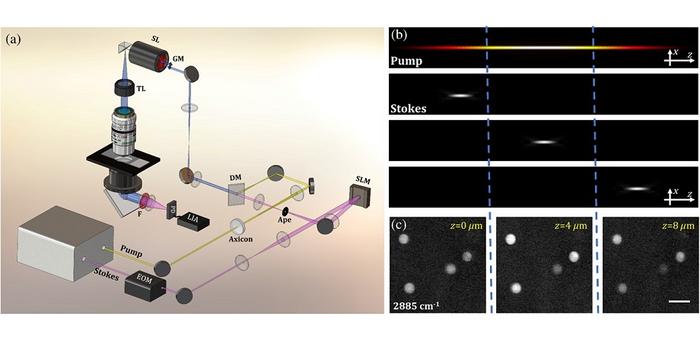
According to Huang, “This method developed by us allows for the direct acquisition of 3D sample information in the spatial domain, without necessitating the postprocessing procedures. We have also demonstrated the utility of the PM-SRST technique for improving both the lateral resolution and imaging depth of SRS 3D imaging of biotissues.”
In this approach, the regular “pump” beam in the SRS method is substituted with a specialized beam known as the Bessel beam. The position of another beam, the focused Stokes beam, is controlled using a device called a spatial light modulator, along the Bessel pump beam in the sample, for mechanical scan-free z-sectioning. Furthermore, by combining the Bessel pump beam with a longer wavelength Stokes beam, the ability of PM-SRST to handle scattering is improved, allowing for the capture of quick and detailed images in deeper tissue areas.
The effectiveness of the method was proven through experiments showcasing rapid label-free volumetric chemical imaging across diverse samples. These included real-time monitoring of the 3D Brownian motion of polymer beads in water, observing the diffusion and uptake processes of deuterium oxide (D2O) in plant roots, and studying the biochemical response of breast cancer cells to acetic acid. Furthermore, the light penetration depth of PM-SRST was compared to that of conventional SRS imaging. In PM-SRST, the signal from deeper tissue areas is notably stronger than in C-SRS, leading to an approximately two-fold improvement in imaging depth.
Huang notes, “The z-scanning-free optical sectioning property in PM-SRST is universal, which can be easily extended to other imaging modalities. For instance, the current system can be readily adapted for coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) tomography, and by utilizing either the pump or Stokes beam alone, the PM-SRST technique can be simplified to facilitate second or third harmonic generation tomography, multiphoton tomography, or fluorescence tomography.”
Capable of rapid and label-free 3D chemical imaging, PM-SRST technique can be used to study metabolic activities and functional dynamic processes related to drug delivery and therapeutics within live cells and tissues.
For details, see the original Gold Open Access article by Weiqi Wang and Zhiwei Huang, “Stimulated Raman scattering tomography for rapid 3D chemical imaging of cells and tissue,” Adv. Photon. 6(2) 026001 (2024), doi 10.1117/1.AP.6.2.026001.
Journal
Advanced Photonics
DOI
10.1117/1.AP.6.2.026001
Article Title
Stimulated Raman scattering tomography for rapid three-dimensional chemical imaging of cells and tissue
Article Publication Date
15-Feb-2024




