New electronics platform provides better data for personalized care
Credit: University of Houston
A team of researchers led by Cunjiang Yu, Bill D. Cook Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Houston, has developed a new form of electronics known as “drawn-on-skin electronics,” allowing multifunctional sensors and circuits to be drawn on the skin with an ink pen.
The advance, the researchers report in Nature Communications, allows for the collection of more precise, motion artifact-free health data, solving the long-standing problem of collecting precise biological data through a wearable device when the subject is in motion.
The imprecision may not be important when your FitBit registers 4,000 steps instead of 4,200, but sensors designed to check heart function, temperature and other physical signals must be accurate if they are to be used for diagnostics and treatment.
The drawn-on-skin electronics are able to seamlessly collect data, regardless of the wearer’s movements.
They also offer other advantages, including simple fabrication techniques that don’t require dedicated equipment.
“It is applied like you would use a pen to write on a piece of paper,” said Yu. “We prepare several electronic materials and then use pens to dispense them. Coming out, it is liquid. But like ink on paper, it dries very quickly.”
Wearable bioelectronics – in the form of soft, flexible patches attached to the skin – have become an important way to monitor, prevent and treat illness and injury by tracking physiological information from the wearer. But even the most flexible wearables are limited by motion artifacts, or the difficulty that arises in collecting data when the sensor doesn’t move precisely with the skin.
The drawn-on-skin electronics can be customized to collect different types of information, and Yu said it is expected to be especially useful in situations where it’s not possible to access sophisticated equipment, including on a battleground.
The electronics are able to track muscle signals, heart rate, temperature and skin hydration, among other physical data, he said. The researchers also reported that the drawn-on-skin electronics have demonstrated the ability to accelerate healing of wounds.
In addition to Yu, researchers involved in the project include Faheem Ershad, Anish Thukral, Phillip Comeaux, Yuntao Lu, Hyunseok Shim, Kyoseung Sim, Nam-In Kim, Zhoulyu Rao, Ross Guevara, Luis Contreras, Fengjiao Pan, Yongcao Zhang, Ying-Shi Guan, Pinyi Yang, Xu Wang and Peng Wang, all from the University of Houston, and Jiping Yue and Xiaoyang Wu from the University of Chicago.
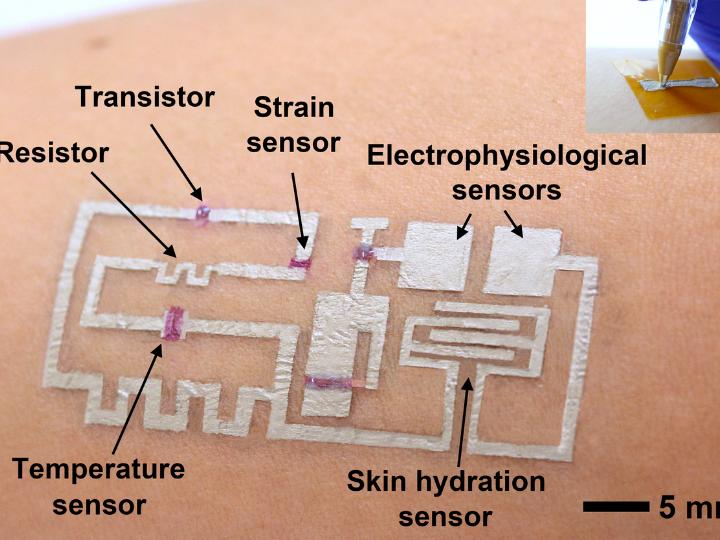
The drawn-on-skin electronics are actually comprised of three inks, serving as a conductor, semiconductor and dielectric.
“Electronic inks, including conductors, semiconductors, and dielectrics, are drawn on-demand in a freeform manner to develop devices, such as transistors, strain sensors, temperature sensors, heaters, skin hydration sensors, and electrophysiological sensors,” the researchers wrote.
###
This research is supported by the Office of Naval Research and National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Jeannie Kever
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




