Developing new drugs is paramount in discovering innovative treatments and preventing diseases. This is vital not only for advancing medicine but also for the overall health and well-being of humanity. Yet, even when drugs demonstrate safety and efficacy in cell and animal models, they frequently encounter hurdles in clinical trials on human.
Credit: POSTECH
Developing new drugs is paramount in discovering innovative treatments and preventing diseases. This is vital not only for advancing medicine but also for the overall health and well-being of humanity. Yet, even when drugs demonstrate safety and efficacy in cell and animal models, they frequently encounter hurdles in clinical trials on human.
A single setback for a drug during clinical trials, which involves diverse population groups, can result in significant economic losses. To address this, it is imperative to understand why certain drugs, despite passing the preclinical stages, falter during clinical trials. Additionally, there’s a pressing need to predict a given drug’s chances for approval in clinical trial.
Recently, a research team led by Professor Sanguk Kim (Department of Life Sciences, School of Convergence Science and Technology) and PhD candidate Minhyuk Park (Department of Life Sciences) at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) used machine learning to achieve success in predicting potential drug outcomes and side effects before the clinical trials begin. Their findings were published in EBioMedicine, a part of The Lancet Discovery Science.
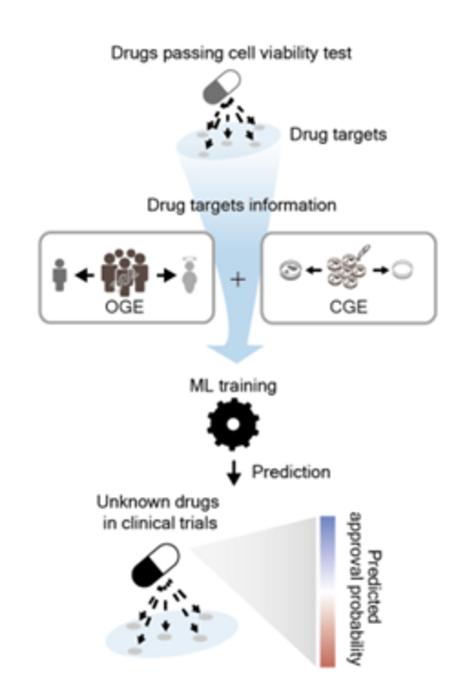
Drugs are primarily tested on cell lines and animal models prior to human clinical trial. However, the observed drug efficacy or toxicity might vary because of the discrepancies in how drug target genes function and are expressed in cells as opposed to humans. Neglecting this discrepancy can lead to severe, unanticipated side effects in actual patients, diverging from lab findings.
In their research, the researchers focused on the discrepancy in drug effects between cells and humans. To evaluate the discrepancy to predict drug approval (1404 approved and 1070 unapproved drugs), they analyzed CRISPR-Cas9 knockout and loss-of-function mutation rate-based gene perturbation effects on cells and humans, respectively. To validate the risk of drug targets with the cells/humans discrepancy, they examined the targets of failed and withdrawn drugs due to safety problems.
Leveraging this knowledge, they developed a machine learning approach to forecast drug approvals in clinical trials. The conventional approaches typically utilize a drug’s chemical properties, omitting the genetic differences between cells and humans. This team, however, integrated both chemical and genetic strategies, refining the accuracy of their drug safety and success predictions.
The study’s lead investigator, Professor Sanguk Kim, explained, “The challenges of drug development rose from the absence of reliable methods for predicting clinical trial outcomes in humans. I hope our research enables us to effectively predict drug approval possibilities, substantially reducing shorten the time and expenses associated with drug development.”
Journal
EBioMedicine
DOI
10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104705
Article Title
Drug approval prediction based on the discrepancy in gene perturbation effects between cells and humans
Article Publication Date
13-Jul-2023




