New system paves the way to construct energetically-independent artificial cells
Credit: Nature Communications
A team led by associate professor Yutetsu Kuruma of the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Tokyo Institute of Technology has constructed simple artificial cells that can produce chemical energy that helps synthesize parts of the cells themselves. This work marks an important milestone in constructing fully photosynthetic artificial cells, and may shed light on how primordial cells used sunlight as an energy source early in life’s history.
Scientists build artificial cells as models of primitive cells, as well as to understand how modern cells function. Many sub-cellular systems have now been built by simply mixing cell components together. However, real living cells construct and organize their own components. It has also been a long time goal of research to build artificial cells that can also synthesize their own constituents using the energy available in the environment.
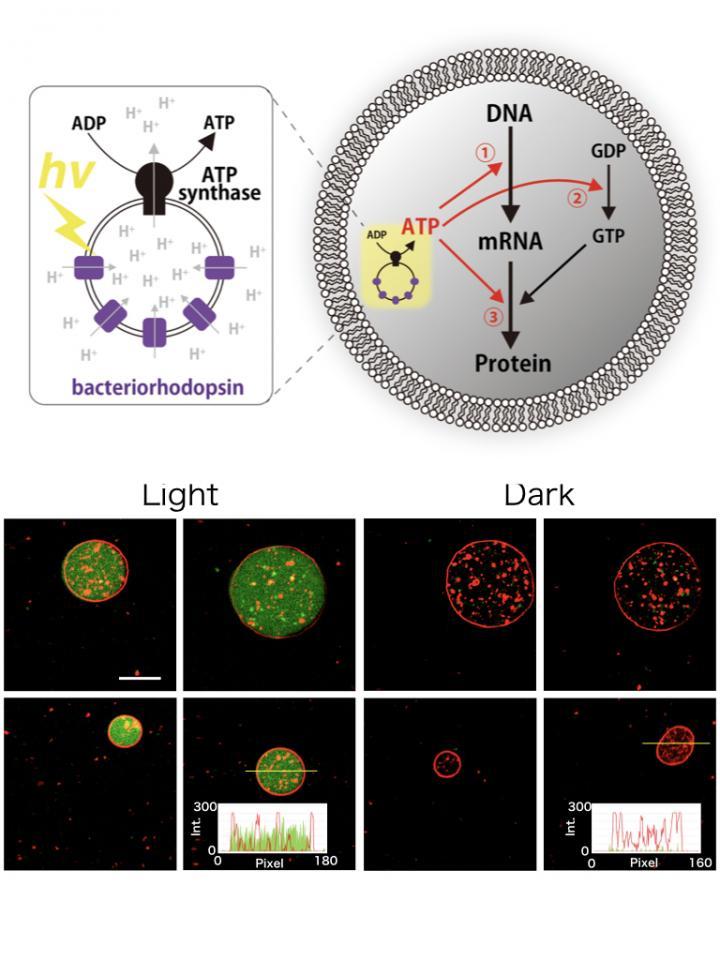
The Tokyo Tech team combined a cell-free protein synthesis system, which consisted of various biological macromolecules harvested from living cells, and small protein-lipids aggregates called proteoliposomes, which contained the proteins ATP synthase and bacteriorhodopsin, also purified from living cells, inside giant synthetic vesicles. ATP synthase is a biological protein complex that uses the potential energy difference between the liquid inside a cell and the liquid in the cell’s environment to make the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy currency of the cell. Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-harvesting protein from primitive microbes that uses light energy to transport hydrogen ions outside of the cell, thus generating a potential energy difference to help ATP synthase operate. Thus, these artificial cells would be able to use light to make a hydrogen ion gradient that would help make the fuel cells use to run their sub-cellular systems, including making more protein.
Just as the scientists hoped, the photosynthesized ATP was consumed as a substrate for transcription, the process by which biology makes messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA, and as an energy for translation, the process by which biology makes protein from mRNA. By also including the genes for parts of the ATP synthase and the light-harvesting bacteriorhodopsin, these processes also eventually drive the synthesis of more bacteriorhodopsin and the constituent proteins of ATP synthase, a few copies of which were included to “jump-start” the proteoliposome. The newly formed bacteriorhodopsin and ATP synthase parts then spontaneously integrated into the artificial photosynthetic organelles and further enhanced ATP photosynthesis activity.
As professor Kuruma states “I have been trying for a long time to construct a living artificial cell, especially focusing on membranes. In this work, our artificial cells were wrapped in lipid membranes, and small membrane structures were encapsulated inside them. In this way, the cell membrane is the most important aspect of forming a cell, and I wanted to show the importance of this point in the study of artificial cell and feedback in origins of life studies.”
Kuruma thinks the most impact point of this work is that artificial cells can produce energy to synthesize the parts of the cell itself. This means that the artificial cells could be made to be energetically independent and then it would be possible to construct self-sustaining cells, just like actual biological ones cells. “The most challenging thing in this work was the photosynthesis of the bacteriorhodopsin and the ATP synthase parts, which are membrane proteins. We tried to photosynthesize a full ATP synthase, which has 8 kinds of component proteins, but we could not because of the low productivity of the cell-free protein synthesis system. But, if it was upgraded, we may photosynthesize the whole 8 kinds component proteins.”
Nevertheless, this work demonstrates that a simple biologically inspired system including two kinds of membrane protein is able to supply energy to drive gene expression inside a microcompartment. Thus, primordial cells using sunlight as a primal energy source could have existed early in life’s evolution before modern autotrophic cells arose. The team believes attempts to construct living artificial cells will help understand the transition from non-living to living matter that took place on early Earth and, help develop biology-based devices that can sense light and drive biochemical reactions. These artificial photosynthetic cell systems also help pave the way to constructing energetically independent artificial cells.
###
Media Contact
Gensei Ishimura
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




