A team of scientists from Ural Federal University (Yekaterinburg), Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology and other collaborator have published an article about a new method for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles
Credit: Aslam Hossein
A team of scientists from Ural Federal University (Yekaterinburg), Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology and other collaborator have published an article about a new method for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Today nanoparticles are used in various fields, from biomedicine to magnetic resonance imaging, data storage systems, environmental reclamation technologies, magnetically controlled liquids, various sensors, and immunoassay systems.
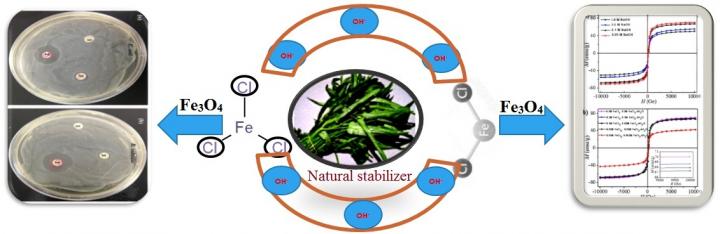
The manufacture of nanomaterials is a popular area today, and like any other industry, it is wanted to be eco-friendly. Scientists work on the so-called green synthesis – environmentally-friendly methods for producing nanomaterials from plant extracts. However, many substances contained in natural materials are unstable and quickly enter into oxidation-reduction reactions with certain components of the environment. Stabilizer is very important substance for newly synthesized nanoparticles which was one of the goals of the study conducted by the team of scientist.
To synthesize iron oxide nanoparticles, the team used inorganic substances such as iron chloride and sodium hydroxide. The scientists also used an extract made of the leaves of Ipomoea aquatica (a plant from the bindweed family) as a stabilizing and reducing agent. It helped prevent the agglutination of the particles and supported their small size.
Besides the green nature of the process, the team paid attention to different properties of the obtained nanoparticles. The ratio between the surface of the particle and its volume played an important role in the reactivity of a magnetic nanoparticles. All these leads to tune the properties that are important for biology and medicine. They also studied the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles stabilized with the Ipomoea aquatica extract. To do so, they placed the particles into an external magnetic field at room temperature and monitored their behavior. The experiments showed certain manifestations of the particles’ superparamagnetic nature. This is a special form of magnetism that is observed specifically in nanosized ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic particles.
According to several studies, it is established that magnetic nature of the nanoparticles enhances the activity of medicines. The team also conducted an experiment to confirm that the new nanoparticles suppressed the growth of bacteria. Thus, the authors claimed that the superparamagnetic nanoparticles at room temperature and their antibacterial properties would make them potential material for biomedical applications.
“Our study of different properties of the new nanoparticles confirmed they met all existing standards. The new methodology is based on plant raw materials and therefore it is eco-friendly”, said Hossain Aslam, a research engineer of Ural Federal University.
Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles (MNPs) have been synthesized through a facile green synthesis route using naturally available Ipomoea aquatica leaf aqueous extract where biomolecules of leaf extract acted as a stabilizer as well as reducing agent. The synthesized MNPs has pronounced antibacterial activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The room temperature superparamagnetic nature and antibacterial activity of MNPs demonstrate that it could be potential materials for biomedical applications.
###
Media Contact
Eugene Tulisov
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




